The Problem
The legal e-discovery market represents a $10-15B annual cost burden, with document review consuming massive resources and time across law firms and corporate legal departments. A midsize litigation group recently cut contract review time by 60% using AI assistants that summarize terms, flag missing clauses, and compare documents to preferred language, yet most firms still rely on junior associates to manually create privilege logs, relevance summaries, and issue-coded memoranda after initial review—a repetitive, error-prone process that extends timelines and inflates costs.
The challenge is compounded by regulatory complexity: GDPR and CCPA impose strict requirements around data handling, retention, and transparency in document processing workflows. Current AI solutions often lack defensible audit trails, explainability mechanisms, and governance controls required by regulators and courts, creating compliance risk alongside efficiency gains. Additionally, corporate legal departments are adopting AI twice as fast as outside counsel (52% vs. 23% adoption rates), creating pressure on law firms to match capability or lose work to in-house teams equipped with AI-generated drafts requiring review.
Existing solutions treat AI as a standalone tool rather than an integrated, governance-first system. The market is shifting toward workflow-embedded AI with human-in-the-loop validation, explainability by design, and provable transparency mechanisms—capabilities that will become table stakes for enterprise buyers by mid-2026. Firms that deploy AI strategically with robust compliance controls will capture the competitive advantage; those treating it as a checkbox feature will struggle to justify ROI and manage regulatory exposure.
Our Approach
Key elements of this implementation
-
Fine-tuned legal LLM with domain-specific training on privilege determinations, relevance coding, and issue classification, integrated natively into Relativity, Concordance, and major e-discovery platforms with real-time audit logging
-
GDPR/CCPA-compliant data governance including data residency controls, automated PII redaction, consent-based processing workflows, and defensible retention policies with provable deletion mechanisms
-
Human-in-the-loop validation framework where senior attorneys review and approve AI-generated privilege logs and memoranda before production, with confidence scoring and explainability for every classification decision
-
Phased 90-day rollout with embedded change champions, 2-day attorney training workshops, parallel running with gradual cutover, and executive sponsorship program to address adoption resistance
Get the Full Implementation Guide
Unlock full details including architecture and implementation
Implementation Overview
This implementation delivers an AI-powered document review system that generates privilege logs, relevance summaries, and issue-coded memoranda while maintaining the defensibility and audit requirements demanded by courts and regulators globally. The architecture prioritizes explainability and human oversight, recognizing that privilege determinations carry significant malpractice risk and require attorney validation before any production decision.
The core architectural decision is a Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) approach using a legal-domain-optimized LLM, combined with a vector database storing firm-specific privilege guidelines, matter precedents, and jurisdiction-specific privilege rules. This approach provides the domain specificity of fine-tuning without the training data burden—critical given that most firms lack the 10,000+ labeled privilege determinations typically required for effective fine-tuning. The system generates confidence scores and citation-backed explanations for every classification, enabling senior attorneys to efficiently validate AI recommendations rather than performing de novo review.
The 8-10 month timeline (extended from initial 5-7 month estimate) reflects the reality of high-complexity legal AI implementations: creating gold-standard training data requires significant attorney time, multi-platform integration introduces dependency risks, and attorney adoption requires sustained change management. The phased approach includes explicit go/no-go gates and parallel running periods to validate accuracy before any production use, with the option to extend Phase 2 if training data quality or model accuracy targets are not met.
