The Problem
EU healthcare systems face significant delays in specialist referrals due to manual processing of GP letters, faxes, and handwritten notes, contributing to extended patient wait times.
Challenges include poor document quality (handwritten text, low-resolution scans), lack of audit trails in paper records, and strict requirements under GDPR for data privacy and MDR (EU 2017/745) for software classified as medical devices requiring clinical validation.
Current manual workflows or basic OCR tools demand substantial human review, lack healthcare-specific ICR/OCR precision, fail EU data residency, and do not provide MDR-compliant validation or GDPR audit logging, slowing integration with EHR systems.
Our Approach
Key elements of this implementation
-
Vision AI with ICR/OCR/NLP for handwritten/printed referrals, auto-validating clinical data completeness per MDR requirements with per-field confidence scores >95%
-
GDPR compliance via EU data centers, end-to-end encryption, pseudonymization, and immutable audit trails logging all access/extractions; MDR as SaMD with clinical evaluation pathway, risk management per Annex I, and CE marking process
-
Native API integration with EU EHRs (Epic Europe, Cerner Millennium, Orbis) for auto-routing validated referrals to scheduling, with human-in-loop for <95% confidence cases
-
Phased rollout: 60-day parallel run, 2-week clinician training via change champions, addressing risks like data quality variances and adoption resistance with 20% timeline buffer
Get the Full Implementation Guide
Unlock full details including architecture and implementation
Implementation Overview
This solution addresses the significant delays in EU specialist referrals caused by manual processing of GP letters, faxes, and handwritten clinical notes[1][2]. The architecture combines OCR for printed text with ICR (Intelligent Character Recognition) for handwritten content[4], supported by clinical NLP for entity extraction and validation. Documents flow through a multi-stage pipeline: ingestion, preprocessing, text extraction, clinical entity recognition, confidence scoring, and either automated EHR routing or human review queue based on configurable thresholds.
The architecture prioritizes regulatory compliance through EU-only data residency, end-to-end encryption, pseudonymization of patient identifiers during processing, and immutable audit trails logging all access and extraction events[5]. For MDR compliance, the system is designed as a Class IIa