The Problem
Fragmented communication across EU care teams creates significant barriers to seamless patient handoffs during cross-border care transitions, compromising safety and efficiency .
Digitalization of health data varies widely between EU member states, with incompatible EHR formats, language barriers, and manual processes delaying access to critical clinical notes, medication lists, and treatment plans . The EHDS Regulation mandates exchange of patient summaries and ePrescriptions across borders by March 2029, yet current systems lack the required interoperability and standardization .
Manual ad-hoc solutions like faxes and translations are error-prone, non-compliant with GDPR/MDR/EHDS, and hinder the single market for digital health, with EHDS expected to generate €11 billion in savings through better data accessibility .
Our Approach
Key elements of this implementation
-
LLM-powered RAG synthesis of EHR data into EHDS-compliant multilingual patient summaries/discharge reports with 95%+ clinician-validated accuracy
-
Native MyHealth@EU integration for primary data exchange, supporting pseudonymized access to clinical notes and treatment plans across borders
-
GDPR/MDR/EHDS compliance: EU data residency, immutable audit trails, automated access logging/reporting, and clinician-in-loop validation
-
Phased 90-day rollout with 10-user pilot, 2-week clinician training, parallel manual review, and change champions to mitigate adoption/data quality risks
Get the Full Implementation Guide
Unlock full details including architecture and implementation
Implementation Overview
This solution addresses the critical challenge of fragmented cross-border care communication within the EU healthcare ecosystem. With the EHDS Regulation mandating exchange of patient summaries and ePrescriptions across borders by March 2029 [1][2], healthcare providers face an urgent need to transform manual, error-prone handoff processes into automated, compliant digital workflows. Our approach leverages retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) to synthesize structured and unstructured EHR data into standardized, multilingual care transition documents that meet EHDS interoperability requirements.
The architecture centres on three core capabilities: intelligent document synthesis using LLMs with domain-specific retrieval, native integration with the MyHealth@EU infrastructure for primary data exchange, and comprehensive compliance orchestration covering GDPR, MDR, and EHDS requirements. The RAG pipeline ingests clinical notes, medication lists, and treatment plans from heterogeneous EHR systems, normalizes them against HL7 FHIR R4 and IHE profiles, and generates clinician-validated summaries in the patient's destination country language. All processing occurs within EU data residency boundaries with immutable audit trails.