UI Mockups
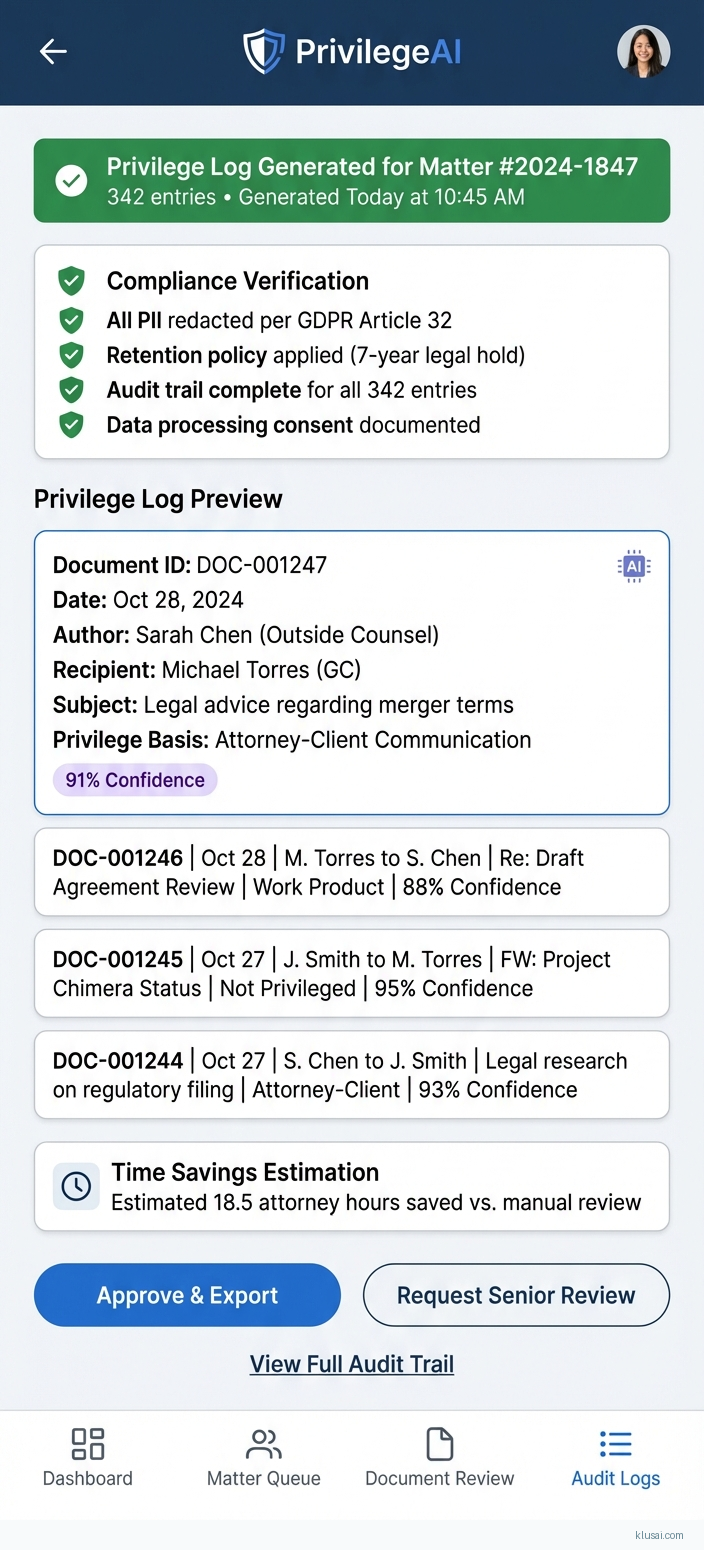
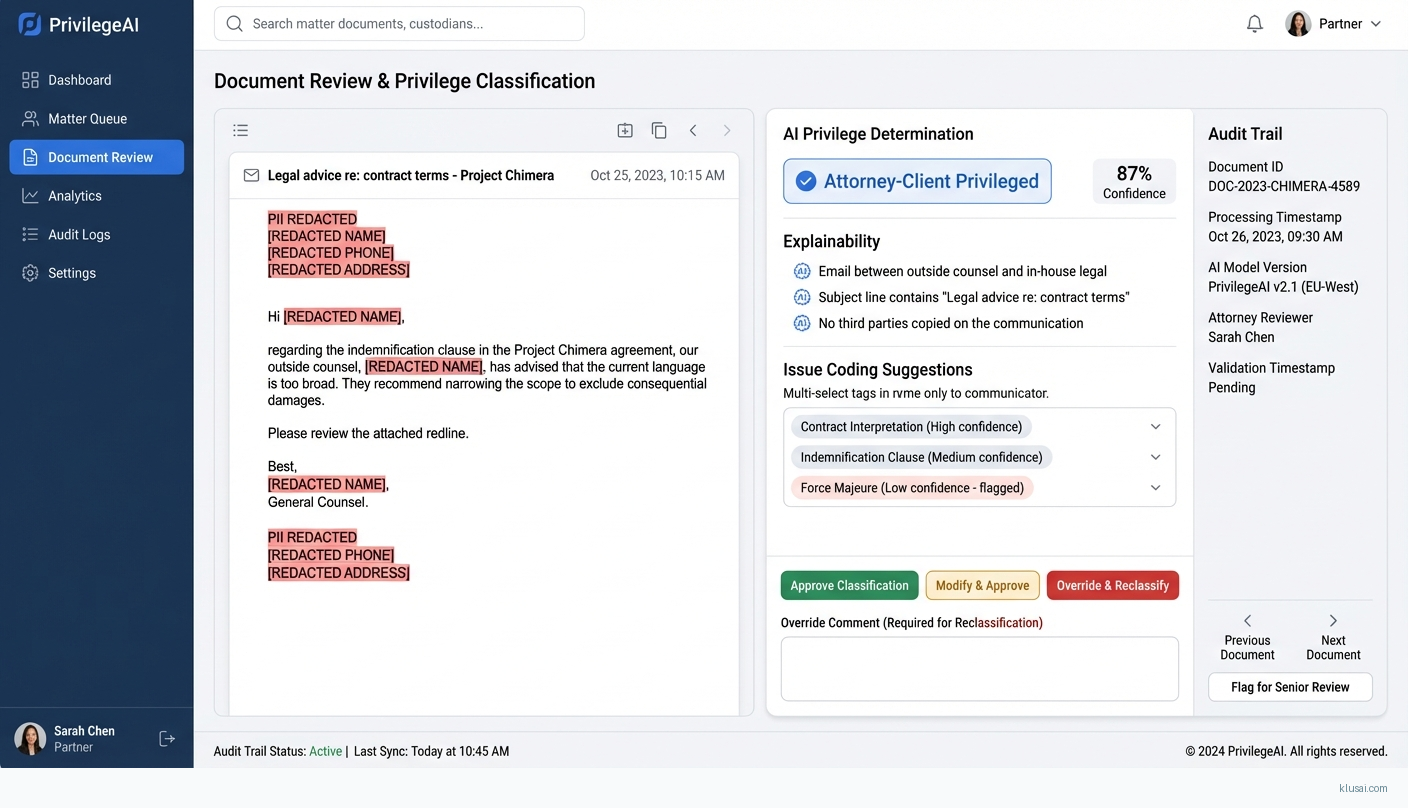
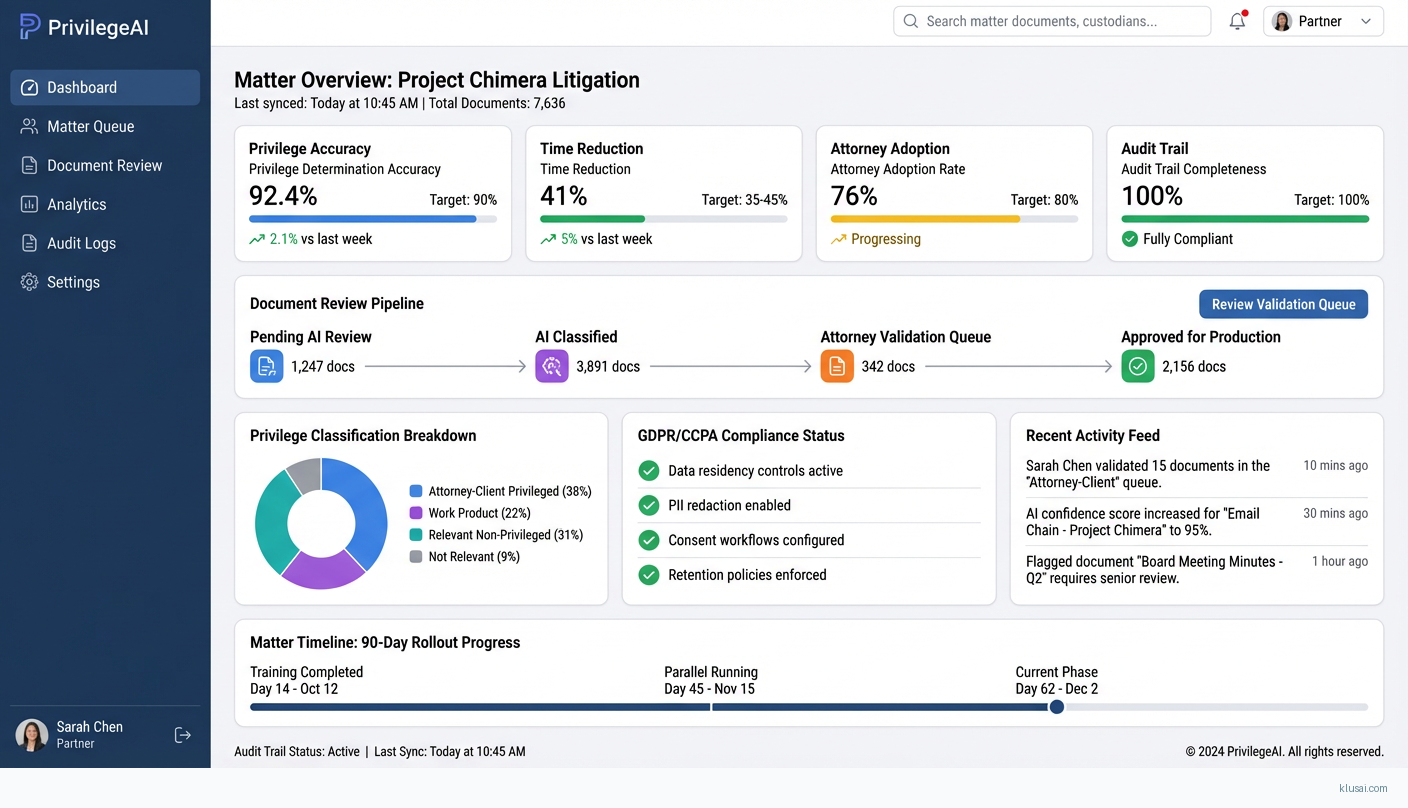
System Architecture
The architecture follows a four-layer pattern: ingestion, processing, validation, and integration. Documents flow from e-discovery platforms through secure connectors into a preprocessing pipeline that handles OCR, text extraction, and PII detection. The processing layer combines vector search over firm-specific knowledge bases with LLM-based classification, generating privilege determinations with confidence scores and supporting citations.
