The Problem
Fragmented communication across care teams leads to substantial safety risks during patient handoffs between facilities, with studies confirming communication gaps as a major issue in care transitions.
Handwritten discharge summaries, medication lists, and referral notes from referring facilities use inconsistent formats, abbreviations, and practices, forcing receiving clinicians to manually interpret and re-enter data into EHRs. This process consumes significant clinician time, contributes to burnout, and delays care initiation while introducing transcription errors.
Current AI solutions focus on intra-facility documentation (e.g., ambient scribes), medical imaging analysis, or remote monitoring, but lack vision-based extraction for unstructured inter-facility handoff documents with automatic EHR population and discrepancy flagging.
Our Approach
Key elements of this implementation
-
Vision model with OCR trained on de-identified handoff docs for extracting patient IDs, meds, allergies, findings; real-time discrepancy flagging vs. receiving EHR
-
Native HL7/FHIR API connectors for Epic, Cerner, Meditech, AllScripts; on-premise option for data residency (HIPAA BAA, GDPR Art. 28, ISO 27001 Annex A.8)
-
Full audit trails, immutable logging, data minimization (auto-purge sources post-extraction), RBAC, encryption at rest/transit; automated regulatory reports
-
Phased rollout (pilot 10 users, 60-day parallel run), 2-day training + change champions; human review for low-confidence extractions (>95% threshold)