Expected outcomes include 60-75% reduction in care transition document preparation time, 95%+ clinician-validated accuracy on generated summaries, and full compliance readiness for the March 2029 EHDS primary use deadline. The phased rollout prioritizes risk mitigation through parallel manual review, clinician-in-the-loop validation, and change champion engagement to address adoption challenges inherent in clinical workflow transformation.
UI Mockups
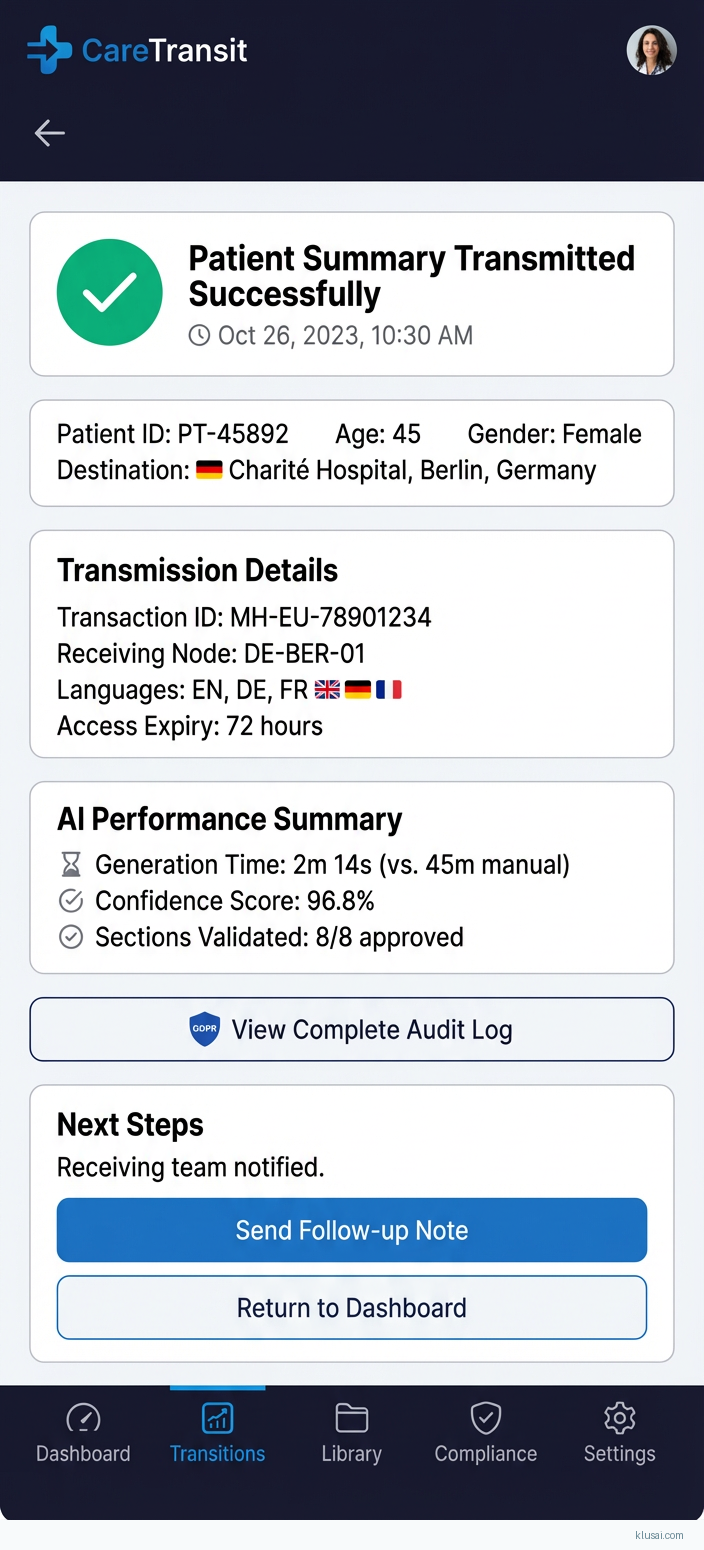
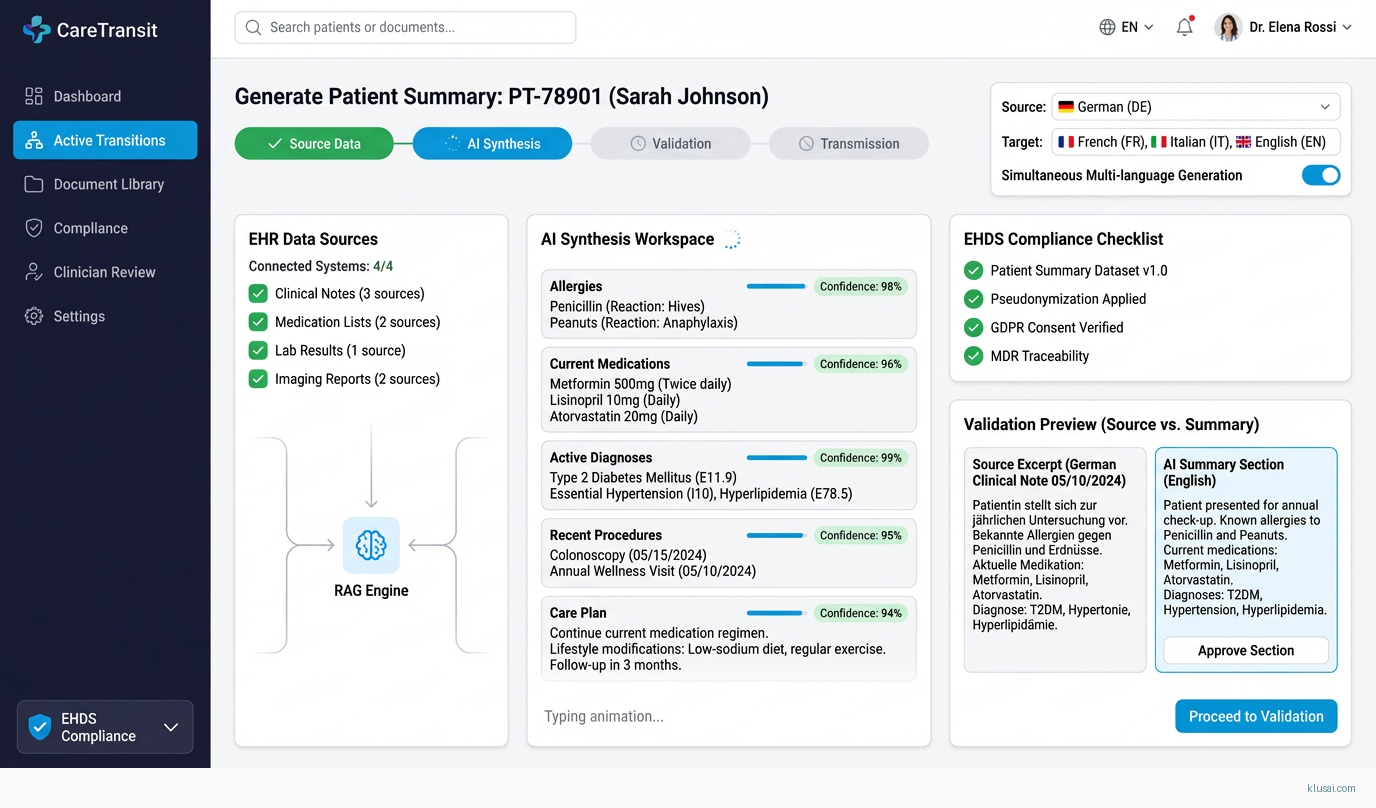
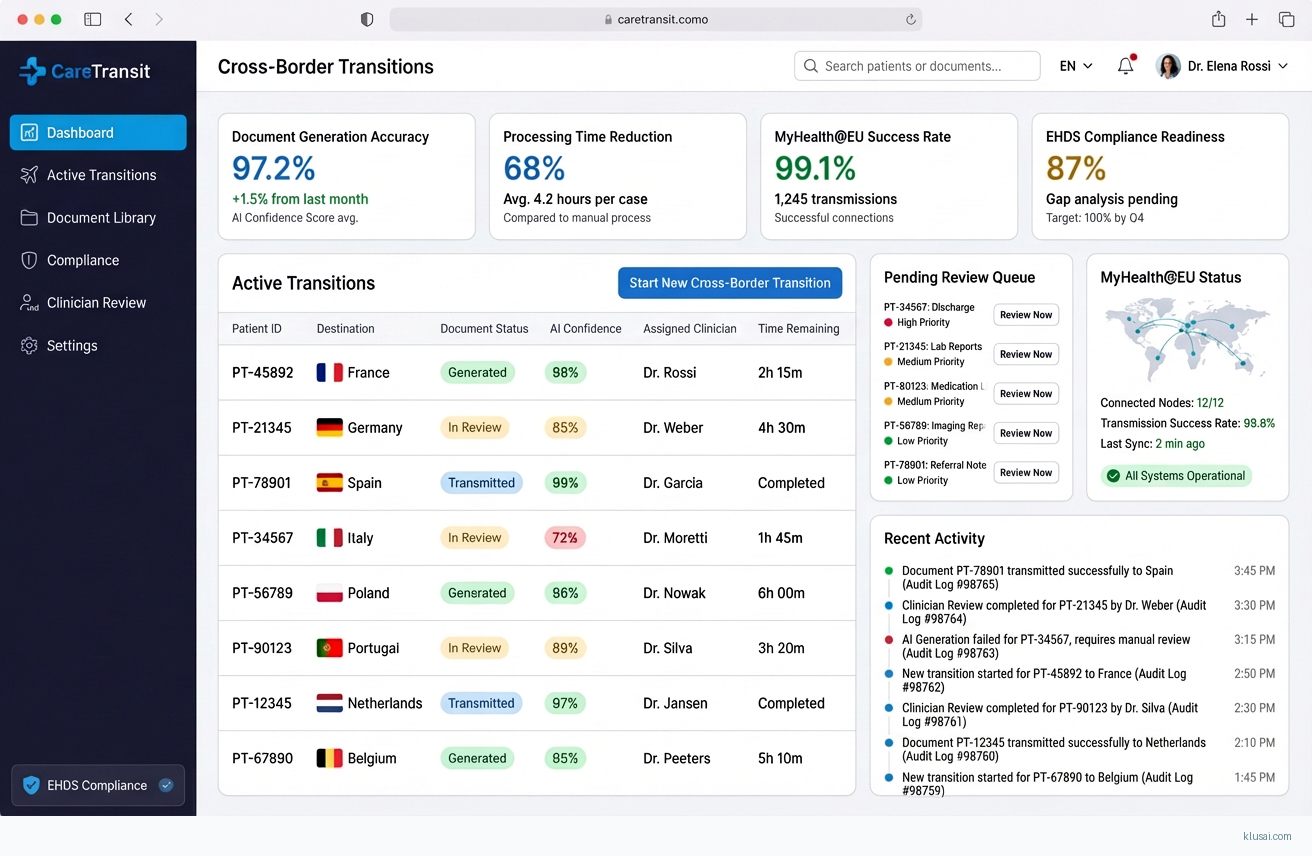
System Architecture
The architecture follows a layered design pattern optimized for healthcare data sensitivity, regulatory compliance, and cross-border interoperability. The ingestion layer connects to source EHR systems via HL7 FHIR R4 APIs and legacy HL7v2 interfaces where necessary, normalizing incoming clinical data against IHE International Patient Summary (IPS) profiles. This layer handles the significant variation in EHR digitalization maturity across EU member states [4], providing adapters for major European EHR vendors including Dedalus, CompuGroup Medical, and Cerner.
The processing layer implements the RAG pipeline with a vector store containing medical terminology embeddings, clinical guidelines, and EHDS-compliant document templates. Source documents are chunked, embedded, and indexed to enable semantic retrieval during generation. The LLM orchestration component manages prompt engineering, context window optimization, and output validation against clinical accuracy criteria. All LLM inference occurs on EU-hosted infrastructure with no data egress to non-EU regions.
The compliance layer provides cross-cutting services including consent management aligned with GDPR Article 9 requirements for health data, automated access logging for EHDS audit requirements, and MDR classification assessment for any components that may qualify as medical devices. The MyHealth@EU integration layer handles the National Contact Point (NCP) protocols for cross-border data exchange, implementing the required eHDSI (eHealth Digital Service Infrastructure) messaging patterns.
The presentation layer exposes clinician-facing interfaces for document review and validation, patient-facing portals for consent management and document access, and administrative dashboards for compliance monitoring. All interfaces support the 24 official EU languages with medical terminology localization validated against national health terminology services.