Software as Medical Device (SaMD), with the implementation timeline structured to support—but not guarantee—the clinical evaluation and CE marking pathway. Notified body engagement timelines are inherently variable and may extend beyond the core implementation phases.
Key architectural decisions include separation of the ML inference layer from the integration layer (enabling independent scaling and updates), a human-in-the-loop workflow for low-confidence extractions[4], and native HL7 FHIR R4 interfaces for EU EHR connectivity. Multi-language support addresses EU linguistic diversity, with initial deployment targeting the primary language of the implementing organization and expansion capability for additional EU languages.
UI Mockups
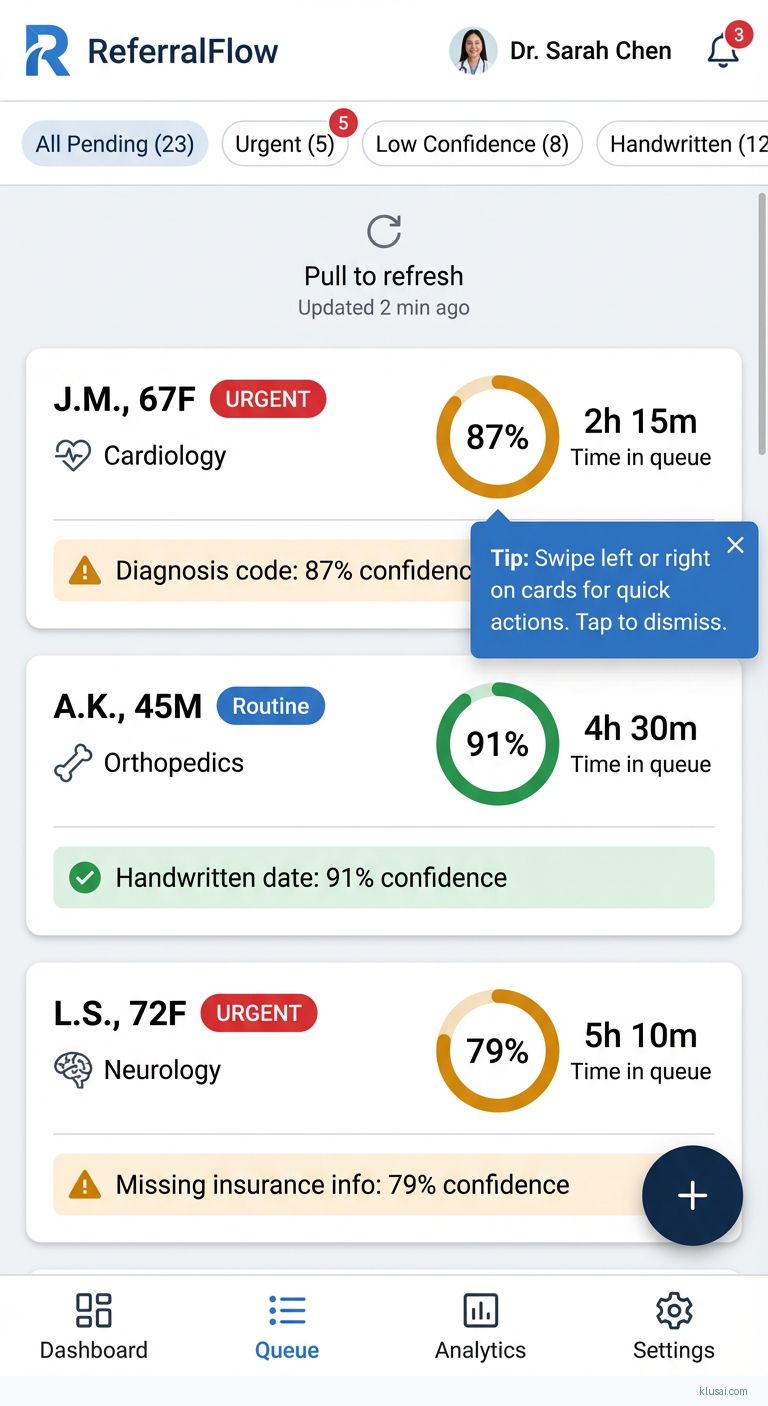
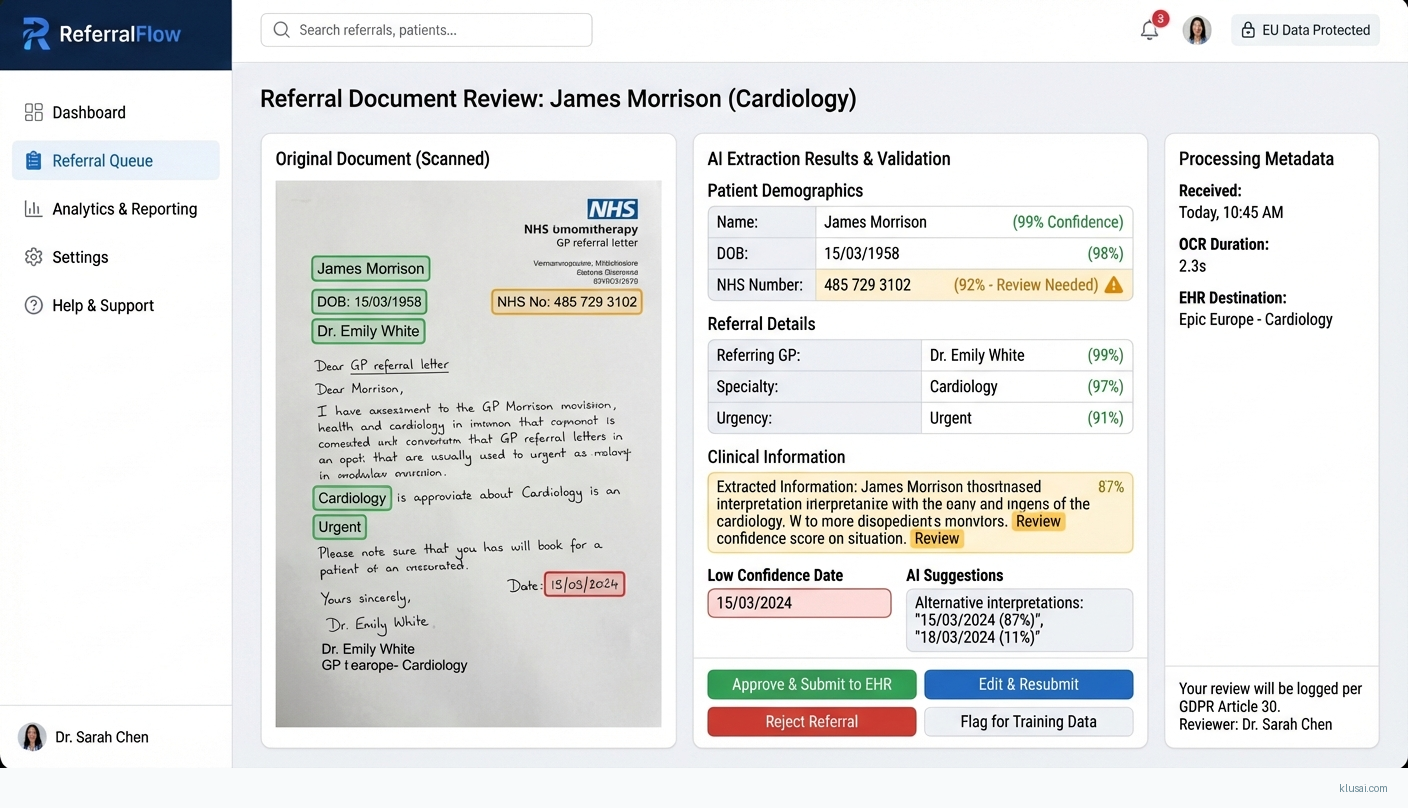
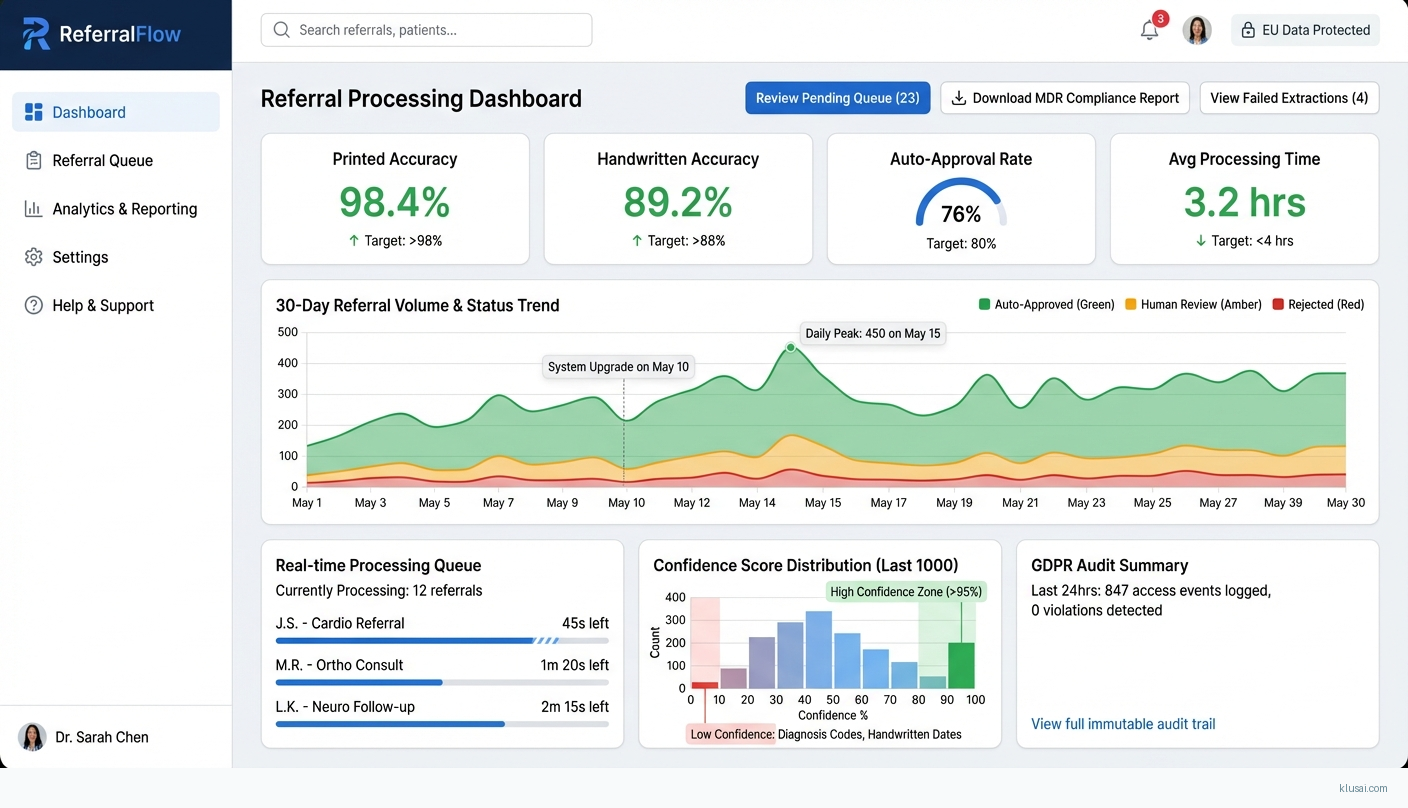
System Architecture
The architecture follows a four-layer design: ingestion, processing, integration, and governance. The ingestion layer handles multi-channel document receipt (secure fax gateway, encrypted email, direct upload portal) with format normalization and initial quality assessment. Documents are stored in EU-resident blob storage with encryption at rest before processing.