The RAG implementation uses a vector database (Pinecone or Weaviate) to store embeddings of firm privilege guidelines, matter-specific precedents, and jurisdiction-specific privilege rules. When processing a document, the system retrieves relevant context—including similar documents from the current matter and applicable privilege standards—before generating classifications. This approach addresses the multi-jurisdictional challenge by dynamically incorporating the relevant privilege framework (attorney-client privilege under US law, legal professional privilege under UK law, etc.) based on matter metadata.
The validation layer implements a tiered review workflow: documents with confidence scores above 0.85 are queued for spot-check review, those between 0.65-0.85 require individual attorney validation, and those below 0.65 are flagged for senior attorney determination. All AI-generated classifications include explainability outputs showing the key factors driving the determination and the retrieved precedents supporting it. The audit subsystem captures every classification decision, attorney override, and validation action with immutable logging for defensibility.
Integration with e-discovery platforms (Relativity, Concordance, Everlaw) occurs through certified connectors that maintain document custody chains and synchronize privilege designations bidirectionally. The architecture supports data residency requirements through regional deployment options, with processing occurring within the jurisdiction specified by matter configuration—critical for GDPR compliance where EU personal data must remain within approved jurisdictions.
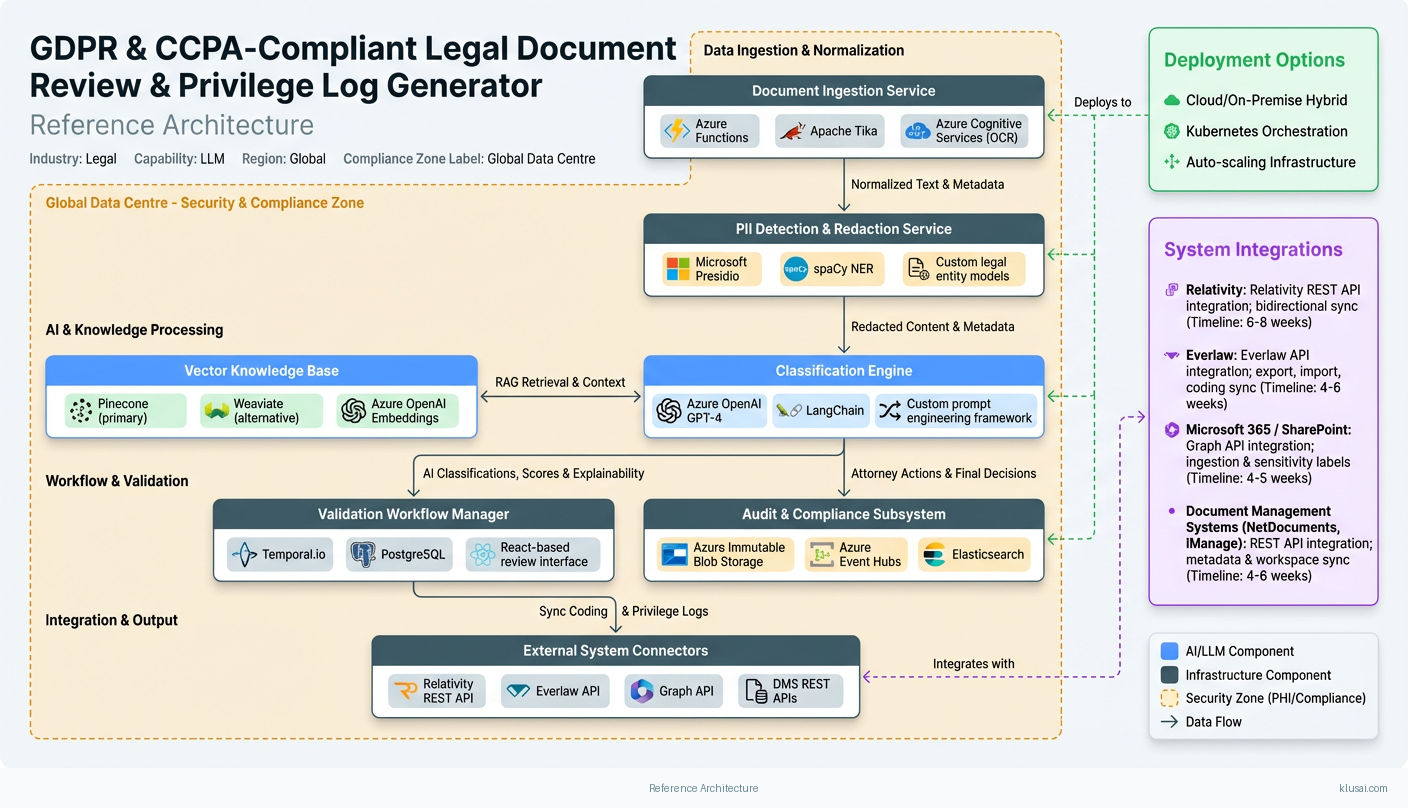
Key Components
| Component | Purpose | Technologies |
|---|---|---|
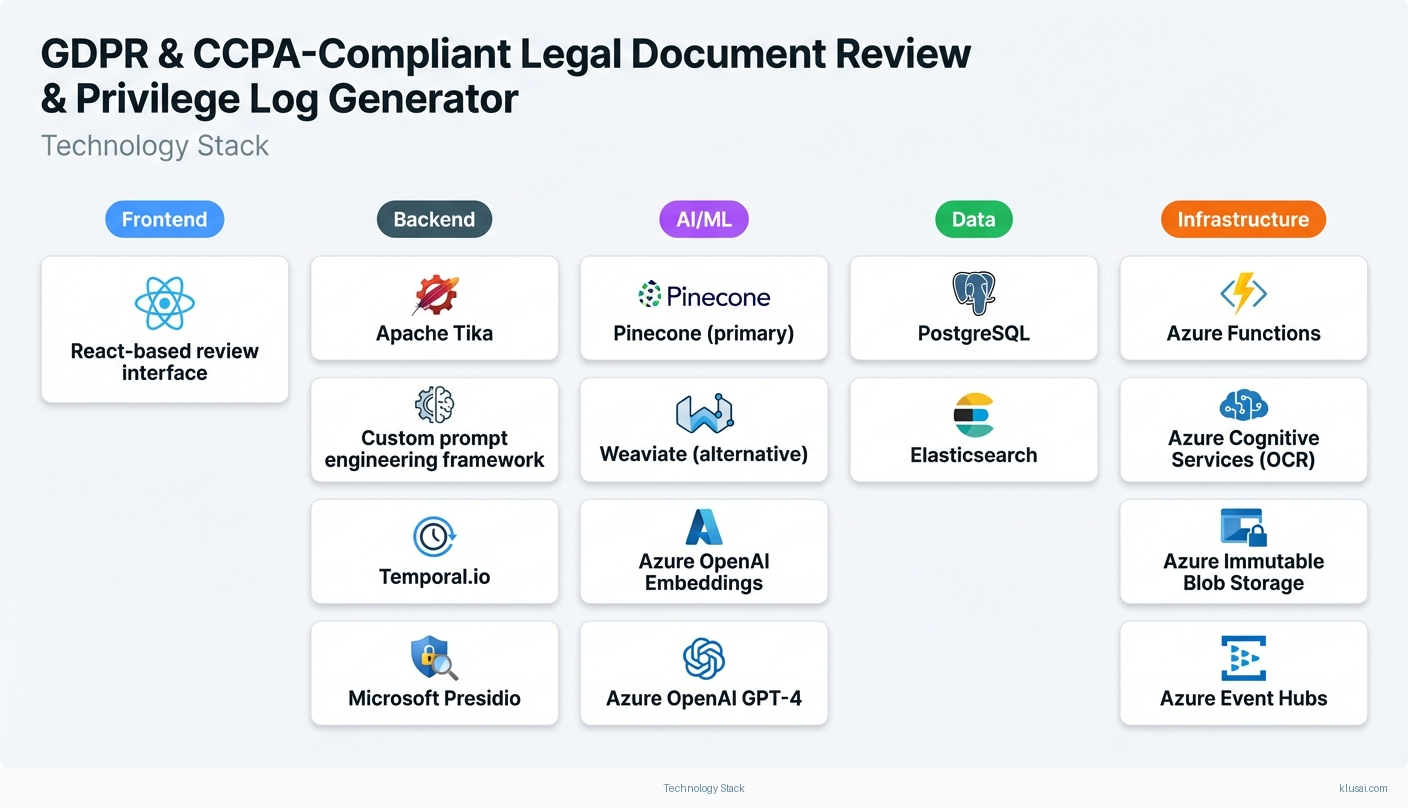
| Document Ingestion Service | Secure document intake from e-discovery platforms with format normalization, OCR processing, and metadata extraction while maintaining chain of custody | Azure Functions Apache Tika Azure Cognitive Services (OCR) |
| Vector Knowledge Base | Stores embeddings of firm privilege guidelines, matter precedents, jurisdiction-specific rules, and validated privilege determinations for RAG retrieval | Pinecone (primary) Weaviate (alternative) Azure OpenAI Embeddings |