Get the Full Implementation Guide
Unlock full details including architecture and implementation
Implementation Overview
This solution addresses the persistent challenge of communication gaps during patient handoffs between healthcare facilities, where handwritten discharge summaries, medication lists, and referral notes create safety risks and administrative burden[1][2]. The architecture combines document vision AI with healthcare-specific extraction models, EHR integration connectors, and comprehensive compliance controls suitable for global deployment across HIPAA, GDPR, and ISO 27001 environments.
The core approach uses a multi-stage pipeline: document ingestion with format normalization, vision-based extraction with specialized models for handwritten medical content, semantic mapping to clinical terminologies (SNOMED CT, RxNorm, ICD-10), discrepancy detection against receiving facility EHR data, and structured output for clinician review. A confidence-based routing system ensures high-confidence extractions (>95%) proceed to EHR population while lower-confidence items receive mandatory human review, maintaining clinical safety while maximizing automation benefits.
Key architectural decisions prioritize data residency flexibility (cloud or on-premise deployment), modular EHR integration via HL7 FHIR R4, and comprehensive audit logging for regulatory compliance. The phased implementation approach includes a 90-day parallel run period where extracted data is validated against manual processes before full automation, with dedicated change management and clinician training programs to ensure adoption success.
UI Mockups
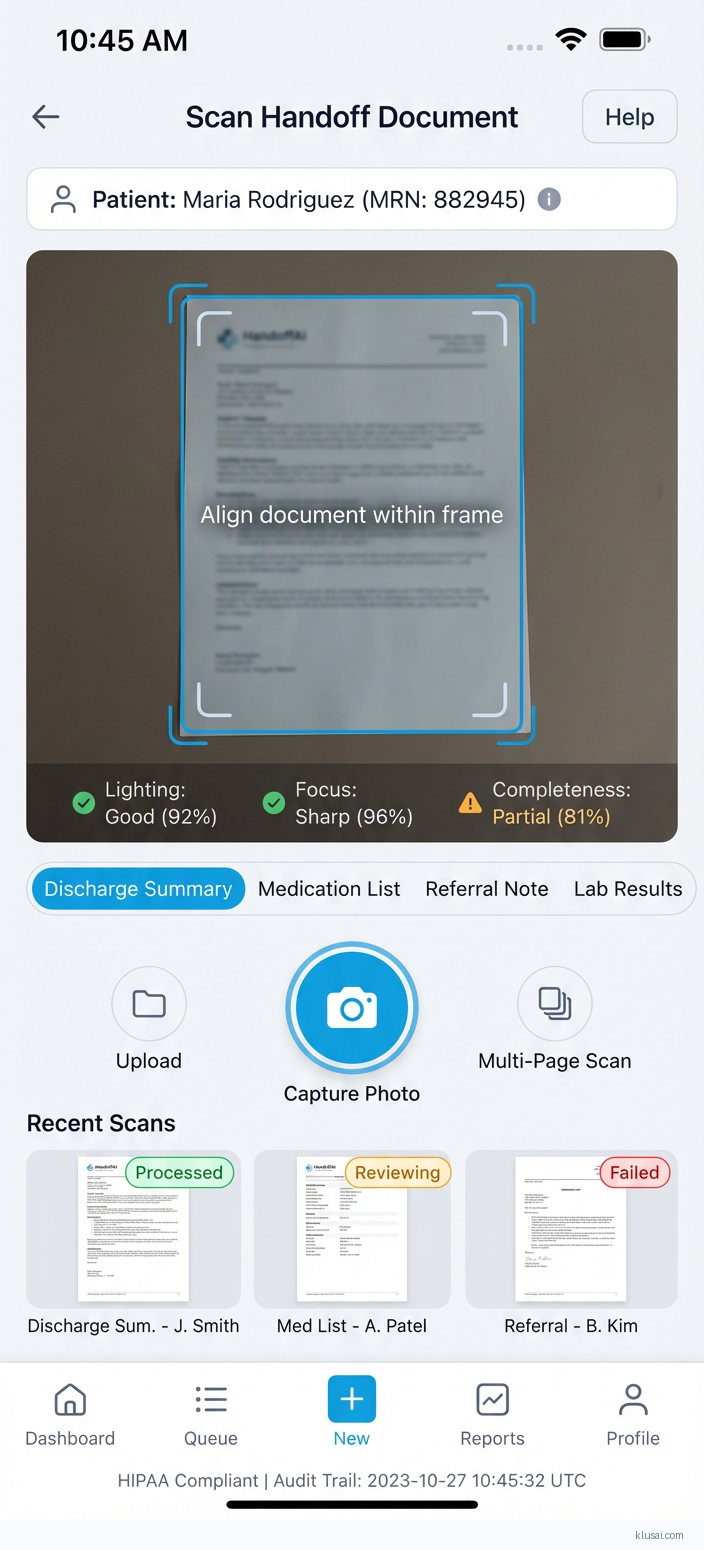
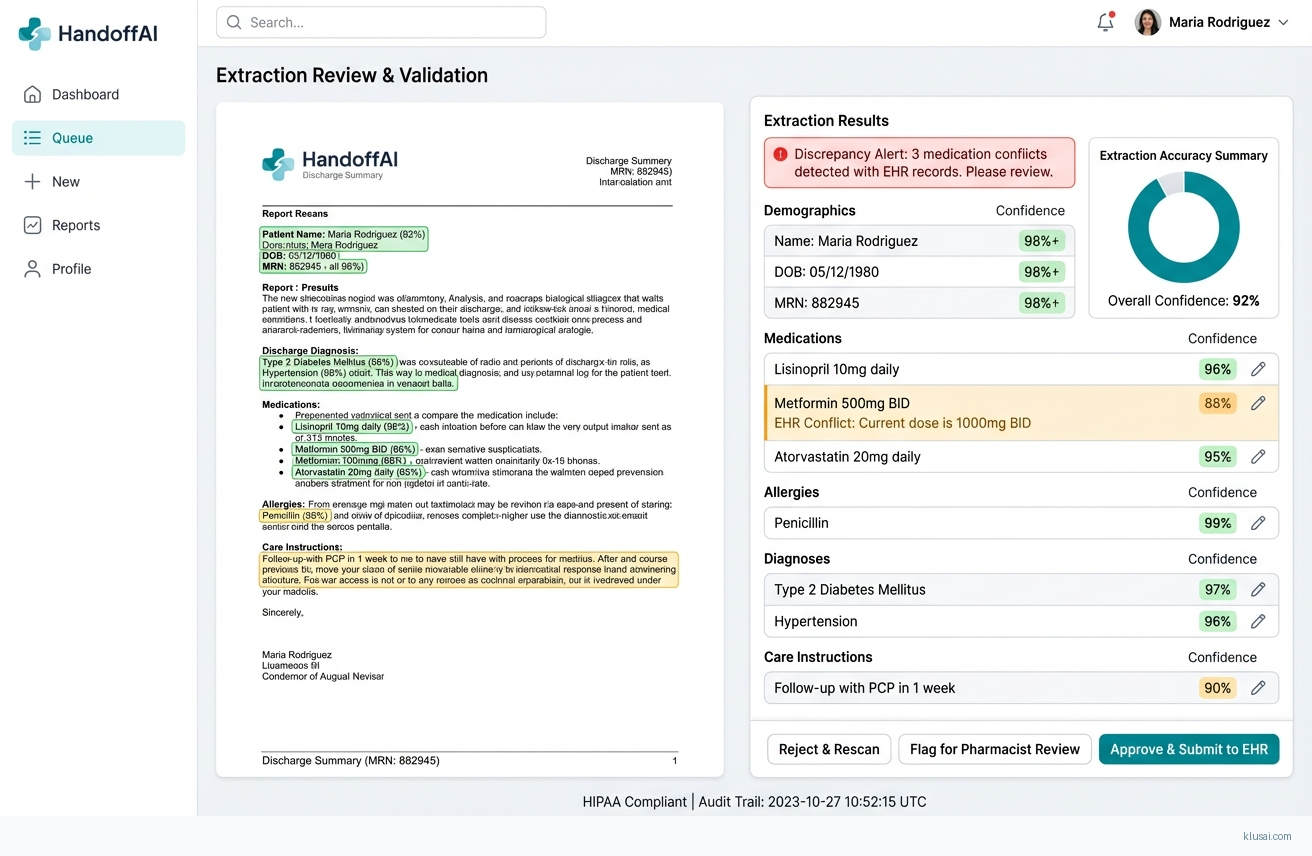
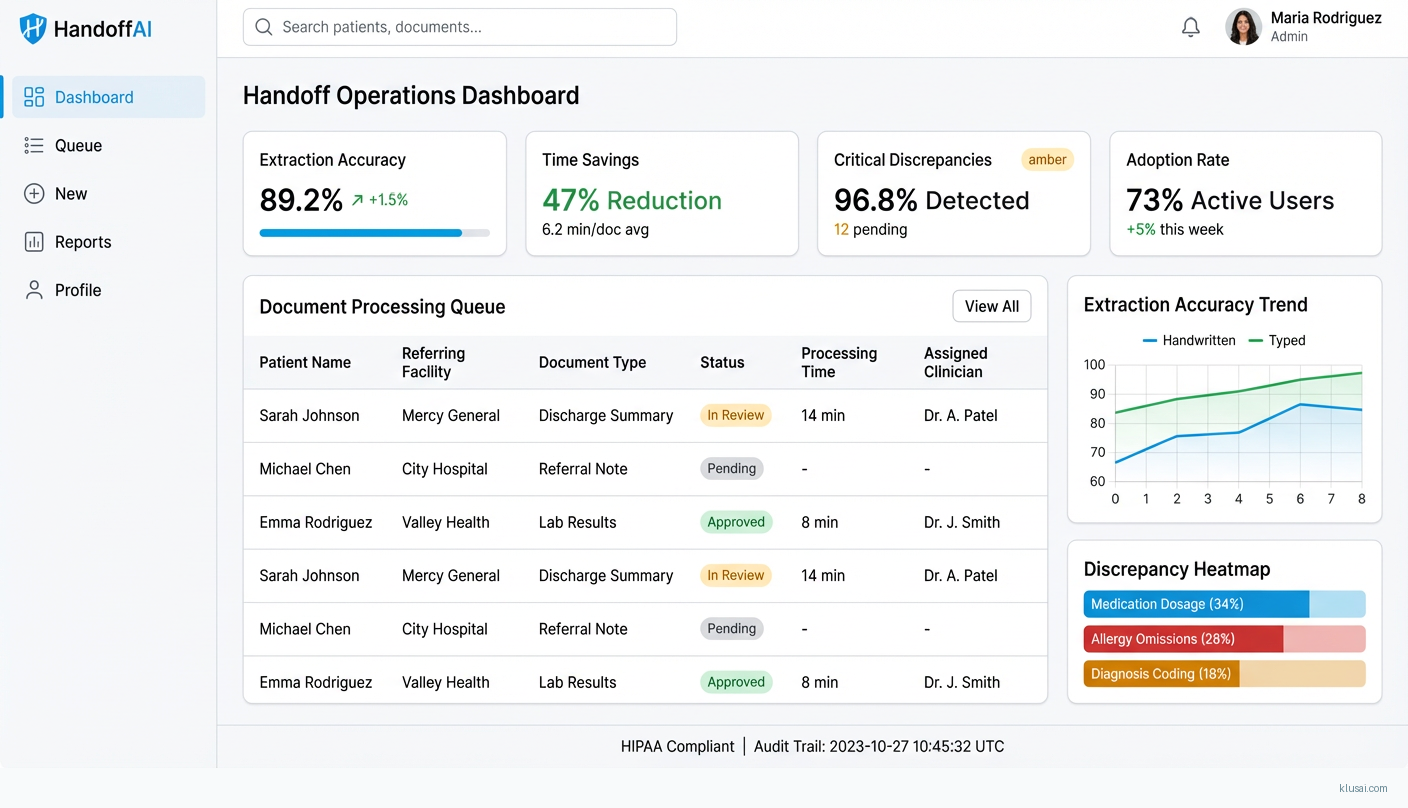
System Architecture
The architecture follows a layered approach with clear separation between document ingestion, AI processing, clinical validation, and EHR integration. The ingestion layer handles multi-format document intake (scanned PDFs, faxes, photos) with preprocessing for image enhancement, deskewing, and quality assessment. Documents failing quality thresholds are flagged for re-scanning rather than processed with degraded accuracy.
The AI processing layer combines commercial OCR engines with fine-tuned vision-language models for handwritten content extraction. A clinical NER (Named Entity Recognition) pipeline identifies medications, allergies, diagnoses, and care instructions, mapping extracted entities to standardized terminologies. The discrepancy detection module compares extracted data against the receiving facility's EHR, flagging conflicts in medications, allergies, or diagnoses for clinician attention.
The integration layer provides standardized FHIR R4 APIs for EHR connectivity, with pre-built connectors for major platforms (Epic, Cerner, Meditech, AllScripts). A message queue architecture ensures reliable delivery and supports both real-time and batch processing modes. The compliance layer implements RBAC, encryption (AES-256 at rest, TLS 1.3 in transit), immutable audit logging, and automated data retention policies with source document purging post-extraction.