The processing layer implements a staged ML pipeline. First, image preprocessing applies deskewing, noise reduction, and contrast enhancement to optimize extraction quality. The OCR/ICR engine then extracts text, with separate models for printed and handwritten content[4]. A clinical NLP layer identifies and structures medical entities (patient identifiers, referring physician, urgency indicators, clinical findings, requested specialty). Each extracted field receives a confidence score; the system routes documents with all fields above threshold (configurable, typically 90-95%) to automated processing, while others enter a human review queue[3][4].
The integration layer provides HL7 FHIR R4 APIs for EHR connectivity, supporting Epic Europe, Cerner Millennium, and Orbis through adapter patterns. Validated referrals are pushed to scheduling systems with structured clinical data. The governance layer maintains comprehensive audit logs[5], manages consent records, and provides compliance reporting for both GDPR and MDR requirements.
All components deploy within EU data centers (Azure West Europe or Germany West Central), with network isolation via private endpoints and no data egress outside the EU. The architecture supports horizontal scaling of the processing layer to handle volume spikes while maintaining consistent latency.
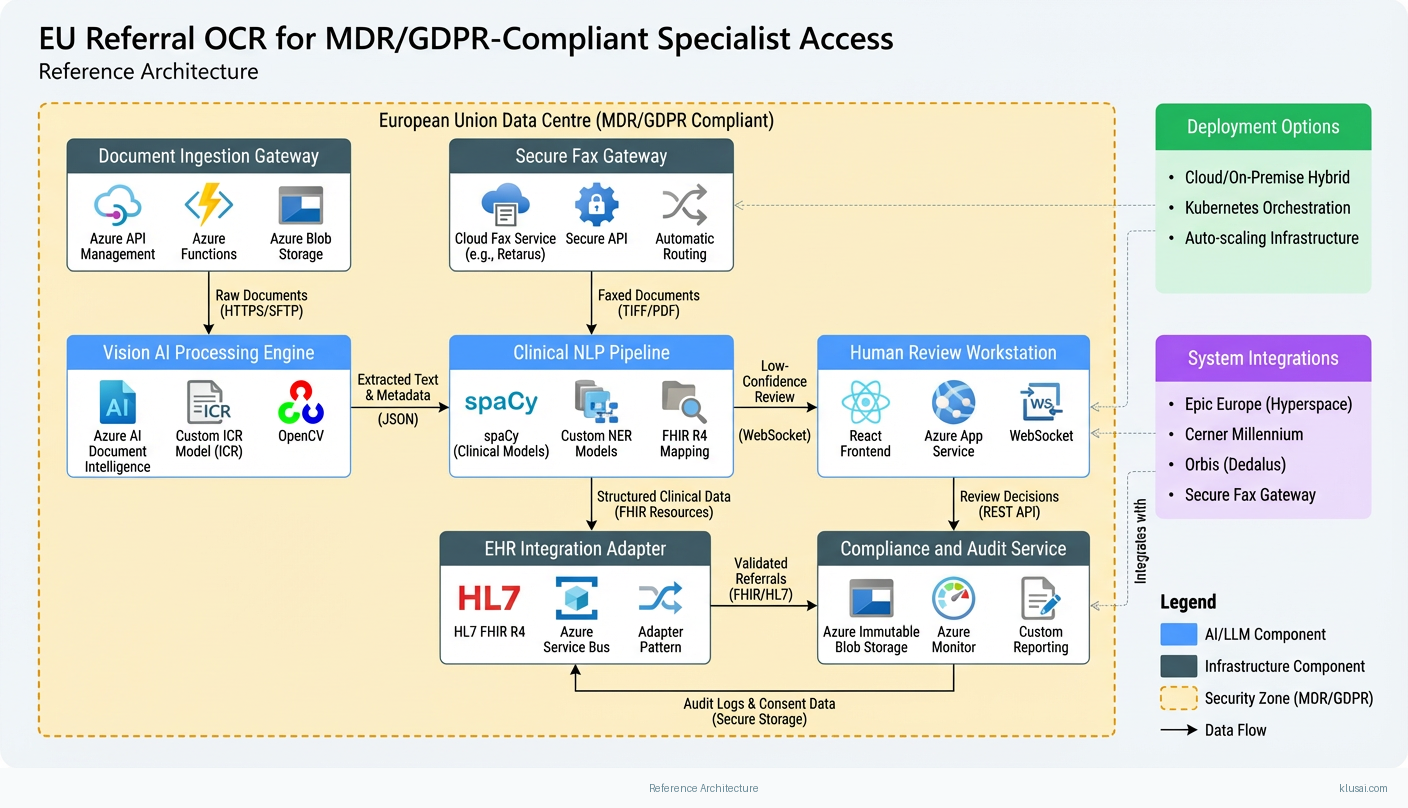
Key Components
| Component | Purpose | Technologies |
|---|---|---|
| Document Ingestion Gateway | Multi-channel document receipt with format normalization, quality scoring, and secure staging | Azure API Management Azure Functions Azure Blob Storage |
| Vision AI Processing Engine | OCR/ICR text extraction with separate model paths for printed and handwritten content | Azure AI Document Intelligence Custom ICR model (PyTorch) OpenCV |
| Clinical NLP Pipeline | Medical entity extraction, structured data mapping, and field-level confidence scoring | spaCy (clinical models) Custom NER models FHIR R4 mapping |
| Human Review Workstation | Web interface for clinical staff to validate low-confidence extractions and correct errors | React Azure App Service WebSocket |
| EHR Integration Adapter | Bidirectional connectivity with EU EHR systems for referral submission and status updates | HL7 FHIR R4 Azure Service Bus Adapter pattern |
| Compliance and Audit Service | Immutable audit logging, consent management, and regulatory reporting | Azure Immutable Blob Storage Azure Monitor Custom reporting |
Technology Stack

Implementation Phases