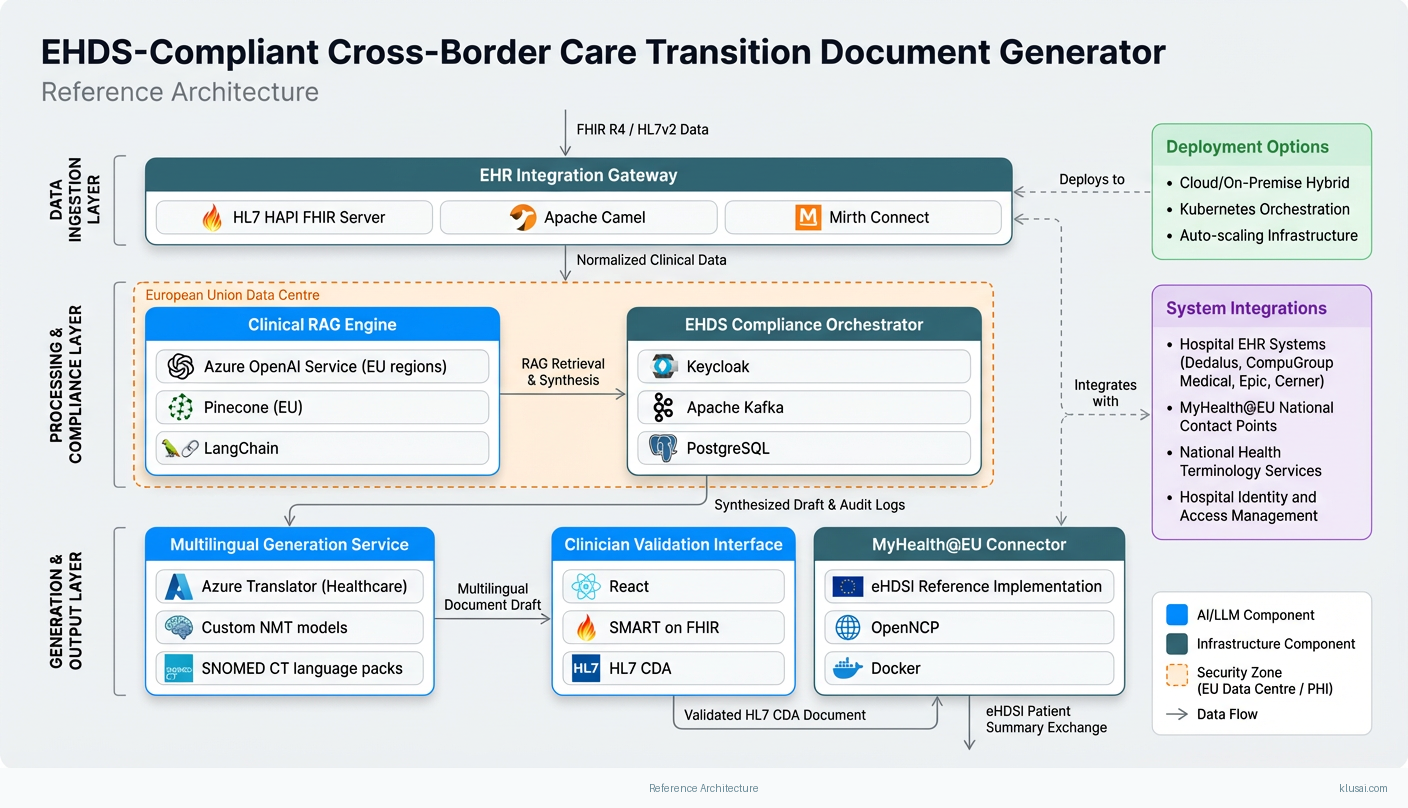
Key Components
| Component | Purpose | Technologies |
|---|---|---|
| EHR Integration Gateway | Normalize and ingest clinical data from heterogeneous European EHR systems via FHIR R4 and legacy protocols | HAPI FHIR Server Apache Camel Mirth Connect |
| Clinical RAG Engine | Semantic retrieval and LLM-powered synthesis of care transition documents from multi-source clinical data | Azure OpenAI Service (EU regions) Pinecone (EU) LangChain |
| EHDS Compliance Orchestrator | Manage consent, audit logging, access control, and regulatory reporting across GDPR/MDR/EHDS requirements | Keycloak Apache Kafka PostgreSQL |
| MyHealth@EU Connector | Interface with National Contact Points for cross-border patient summary and ePrescription exchange | eHDSI Reference Implementation OpenNCP Docker |
| Multilingual Generation Service | Produce clinician-validated care documents in destination country language with medical terminology accuracy | Azure Translator (Healthcare) Custom NMT models SNOMED CT language packs |
| Clinician Validation Interface | Enable human-in-the-loop review, correction, and approval of generated care transition documents | React SMART on FHIR HL7 CDA |
Technology Stack
Implementation Phases
Foundation & Compliance Framework
Establish EU-compliant infrastructure with data residency guarantees and security controls
- • Establish EU-compliant infrastructure with data residency guarantees and security controls
- • Implement GDPR/EHDS consent management and audit logging framework
- • Deploy EHR integration gateway with initial FHIR R4 connectivity to pilot site
- Production-ready Azure infrastructure in EU regions with security hardening and penetration test report
- Consent management system with patient-facing portal and clinician access controls
- EHR integration gateway connected to pilot hospital's primary EHR system with data flow validation
RAG Pipeline & Document Generation
Deploy clinical RAG engine with medical terminology embeddings and retrieval optimization
- • Deploy clinical RAG engine with medical terminology embeddings and retrieval optimization
- • Implement multilingual document generation with clinician validation workflow
- • Achieve 90%+ accuracy on synthetic test cases before real patient data processing
- Functional RAG pipeline generating IPS-compliant patient summaries from pilot site EHR data
- Clinician validation interface integrated into pilot site clinical workflow
- Accuracy validation report demonstrating 90%+ concordance with clinician-authored summaries on test dataset