All components support deployment in cloud (Azure, AWS, GCP), hybrid, or fully on-premise configurations to accommodate varying data residency requirements across jurisdictions. The modular design allows facilities to start with specific document types (e.g., medication lists) and expand to full handoff document coverage incrementally.
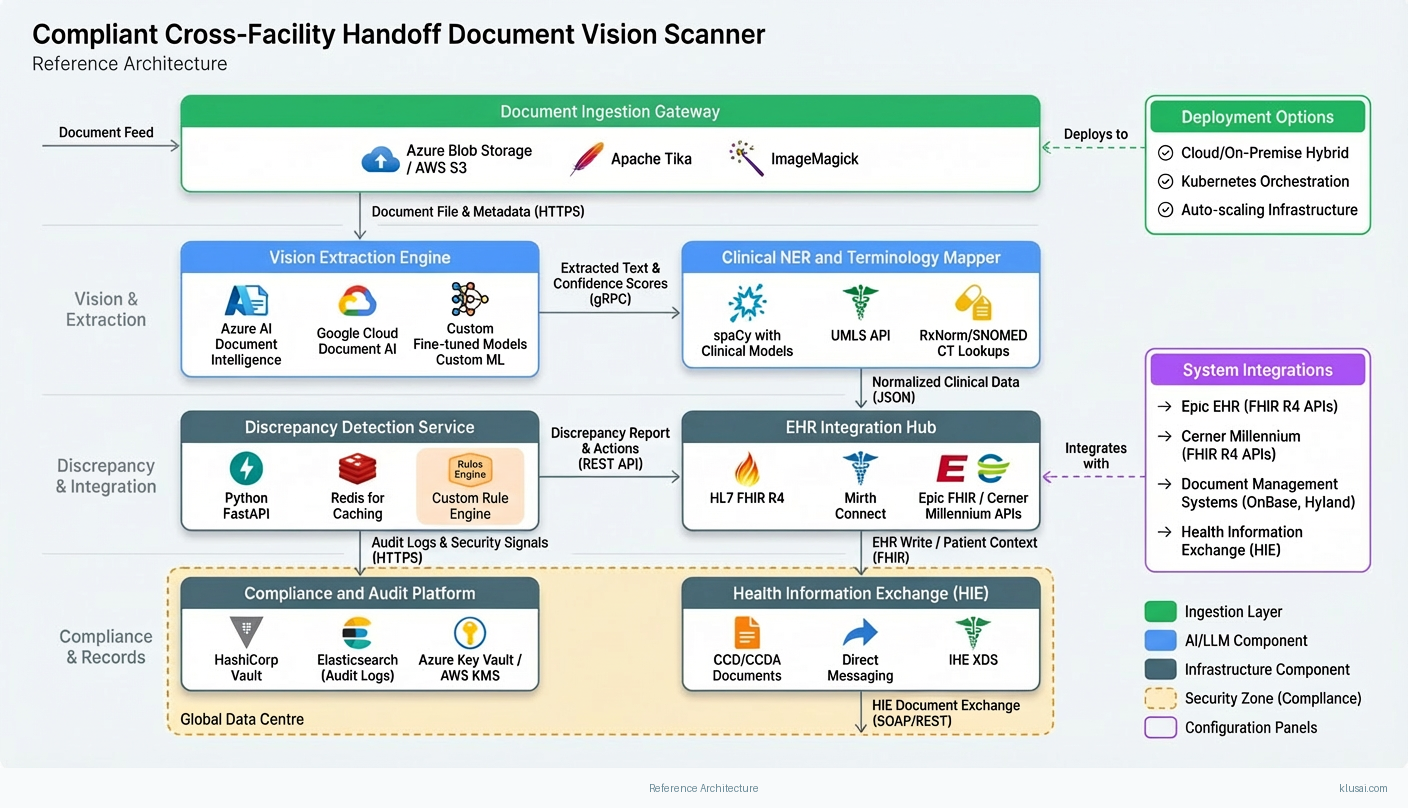
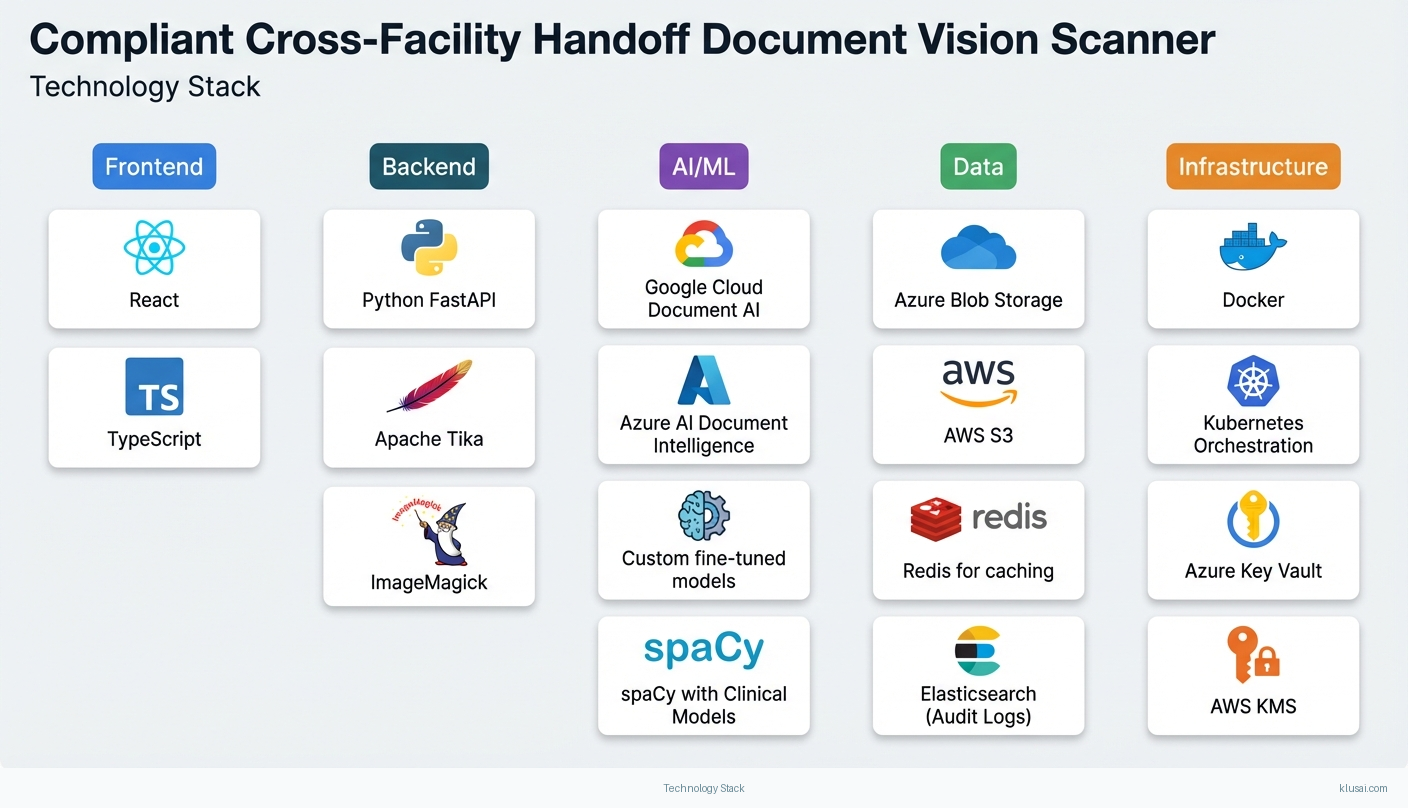
Key Components
| Component | Purpose | Technologies |
|---|---|---|
| Document Ingestion Gateway | Receives documents from multiple channels (secure upload, fax integration, EHR document feeds) with format normalization and quality assessment | Azure Blob Storage / AWS S3 Apache Tika ImageMagick |
| Vision Extraction Engine | Performs OCR and handwriting recognition with confidence scoring for each extracted field | Azure AI Document Intelligence Google Cloud Document AI Custom fine-tuned models |
| Clinical NER and Terminology Mapper | Identifies clinical entities and maps to standardized terminologies for interoperability | spaCy with clinical models UMLS API RxNorm/SNOMED CT lookups |
| Discrepancy Detection Service | Compares extracted data against receiving EHR to identify conflicts requiring clinician attention | Python FastAPI Redis for caching Custom rule engine |