Foundation and Compliance Framework
Establish EU-resident infrastructure with security controls meeting GDPR requirements
- • Establish EU-resident infrastructure with security controls meeting GDPR requirements
- • Deploy baseline OCR/ICR pipeline with initial model configuration
- • Initiate MDR compliance documentation and risk management file per Annex I
- Production infrastructure in Azure West Europe with network isolation and encryption
- Document ingestion pipeline processing test documents with >95% printed text accuracy
- MDR technical file structure and initial clinical evaluation plan
Model Training and Validation
Train and validate ICR model on representative handwritten clinical samples
- • Train and validate ICR model on representative handwritten clinical samples
- • Implement clinical NLP pipeline with entity extraction and confidence scoring
- • Establish human review workflow with clinical staff feedback integration
- ICR model achieving target accuracy on held-out validation set (target: >88% character accuracy on handwritten notes)
- Clinical NLP pipeline extracting core referral fields with per-field confidence scores[3]
- Human review interface deployed with initial clinical user acceptance testing
EHR Integration and Parallel Run
Complete EHR integration with primary system (Epic Europe, Cerner, or Orbis)
- • Complete EHR integration with primary system (Epic Europe, Cerner, or Orbis)
- • Execute 60-day parallel run comparing automated vs. manual processing
- • Train clinical and administrative staff via change champion program
- Bidirectional EHR integration with validated referral submission and status tracking
- Parallel run report documenting accuracy, processing time, and exception rates
- Trained change champions (minimum 2 per department) and user documentation
Production Transition and MDR Pathway
Transition to production operation with full automation for high-confidence referrals
- • Transition to production operation with full automation for high-confidence referrals
- • Complete clinical evaluation and submit MDR technical file to notified body
- • Establish post-market surveillance and continuous improvement processes
- Production system processing live referrals with defined SLOs
- MDR technical file submitted to notified body (CE marking timeline dependent on notified body capacity)
- Post-market surveillance plan and quarterly review cadence established
Key Technical Decisions
Should we use a single unified model or separate models for printed vs. handwritten text?