| Classification Engine | RAG-based privilege determination combining retrieved context with LLM reasoning to generate classifications, confidence scores, and explainability outputs | Azure OpenAI GPT-4 LangChain Custom prompt engineering framework |
| Validation Workflow Manager | Routes AI-generated classifications to appropriate review queues based on confidence thresholds, tracks attorney validations, and manages approval workflows | Temporal.io PostgreSQL React-based review interface |
| Audit & Compliance Subsystem | Immutable logging of all classification decisions, attorney actions, and system events with tamper-evident storage for court defensibility | Azure Immutable Blob Storage Azure Event Hubs Elasticsearch |
| PII Detection & Redaction Service | Identifies and redacts personal data per GDPR/CCPA requirements before processing, with configurable redaction policies per jurisdiction | Microsoft Presidio spaCy NER Custom legal entity models |
Technology Stack
Implementation Phases
Phase 1: Foundation & Knowledge Base Development
Establish secure infrastructure with data residency controls for target jurisdictions (US, EU, UK minimum)
- • Establish secure infrastructure with data residency controls for target jurisdictions (US, EU, UK minimum)
- • Build vector knowledge base with firm privilege guidelines, 500+ validated privilege determinations as seed data, and jurisdiction-specific rules
- • Develop and validate RAG pipeline with baseline accuracy measurement against held-out test set
- Production-ready Azure infrastructure with security controls, private endpoints, and regional deployment capability
- Vector knowledge base populated with firm guidelines and seed precedents, with documented embedding strategy
- RAG pipeline achieving >80% accuracy on privilege determination test set (200+ documents), with baseline metrics documented
Phase 2: Training Data Creation & Model Validation
Create gold-standard training dataset of 2,000+ attorney-validated privilege determinations across practice areas
- • Create gold-standard training dataset of 2,000+ attorney-validated privilege determinations across practice areas