| EHR Integration Hub | Manages bidirectional communication with EHR systems via standardized APIs | HL7 FHIR R4 Mirth Connect Epic FHIR / Cerner Millennium APIs |
| Compliance and Audit Platform | Implements security controls, access management, and regulatory reporting | HashiCorp Vault Elasticsearch (audit logs) Azure Key Vault / AWS KMS |
Technology Stack
Implementation Phases
Phase 1: Foundation and Data Strategy
Establish secure infrastructure with compliance controls validated by client security team
- • Establish secure infrastructure with compliance controls validated by client security team
- • Develop data acquisition strategy with 3-5 referring facilities for training document collection
- • Complete EHR integration assessment and API access provisioning for primary EHR platform
- Deployed infrastructure with security certification documentation
- Data sharing agreements with referring facilities; initial corpus of 500+ de-identified documents
- EHR integration technical specification and sandbox environment access
Phase 2: Model Development and Clinical Validation
Train and validate extraction models achieving >85% accuracy on handwritten content (pilot threshold)
- • Train and validate extraction models achieving >85% accuracy on handwritten content (pilot threshold)
- • Develop discrepancy detection rules with clinical informaticist input
- • Establish human review workflows and clinician training program
- Validated extraction models with documented accuracy metrics on held-out test set
- Discrepancy detection rule library covering medications, allergies, and key diagnoses
- Clinician training curriculum and change champion identification (minimum 2 per pilot unit)
Phase 3: Pilot Deployment and Parallel Run
Deploy to pilot unit (10-15 users) with 90-day parallel run comparing AI extraction to manual process
- • Deploy to pilot unit (10-15 users) with 90-day parallel run comparing AI extraction to manual process
- • Achieve >90% extraction accuracy and <5% critical error rate by end of parallel run
- • Validate time savings and refine automation thresholds based on real-world performance
- Pilot deployment with full monitoring and support coverage
- Weekly accuracy reports with error categorization and model improvement tracking
- Validated ROI metrics from parallel run data; go/no-go recommendation for expansion
Phase 4: Optimization and Expansion
Expand to additional units/facilities based on pilot success
- • Expand to additional units/facilities based on pilot success
- • Optimize automation rate to target 60-75% (validated, not assumed)
- • Establish ongoing model monitoring and retraining processes
- Expanded deployment to 3-5 additional units with documented rollout playbook
- Model monitoring dashboard with drift detection and retraining triggers
- Operational runbook for ongoing support and continuous improvement
Key Technical Decisions
Should we use commercial document AI services or build custom extraction models?