MyHealth@EU Integration & Cross-Border Testing
Complete MyHealth@EU NCP integration with conformance certification
- • Complete MyHealth@EU NCP integration with conformance certification
- • Execute cross-border data exchange tests with partner member state NCPs
- • Validate end-to-end workflow from source EHR to destination care team receipt
- MyHealth@EU conformance certification for patient summary exchange
- Successful cross-border test transactions with minimum 3 partner member state NCPs
- End-to-end workflow documentation with clinician training materials
Pilot Expansion & Production Hardening
Expand pilot from 10 to 50 users across multiple clinical departments
- • Expand pilot from 10 to 50 users across multiple clinical departments
- • Achieve 95%+ clinician-validated accuracy on production documents
- • Complete change management program with trained change champions
- Production system supporting 50 concurrent users with <3s document generation latency
- Accuracy validation report demonstrating 95%+ clinician concordance on 500+ production documents
- Trained change champion network (minimum 5 champions) with ongoing support program
Key Technical Decisions
Should we use a general-purpose LLM or a healthcare-specific fine-tuned model for clinical document generation?
General-purpose models with strong RAG grounding provide faster time-to-value and avoid the 6-12 month investment in fine-tuning infrastructure. Healthcare-specific prompting combined with retrieval from authoritative clinical sources achieves comparable accuracy for structured document generation tasks. Fine-tuning pathway preserves option to specialize based on accumulated pilot data and identified edge cases.
- Faster deployment (weeks vs months) with proven model capabilities
- Lower initial investment; fine-tuning can be data-driven based on actual production patterns
- May require more extensive prompt engineering for edge cases
- Potential for higher per-inference costs compared to optimized fine-tuned model at scale
Should we build custom MyHealth@EU integration or leverage the OpenNCP reference implementation?
OpenNCP is the EU-endorsed reference implementation for eHDSI/MyHealth@EU connectivity, maintained by the European Commission and validated against all member state NCPs. Building custom integration would require 12-18 months of development and certification effort with significant risk of interoperability issues. OpenNCP provides conformance assurance while allowing extension points for operational enhancements.