- • Achieve >90% privilege determination accuracy validated against held-out test set with statistical significance
- • Develop explainability framework generating citation-backed rationales for every classification
- Gold-standard dataset with 2,000+ validated determinations, documented labeling methodology, and inter-rater reliability metrics
- Validated RAG pipeline achieving >90% accuracy with confidence calibration (high-confidence predictions >95% accurate)
- Explainability outputs showing key factors and retrieved precedents for each determination, validated by senior attorneys
Phase 3: Integration & Parallel Running
Complete bidirectional integration with primary e-discovery platform (Relativity or Everlaw)
- • Complete bidirectional integration with primary e-discovery platform (Relativity or Everlaw)
- • Execute 4-week parallel running period comparing AI classifications to attorney determinations on live matters
- • Validate audit trail completeness and defensibility with litigation support team
- Production integration with primary e-discovery platform, including privilege log export and document tagging synchronization
- Parallel running report documenting accuracy metrics, attorney override patterns, and efficiency gains on 3+ live matters
- Audit trail validation report confirming defensibility requirements met, reviewed by litigation partner
Phase 4: Rollout & Optimization
Complete attorney training for all document review staff (target: 50+ attorneys across practice groups)
- • Complete attorney training for all document review staff (target: 50+ attorneys across practice groups)
- • Achieve 40-50% efficiency improvement on privilege log creation validated through time tracking
- • Establish ongoing model monitoring and continuous improvement processes
- Training completion for all target attorneys with competency validation and reference materials
- Efficiency metrics report documenting time savings, accuracy rates, and attorney satisfaction scores
- Operational runbook including model monitoring dashboards, retraining triggers, and escalation procedures
Key Technical Decisions
RAG vs. fine-tuning for legal domain specialization?