Commercial services provide reliable baseline for printed content with minimal development effort. Handwritten medical content requires specialized training due to domain-specific abbreviations and terminology. Custom clinical NER ensures accurate entity extraction and terminology mapping.
- Faster time-to-value with commercial OCR for printed content (60-70% of typical documents)
- Custom models can be continuously improved with production data
- Higher initial development cost for custom handwriting models
- Dependency on commercial API availability and pricing changes
How should we handle documents with low extraction confidence?
Clinical safety requires human oversight for uncertain extractions. Starting with conservative thresholds (85% mandatory review) allows the system to build trust while collecting feedback for model improvement. Thresholds can be adjusted based on pilot data and clinical risk tolerance.
- Maintains clinical safety while maximizing automation where confidence is high
- Provides structured feedback loop for model improvement
- Higher human review volume in early deployment reduces initial time savings
- Requires clear UI for efficient human review workflow
Should we deploy cloud-native or support on-premise installation?
Cloud deployment reduces infrastructure burden and enables faster updates. However, some healthcare organizations (particularly in EU/UK and government facilities) require on-premise deployment for data sovereignty. Containerized architecture (Kubernetes) supports both models with minimal code changes.
- Cloud deployment enables rapid iteration and reduces client infrastructure burden
- On-premise option expands addressable market to high-security environments
- Supporting both deployment models increases testing and maintenance complexity
- On-premise deployments have longer update cycles and higher support costs
Integration Patterns
| System | Approach | Complexity | Timeline |
|---|---|---|---|
| Epic EHR | FHIR R4 APIs via Epic App Orchard certification; read patient context, write extracted data to appropriate flowsheets and medication lists; leverage Epic's existing document management for source storage | high | 8-12 weeks including App Orchard certification |
| Cerner Millennium | FHIR R4 APIs with Cerner Code program registration; integrate with PowerChart for clinician review workflow; use Millennium Objects for complex data writes | high | 8-10 weeks |
| Document Management Systems (OnBase, Hyland) | Integrate with existing document ingestion workflows; receive documents from DMS rather than requiring separate upload; write extraction results back to DMS metadata | medium | 4-6 weeks |
| Health Information Exchange (HIE) | Receive CCD/CCDA documents via Direct messaging or IHE XDS; extract structured data from semi-structured sections; flag discrepancies against local EHR | medium | 4-6 weeks |
ROI Framework
ROI is driven by clinician time savings from reduced manual transcription, faster care initiation from eliminated data entry delays, and reduced adverse events from improved medication reconciliation accuracy. The framework uses conservative assumptions validated during pilot deployment[2][4].
Key Variables
Example Calculation
Build vs. Buy Analysis
Internal Build Effort
Internal build requires 14-20 months with a team of 8-10 FTEs including ML engineers with healthcare NLP experience, integration specialists with EHR expertise, compliance/security specialists, and clinical informaticists. Key challenges include acquiring sufficient training data (2,000+ annotated documents), achieving regulatory compliance certification, and maintaining EHR integrations as vendor APIs evolve. Estimated build cost: $1.2M-$1.8M; ongoing maintenance: $400K-$600K annually.
