The Problem
Government agencies process thousands of grant applications daily, with manual document review creating significant bottlenecks. Traditional approaches require staff to manually search through complex documentation—one case study showed staff manually reviewing 200-page manuals, causing substantial delays in grant approval workflows . This manual burden is compounded by budget constraints: public sector organizations face 10%+ annual increases in service requests while operating under fixed or declining budgets .
The challenge extends beyond efficiency. Grant applications arrive in multiple formats (scanned forms, PDFs, images, certifications) and languages, requiring consistent data extraction, validation, and compliance verification. Manual data entry introduces errors, inconsistencies, and audit risks—particularly critical when handling sensitive applicant information subject to GDPR, Freedom of Information Acts, and Government Paperwork Elimination Act requirements. Current workarounds lack proper audit trails, data governance controls, and regulatory reporting capabilities.
Existing document processing solutions either operate as generic tools disconnected from grant workflows or require 40-60% manual review, negating efficiency gains . Grant-native AI platforms are emerging but often lack comprehensive compliance controls for multi-jurisdictional regulatory frameworks . Organizations need an AI-powered OCR solution that extracts and validates data while maintaining strict regulatory compliance, audit accountability, and data governance across multiple languages and document types.
Our Approach
Key elements of this implementation
-
Multi-language OCR with intelligent document classification, field extraction, and automated validation against predefined grant eligibility rules, reducing manual data entry by up to 40% while maintaining GDPR compliance through encrypted data pipelines and PII masking
-
Native integrations with grant management platforms (GovGrants, Fluxx, GrantSolutions) and government systems via secure APIs, with configurable workflows that enforce compliance rules at each processing stage
-