Fine-tuning requires 10,000+ high-quality labeled examples—most firms lack this volume of consistently labeled privilege determinations. RAG allows immediate use of firm-specific guidelines and precedents without the 3-6 month data preparation effort. The knowledge base can be incrementally improved as attorneys validate determinations, creating a flywheel effect. Fine-tuning remains available as Phase 2 contingency if RAG accuracy plateaus below 90%.
- Faster time-to-value: RAG pipeline operational in weeks vs. months for fine-tuning
- Transparent reasoning: retrieved precedents provide clear basis for classifications
- Easier updates: new guidelines added to knowledge base without model retraining
- Retrieval quality dependent on embedding model and knowledge base organization
- May not capture nuanced privilege patterns that fine-tuning could learn
- Higher per-inference cost due to retrieval and longer context windows
Vector database selection: Pinecone vs. Weaviate vs. pgvector?
Pinecone offers the strongest managed service with sub-100ms retrieval at scale, critical for interactive review workflows. However, some firms require all data to remain on-premises or within specific cloud regions—Weaviate provides a self-hosted option with comparable performance. pgvector is insufficient for the 5M+ vector scale anticipated and lacks the hybrid search capabilities needed for combining semantic and metadata filtering.
- Pinecone: fully managed, proven at scale, excellent filtering capabilities
- Weaviate: self-hosted option addresses strict data residency requirements
- Pinecone: data leaves firm infrastructure (mitigated by SOC 2, encryption)
- Weaviate: requires infrastructure management expertise, higher operational burden
Confidence threshold strategy for human-in-the-loop validation?
Privilege errors carry significant malpractice risk—the threshold strategy must balance efficiency gains against error exposure. Initial thresholds are conservative; empirical accuracy data from parallel running will inform threshold optimization. The tiered approach ensures senior attorney time focuses on genuinely ambiguous determinations while allowing efficient batch processing of clear cases.
- Conservative thresholds minimize privilege waiver risk during initial deployment
- Configurable per-matter allows adjustment based on risk tolerance and document complexity
- Conservative thresholds may limit initial efficiency gains until confidence calibration validated
- Three tiers add workflow complexity compared to binary approve/review model
Multi-jurisdictional privilege handling approach?
Privilege standards vary significantly across jurisdictions—US attorney-client privilege, UK legal professional privilege, EU variations, and common interest doctrine all have distinct requirements. The knowledge base maintains separate namespaces for each jurisdiction's rules, with matter configuration specifying which jurisdictions apply. For multi-jurisdictional matters, the system retrieves from all applicable namespaces and flags potential conflicts for attorney resolution.
- Explicit jurisdiction handling prevents incorrect application of privilege standards
- Conflict flagging surfaces issues that might be missed in manual review
- Requires ongoing maintenance as privilege law evolves across jurisdictions
- Multi-jurisdiction matters may generate more flags, reducing efficiency gains
Integration Patterns
| System | Approach | Complexity | Timeline |
|---|---|---|---|
| Relativity | Relativity REST API integration using certified connector pattern; bidirectional sync of document metadata, privilege designations, and coding decisions; leverage Relativity's audit infrastructure for chain of custody | high | 6-8 weeks |
| Everlaw | Everlaw API integration for document export, prediction import, and coding synchronization; leverage Everlaw's native AI capabilities for complementary analysis | medium | 4-6 weeks |
| Microsoft 365 / SharePoint | Graph API integration for document ingestion from SharePoint document libraries and Teams channels; sensitivity labels for privilege designation synchronization | medium | 4-5 weeks |
| Document Management Systems (NetDocuments, iManage) | REST API integration for document retrieval and metadata synchronization; workspace-level integration for matter organization alignment | medium | 4-6 weeks |
ROI Framework
ROI derives primarily from attorney time savings on privilege log creation and relevance memoranda—tasks that consume significant junior and mid-level associate hours. The 60% time reduction benchmark[2] applies to contract review; we use a conservative 35-45% estimate for privilege logging given higher complexity and validation requirements. Secondary benefits include reduced review cycle times and decreased privilege waiver risk.
Key Variables
Example Calculation
Build vs. Buy Analysis
Internal Build Effort
Internal build requires 18-24 months with dedicated team of 8-10 FTEs including ML engineers (3-4), legal domain specialists (2), security/compliance resources (2), and platform engineers (2). Key challenges include acquiring sufficient training data, building defensible audit infrastructure, and maintaining e-discovery platform integrations. Estimated cost $2-3M before ongoing maintenance, with significant opportunity cost from delayed time-to-value. Most firms lack the ML expertise and legal-AI intersection skills required.