Market Alternatives
EHR Vendor Native Solutions (Epic Scan, Cerner Document Management)
Included in EHR licensing or modest add-on ($10K-$30K annually)Built-in document scanning with basic OCR; optimized for intra-facility documents rather than cross-facility handoffs
- • Native integration with existing EHR workflows
- • No additional vendor relationship or security review
- • Familiar interface for clinical staff
- • Limited handwriting recognition capability
- • No cross-facility discrepancy detection
- • Minimal automation—primarily digitization, not extraction
ABBYY FlexiCapture for Healthcare
$50K-$120K annually plus implementationEnterprise document capture platform with healthcare templates; requires significant customization for handoff use case
- • Mature OCR technology with strong printed text accuracy
- • Established enterprise deployment track record
- • Flexible workflow configuration
- • Limited handwriting recognition for medical content
- • EHR integration requires custom development
- • Not designed for clinical discrepancy detection
General Document AI Platforms (Azure AI Document Intelligence, Google Document AI)
$20K-$60K annually based on volume (API pricing)Cloud-native document processing with pre-built models; requires healthcare-specific customization
- • Strong baseline OCR and layout analysis
- • Continuous model improvements from vendor
- • Scalable cloud infrastructure
- • No healthcare-specific entity extraction out of box
- • Requires custom development for clinical workflows
- • Data residency concerns for some organizations
Our Positioning
KlusAI is the right choice when organizations need a solution specifically designed for cross-facility handoff complexity—handling diverse document formats, handwritten content, and multi-EHR environments with clinical discrepancy detection. Our approach assembles specialized expertise in healthcare vision AI, clinical informatics, and regulatory compliance, delivering a tailored solution with dedicated change management support. We're particularly suited for health systems where document variability is high, existing solutions have proven inadequate, and clinical safety during transitions is a strategic priority.
Team Composition
KlusAI assembles a cross-functional team combining healthcare AI expertise, clinical informatics knowledge, enterprise integration experience, and dedicated change management support. Team composition scales based on deployment complexity, number of EHR platforms, and organizational change readiness.
| Role | FTE | Focus |
|---|---|---|
| Healthcare AI/ML Engineer | 1.5 | Vision model development, fine-tuning for handwritten medical documents, clinical NER pipeline development |
| Clinical Informaticist | 0.5 | Clinical workflow design, discrepancy rule configuration, terminology mapping validation, safety review protocols |
| Integration Engineer | 1.0 | EHR API integration, HL7 FHIR implementation, document management system connectivity |
| Change Management Lead | 0.5 | Clinician training program development, change champion coordination, adoption monitoring, workflow optimization |
| DevOps/Platform Engineer | 0.75 | Infrastructure deployment, CI/CD pipelines, monitoring and observability, security controls |
Supporting Evidence
Performance Targets
>85% at pilot launch, >90% by end of parallel run
40-60% reduction in processing time, validated during pilot
>80% of pilot users actively using system by week 8 of pilot
>95% of medication/allergy conflicts identified
Team Qualifications
- KlusAI's network includes professionals with healthcare AI implementation experience across document processing, clinical NLP, and EHR integration projects
- Our teams are assembled with specific expertise in healthcare compliance frameworks (HIPAA, GDPR, ISO 27001) and clinical workflow optimization
- We bring together technical specialists in vision AI and clinical informaticists who understand medication reconciliation and handoff safety requirements
Source Citations
communication gaps as a major issue in care transitions
directionalGenAI automates documentation, surfaces care gaps, streamlines communications; reduces administrative burden
directionalCurrent solutions in medical imaging (Aidoc, Viz.ai), remote monitoring (Biofourmis); no mention of handoff document OCR
directionalAmbient scribe tools reducing clinician burnout by automating charting; AI handles tedious error-prone details
directionalProviders focused on AI for administrative work like ambient scribes, revenue cycle; not inter-facility handoffs
directionalReady to discuss?
Let's talk about how this could work for your organization.
Schedule a Consultation
Pick a date that works for you
Times shown in your local timezone ()
Prefer email? Contact us directly
Almost there!
at
Your details
at
You're all set!
Check your email for confirmation and calendar invite.
Your booking is confirmed! Our team will reach out to confirm the details.
Your consultation
· min
( team time)
Quick Overview
- Technology
- Computer Vision
- Complexity
- high
- Timeline
- 5-7 months
- Industry
- Healthcare