Printed text extraction is a mature capability where cloud services (Azure Document Intelligence) achieve >98% accuracy. Handwritten clinical notes require specialized ICR models trained on medical handwriting patterns[4]. A lightweight classifier routes documents to the appropriate model, optimizing both accuracy and cost.
- Higher accuracy on each document type by using specialized models
- Ability to update handwriting model independently without affecting printed text processing
- Additional complexity in model management and deployment
- Routing classifier errors could send documents to wrong model
What confidence threshold should trigger human review?
A 90% threshold balances automation benefits against error risk. Critical fields (patient identifier, urgency) may warrant higher thresholds (95%), while less critical fields (referring physician name) may accept lower thresholds. The threshold should be tunable based on parallel run data and organizational risk tolerance[3][4].
- Flexibility to optimize automation rate vs. accuracy based on real-world performance
- Different thresholds for different fields reflects varying clinical importance
- Complexity in explaining variable thresholds to clinical staff
- Risk of threshold creep reducing human oversight over time
How should we handle MDR compliance given uncertain notified body timelines?
MDR Class IIa devices require notified body review, with timelines varying from 3-12+ months depending on notified body capacity and any questions raised. The system should be designed to meet all MDR requirements (risk management, clinical evaluation, post-market surveillance), but operational planning should assume an extended period of supervised clinical use pending formal CE marking.
- System can deliver value during notified body review period under clinical supervision
- Full MDR-compliant design avoids costly retrofitting
- Higher upfront investment in compliance infrastructure
- Uncertainty in timeline for full autonomous operation
Integration Patterns
| System | Approach | Complexity | Timeline |
|---|---|---|---|
| Epic Europe (Hyperspace) | FHIR R4 APIs for ServiceRequest creation; Epic MyChart integration for patient notifications; Epic Interconnect for real-time status updates | high | 6-8 weeks |
| Cerner Millennium | FHIR R4 APIs via Cerner Ignite platform; CareAware integration for document viewing; PowerChart workflow integration | high | 6-8 weeks |
| Orbis (Dedalus) | HL7 v2.x messaging for legacy installations; FHIR R4 for newer deployments; custom adapter for Orbis-specific workflows | medium | 4-6 weeks |
| Secure Fax Gateway | Cloud fax service (e.g., Retarus, eFax Corporate) with API integration; automatic document routing based on fax number; quality assessment before processing | low | 2-3 weeks |
ROI Framework
ROI is driven by administrative time savings from automated referral processing, with secondary benefits from reduced error-related rework and faster specialist access. The framework focuses on quantifiable time savings while acknowledging that patient outcome improvements, though significant, are harder to monetize directly[1][2].
Key Variables
Example Calculation
Build vs. Buy Analysis
Internal Build Effort
Internal build would require 18-24 months with a team including ML engineers (2-3 FTE), healthcare integration specialists (1-2 FTE), regulatory affairs expertise (0.5-1 FTE), and clinical informaticists (0.5 FTE). MDR compliance pathway requires specialized regulatory knowledge and typically 6-12+ months for notified body engagement. Estimated internal build cost: €600,000-900,000 excluding ongoing maintenance, regulatory updates, and notified body fees.