Market Alternatives
Relativity aiR for Review
$15-30 per GB processed, volume discounts availableNative Relativity integration with AI-assisted review; strong choice for firms deeply committed to Relativity ecosystem seeking turnkey solution
- • Seamless Relativity integration with no connector development
- • Established vendor with legal industry credibility
- • Rapid deployment for Relativity-native workflows
- • Limited customization to firm-specific privilege guidelines
- • Less flexibility for multi-platform environments
- • Explainability and audit trail depth may not meet all court requirements
Everlaw AI Assistant
$25-45 per GB, platform subscription modelCloud-native e-discovery with integrated AI; appeals to firms seeking modern platform with strong AI throughout
- • Modern UX with AI integrated throughout workflow
- • Strong innovation pace with frequent releases
- • Good fit for cloud-first organizations
- • Requires platform migration for non-Everlaw firms
- • Less established in AmLaw 100 segment
- • Customization options more limited than custom build
Harvey AI
Enterprise pricing, typically $150K-600K annuallyLegal-specific AI platform with broad capabilities; positioned as strategic AI partner beyond document review
- • Purpose-built for legal with strong domain understanding
- • Expanding capability set across legal workflows
- • Strong brand recognition in legal AI space
- • Newer entrant with less e-discovery-specific track record
- • Integration with existing platforms still maturing
- • Premium pricing may not suit all firm economics
Our Positioning
KlusAI's approach is optimal for firms requiring deep customization to specific privilege guidelines, multi-platform environments where vendor lock-in is a concern, or situations where existing solutions don't address unique compliance requirements. We assemble teams with the specific legal-AI and compliance expertise needed for each engagement, providing flexibility that product-based solutions cannot match. Our governance-first architecture addresses explainability and audit requirements that will become mandatory[3][5]—building this capability now positions firms ahead of regulatory requirements.
Team Composition
KlusAI assembles specialized teams combining ML engineering, legal technology, and compliance expertise tailored to each engagement. The composition below reflects typical staffing for a full implementation; actual team structure is adjusted based on firm size, existing capabilities, and specific requirements.
| Role | FTE | Focus |
|---|---|---|
| ML/AI Engineer | 1.5 | RAG pipeline development, embedding optimization, LLM integration, confidence calibration, and model monitoring infrastructure |
| Legal Technology Specialist | 1.0 | E-discovery platform integration, privilege workflow design, legal domain requirements translation, and attorney training development |
| Security & Compliance Engineer | 0.75 | Data residency controls, PII handling, audit trail implementation, GDPR/CCPA compliance validation |
| Project Manager | 0.5 | Timeline management, stakeholder coordination, risk tracking, change management facilitation |
| Solutions Architect | 0.25 | Architecture oversight, technical decision guidance, integration pattern design, quality assurance |
Supporting Evidence
Performance Targets
>90% agreement with senior attorney validation
35-45% reduction in attorney hours
>80% of trained attorneys using system for applicable matters within 90 days of training
100% of classification decisions logged with required defensibility fields
Team Qualifications
- KlusAI's network includes professionals with e-discovery platform implementation experience across Relativity, Everlaw, and Concordance environments
- Our teams are assembled with ML engineers experienced in RAG architectures and legal-domain NLP applications
- We bring together compliance specialists familiar with GDPR, CCPA, and legal industry regulatory requirements for AI systems
Source Citations
$10-15B annual e-discovery market
"Massive cost and time for document review ($10-15B annual e-discovery market)"exact
60% reduction in contract review time using AI assistants
"a midsize litigation group cut contract review time by 60% using an AI assistant that summarizes terms, flags missing clauses, and compares documents to preferred language"exact
Regulators and courts will require provable transparency and audit trails for AI tools
directionalCorporate legal departments adopting AI at 52% vs. outside counsel at 23%
"The ACC/Everlaw GenAI Survey found corporate legal AI adoption more than doubled in one year, jumping from 23% to 52%"exact
Workflow-embedded AI with human-in-the-loop validation and explainability by design becoming table stakes
directionalReady to discuss?
Let's talk about how this could work for your organization.
Schedule a Consultation
Pick a date that works for you
Times shown in your local timezone ()
Prefer email? Contact us directly
Almost there!
at
Your details
at
You're all set!
Check your email for confirmation and calendar invite.
Your booking is confirmed! Our team will reach out to confirm the details.
Your consultation
· min
( team time)
Quick Overview
- Technology
- Large Language Models
- Complexity
- high
- Timeline
- 5-7 months
- Industry
- Legal Services