- Pre-certified conformance with MyHealth@EU requirements reduces certification timeline by 6+ months
- Active community and EC support for ongoing eHDSI specification changes
- Less flexibility in protocol handling and error recovery compared to custom implementation
- Dependency on OpenNCP release cycle for new features and bug fixes
How should we handle the varying EHR maturity levels across EU member states?
EHR digitalization varies widely between EU member states [4], with some hospitals operating fully FHIR-native systems while others rely on legacy HL7v2 or even paper-based records. A tiered approach maximizes coverage while prioritizing modern standards. The integration gateway abstracts source system complexity from the RAG pipeline, enabling consistent document generation regardless of source format.
- Maximizes addressable market across EU healthcare landscape
- Graceful degradation maintains functionality even with limited source data
- Legacy integration increases maintenance burden and testing complexity
- Document-based ingestion may have lower accuracy due to OCR/NLP extraction errors
Should audit logs be stored in a centralized EU location or distributed across member state boundaries?
EHDS requires comprehensive audit trails for cross-border data access [1][3], but individual member states may have additional data localization requirements. Centralized storage simplifies compliance reporting and security monitoring while logical partitioning enables member state-specific data residency compliance. Immutable append-only storage with cryptographic verification ensures audit integrity.
- Simplified compliance reporting and security monitoring across all transactions
- Consistent audit trail format enables cross-border incident investigation
- May require additional data residency controls for specific member states
- Single point of audit storage requires robust disaster recovery
Integration Patterns
| System | Approach | Complexity | Timeline |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hospital EHR Systems (Dedalus, CompuGroup Medical, Epic, Cerner) | FHIR R4 REST API integration using SMART on FHIR for authentication and IHE IPS profile for patient summary retrieval; fallback to HL7v2 ADT/ORU messages via Mirth Connect for legacy systems | high | 6-10 weeks per EHR vendor |
| MyHealth@EU National Contact Points | OpenNCP-based integration implementing eHDSI Patient Summary and ePrescription profiles; asynchronous message exchange with guaranteed delivery via Kafka | high | 8-12 weeks including conformance testing |
| National Health Terminology Services | REST API integration with national SNOMED CT/ICD-10 terminology servers for code validation and translation; caching layer for high-frequency lookups | medium | 3-4 weeks per member state |
| Hospital Identity and Access Management | SAML 2.0/OIDC federation with hospital identity providers; role-based access control mapped to clinical roles; integration with national eID schemes where available | medium | 4-6 weeks |
ROI Framework
ROI is driven by clinician time savings in care transition documentation, reduction in adverse events from communication gaps, and compliance cost avoidance as EHDS deadlines approach. The framework quantifies direct labour savings while acknowledging that patient safety improvements and regulatory compliance provide additional strategic value that is harder to monetize [1].
Key Variables
Example Calculation
Build vs. Buy Analysis
Internal Build Effort
Internal build would require 18-24 months with a team of 6-8 FTEs including FHIR/HL7 integration specialists, ML engineers with healthcare NLP experience, and compliance/regulatory expertise. Key challenges include MyHealth@EU conformance certification (6-12 months alone), multilingual medical terminology accuracy, and ongoing EHDS specification changes. Estimated internal build cost: €1.2-1.8M excluding opportunity cost and ongoing maintenance.