Market Alternatives
ABBYY FlexiCapture for Healthcare
€50,000-150,000 annually depending on volumeEstablished document capture platform with healthcare templates; mature OCR technology but limited ICR for handwritten clinical notes; requires significant customization for MDR compliance pathway
- • Proven OCR accuracy on printed documents with existing healthcare templates
- • Established vendor with healthcare customer references
- • Limited handwriting recognition for GP letters and clinical notes[4]
- • MDR compliance and clinical validation must be built separately
- • EHR integration requires additional middleware development
Microsoft Azure AI Document Intelligence
€30,000-80,000 annually based on document volumeCloud-native document processing with pre-built healthcare models; strong platform integration but requires customization for EU regulatory compliance and clinical workflows
- • Native Azure integration simplifies infrastructure for Azure-based organizations
- • Continuous model improvements from Microsoft
- • Strong security and compliance certifications
- • MDR compliance pathway not included; must be designed and documented separately
- • Limited customization for EU-specific referral formats and workflows
- • Human review workflow and clinical validation require custom development
Kofax Healthcare Solutions
€100,000-250,000 annually for enterprise deploymentEnterprise capture platform with healthcare vertical; comprehensive capabilities but complex implementation typically requiring systems integrator involvement
- • Comprehensive capture and workflow capabilities
- • Strong enterprise integration features and scalability
- • High implementation complexity and professional services cost
- • MDR/GDPR compliance requires additional configuration and documentation
- • May be over-engineered for focused referral processing use case
Our Positioning
KlusAI's approach is suited for healthcare organizations requiring a tailored solution at the intersection of MDR compliance, GDPR data residency, and EU EHR integration. We assemble specialized teams combining vision AI expertise with healthcare regulatory knowledge, delivering a solution customized to your specific referral workflows and document types. This approach is particularly valuable when handwritten document processing is significant, when MDR clinical evaluation pathway support is essential, or when existing solutions don't adequately address your EHR integration requirements.
Team Composition
KlusAI assembles a cross-functional team combining vision AI engineering, healthcare integration expertise, regulatory affairs knowledge, and clinical informatics. Team composition scales across phases, with heavier ML focus early and regulatory/integration focus in later phases.
| Role | FTE | Focus |
|---|---|---|
| ML/Vision AI Engineer | 1.5 | OCR/ICR model development, training pipeline, accuracy optimization, confidence calibration, and model monitoring |
| Healthcare Integration Specialist | 1.0 | EHR connectivity, HL7 FHIR implementation, clinical workflow design, and interface testing |
| Regulatory Affairs Consultant | 0.5 | MDR compliance documentation, clinical evaluation planning, notified body liaison, and post-market surveillance design |
| Clinical Informaticist | 0.5 | Clinical validation, NLP entity mapping, workflow optimization, and clinical staff training |
| DevOps/Platform Engineer | 0.75 | Infrastructure provisioning, CI/CD pipelines, security implementation, and production operations |
Supporting Evidence
Performance Targets
>98% character accuracy
>88% character accuracy
70-80% of referrals processed without human intervention
<4 hours from receipt to EHR submission for auto-approved referrals
Team Qualifications
- KlusAI's network includes professionals with healthcare AI implementation experience across EU markets, including familiarity with Epic Europe, Cerner Millennium, and regional EHR systems
- Our teams are assembled with regulatory affairs expertise relevant to MDR SaMD classification and GDPR data protection requirements
- We bring together ML engineers experienced in document AI and clinical NLP, combined with healthcare integration specialists familiar with HL7 FHIR and EU interoperability standards
Source Citations
significant delays in specialist referrals due to manual processing
directionalManual data entry is prone to errors and reduces administrative efficiency
"Manual data entry is prone to errors – misreading handwriting, mistyping, or missing important details"directional
requires full traceability... per-field confidence scores... handling of errors such as unreadable documents
"full traceability—knowing who submitted which document, when, and which data was extracted or modified—as well as integrated quality controls such as per-field confidence scores"exact
ICR for handwritten character recognition... rules... queued for human review
"ICR (Intelligent Character Recognition) for handwritten character recognition... Simple rules... queued for human review"exact
audit trails... complying with laws like... GDPR in Europe
"access controls, audit trails, and data encryption, which are essential for complying with laws like HIPAA in the United States and GDPR in Europe"exact
MDR (Regulation EU 2017/745) regulates medical devices... software's classification as a device
directionalReady to discuss?
Let's talk about how this could work for your organization.
Schedule a Consultation
Pick a date that works for you
Times shown in your local timezone ()
Prefer email? Contact us directly
Almost there!
at
Your details
at
You're all set!
Check your email for confirmation and calendar invite.
Your booking is confirmed! Our team will reach out to confirm the details.
Your consultation
· min
( team time)
Quick Overview
- Technology
- Computer Vision
- Complexity
- high
- Timeline
- 5-7 months
- Industry
- Healthcare
- Region
- European Union