Market Alternatives
InterSystems HealthShare
€200-500K initial + €80-150K annualEnterprise health information exchange platform with strong FHIR capabilities; established in EU market with some MyHealth@EU deployments
- • Mature platform with proven EU healthcare deployments
- • Strong interoperability capabilities and vendor support
- • Limited native LLM/AI capabilities for document generation
- • Significant customization required for EHDS-specific workflows
Rhapsody (Rhapsody Health)
€100-250K initial + €40-80K annualIntegration engine focused on healthcare data exchange; strong HL7/FHIR support but requires additional components for document generation
- • Flexible integration capabilities across legacy and modern systems
- • Lower entry cost for basic interoperability
- • No native AI/LLM capabilities; requires separate solution for document generation
- • MyHealth@EU integration would require custom development
Custom Development with Cloud AI Services
€400-800K development + €60-120K annual cloud costsBuild using Azure OpenAI, AWS HealthLake, or Google Cloud Healthcare API with custom integration layer
- • Maximum flexibility and control over architecture
- • Can leverage latest AI capabilities as they emerge
- • Requires deep healthcare interoperability expertise
- • MyHealth@EU conformance certification is complex and time-consuming
Our Positioning
KlusAI is the right choice for organizations that need EHDS compliance readiness with AI-powered document generation but lack the internal expertise to navigate healthcare interoperability, regulatory compliance, and LLM implementation simultaneously. We assemble specialized teams combining healthcare IT integration, clinical informatics, and AI engineering expertise tailored to each engagement, providing faster time-to-value than internal build while offering more customization than off-the-shelf platforms.
Team Composition
KlusAI assembles cross-functional teams combining healthcare interoperability expertise, AI/ML engineering, clinical informatics, and regulatory compliance. Team composition scales based on implementation complexity and client internal capabilities.
| Role | FTE | Focus |
|---|---|---|
| Healthcare Integration Architect | 1.0 | EHR connectivity, FHIR/HL7 integration, MyHealth@EU NCP protocols |
| ML/AI Engineer | 1.0 | RAG pipeline development, LLM integration, accuracy optimization |
| Clinical Informatics Specialist | 0.5 | Clinical workflow design, accuracy validation, clinician training |
| Compliance & Security Lead | 0.5 | GDPR/MDR/EHDS compliance, security architecture, audit framework |
| Project Manager | 0.75 | Delivery coordination, stakeholder management, risk mitigation |
Supporting Evidence
Performance Targets
95%+ clinician-validated concordance
60-75% reduction in care transition documentation time
>98% successful MyHealth@EU transactions
100% compliance with EHDS primary use requirements by March 2029 deadline
Team Qualifications
- KlusAI's network includes professionals with extensive experience in HL7 FHIR implementation, eHDSI integration, and EU healthcare interoperability standards
- Our teams are assembled with specific expertise in healthcare AI applications, including clinical NLP, medical terminology systems, and LLM deployment in regulated environments
- We bring together technical specialists and domain experts with backgrounds in GDPR health data compliance, MDR classification, and emerging EHDS requirements
Source Citations
Fragmented communication across EU care teams creates significant barriers
directionalEHDS mandates exchange of patient summaries and ePrescriptions by March 2029
"March 2029: Key parts of the EHDS Regulation will enter into application, including, for primary use, the exchange of the first group of priority categories of health data (Patient Summaries, ePrescriptions/eDispensations)"exact
EHDS expected to generate €11 billion in savings
"generate €11 billion in savings over the next decade by enhancing data accessibility"exact
By March 2029, EU citizens will be able to access patient summaries, electronic prescriptions
"By March 2029, EU citizens will be able to access and use electronic patient summaries, electronic prescriptions and electronic dispensations in all EU member states"exact
Health care providers must comply with EHDS requirements for data sharing, interoperability
"Health care providers established in the EU, including hospitals, clinics and private practices, must comply with EHDS requirements for data sharing, interoperability and patient access"exact
incompatible EHR formats, language barriers, and manual processes delaying access
directionalfirst data exchanges are scheduled to begin in 2029
"The regulation establishing the EHDS went into effect in late March 2025 and its first data exchanges are scheduled to begin in 2029"exact
Ready to discuss?
Let's talk about how this could work for your organization.
Schedule a Consultation
Pick a date that works for you
Times shown in your local timezone ()
Prefer email? Contact us directly
Almost there!
at
Your details
at
You're all set!
Check your email for confirmation and calendar invite.
Your booking is confirmed! Our team will reach out to confirm the details.
Your consultation
· min
( team time)
Quick Overview
- Technology
- Large Language Models
- Complexity
- high
- Timeline
- 5-7 months
- Industry
- Healthcare
- Region
- European Union