Comprehensive audit trail and logging mechanisms capturing all document processing decisions, data transformations, and user actions with immutable records; automated regulatory reporting for GDPR data processing activities, FOIA request handling, and Government Paperwork Elimination Act compliance documentation
-
Phased 12-week rollout with parallel processing validation (60 days), embedded change champions in each agency department, and human-in-the-loop review for high-risk applications or confidence scores below 95%, ensuring staff transition from manual entry to higher-value compliance analysis and decision-making
Implementation Overview
This implementation addresses the documented challenge of staff manually searching through 200-page manuals causing significant delays in grant approval workflows [1], while accommodating the 10%+ annual increase in service requests that public sector organizations face under fixed or declining budgets [2]. The architecture employs a modular, compliance-first approach where GDPR requirements are embedded at every processing stage rather than bolted on afterward.
The solution centers on an intelligent document processing pipeline that combines multi-language OCR with grant-specific field extraction and validation. Documents flow through classification, extraction, validation, and human review stages, with configurable confidence thresholds determining automation levels. The architecture maintains strict data residency controls, with all processing occurring within EU-based infrastructure and comprehensive audit logging for regulatory compliance.
Key architectural decisions prioritize auditability and reversibility over pure automation speed. The system implements a "trust but verify" model where AI-extracted data is validated against predefined grant eligibility rules, with human-in-the-loop review triggered for applications below 95% confidence scores or flagged as high-risk. This approach addresses the documented limitation that current solutions require 40-60% manual review [3] by focusing automation on high-confidence, routine extractions while preserving human judgment for complex cases.
UI Mockups
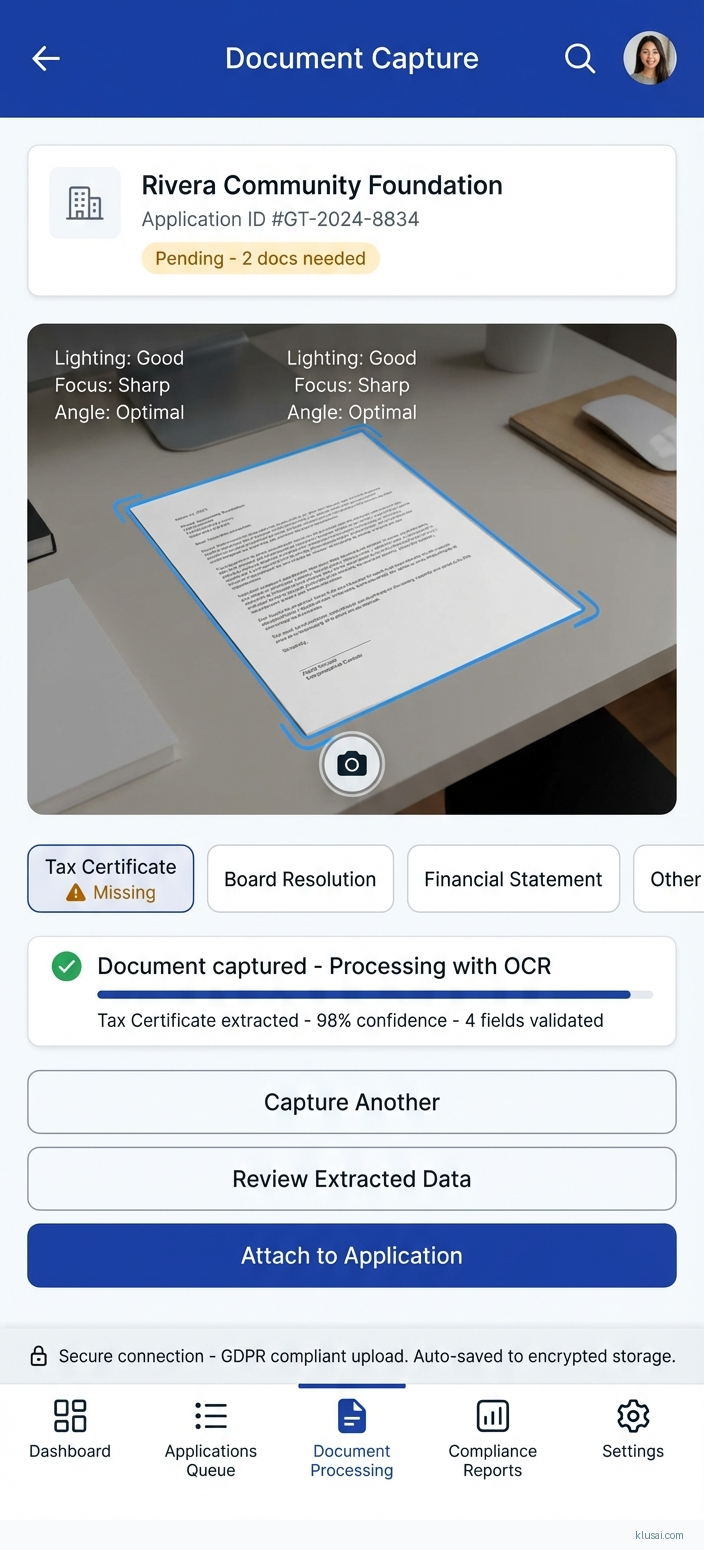
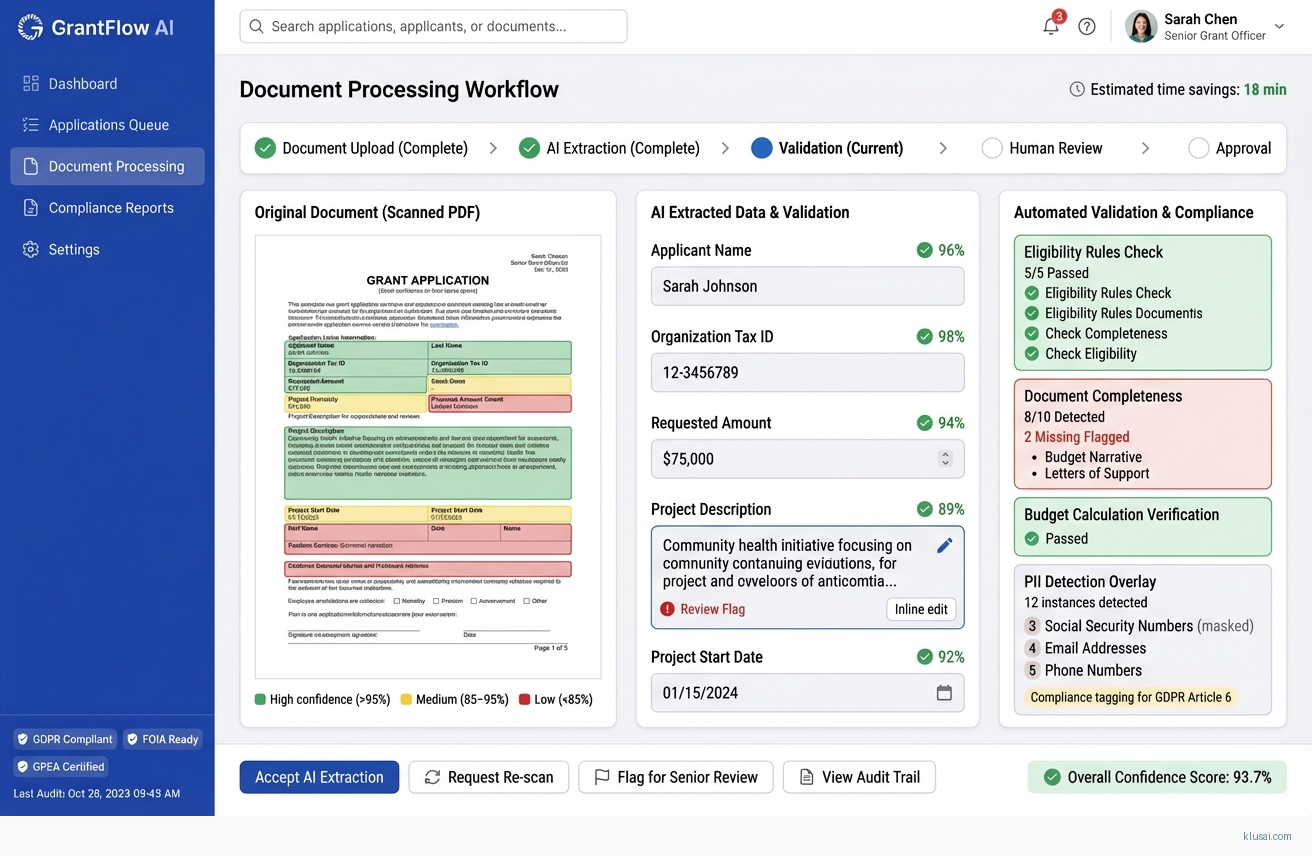
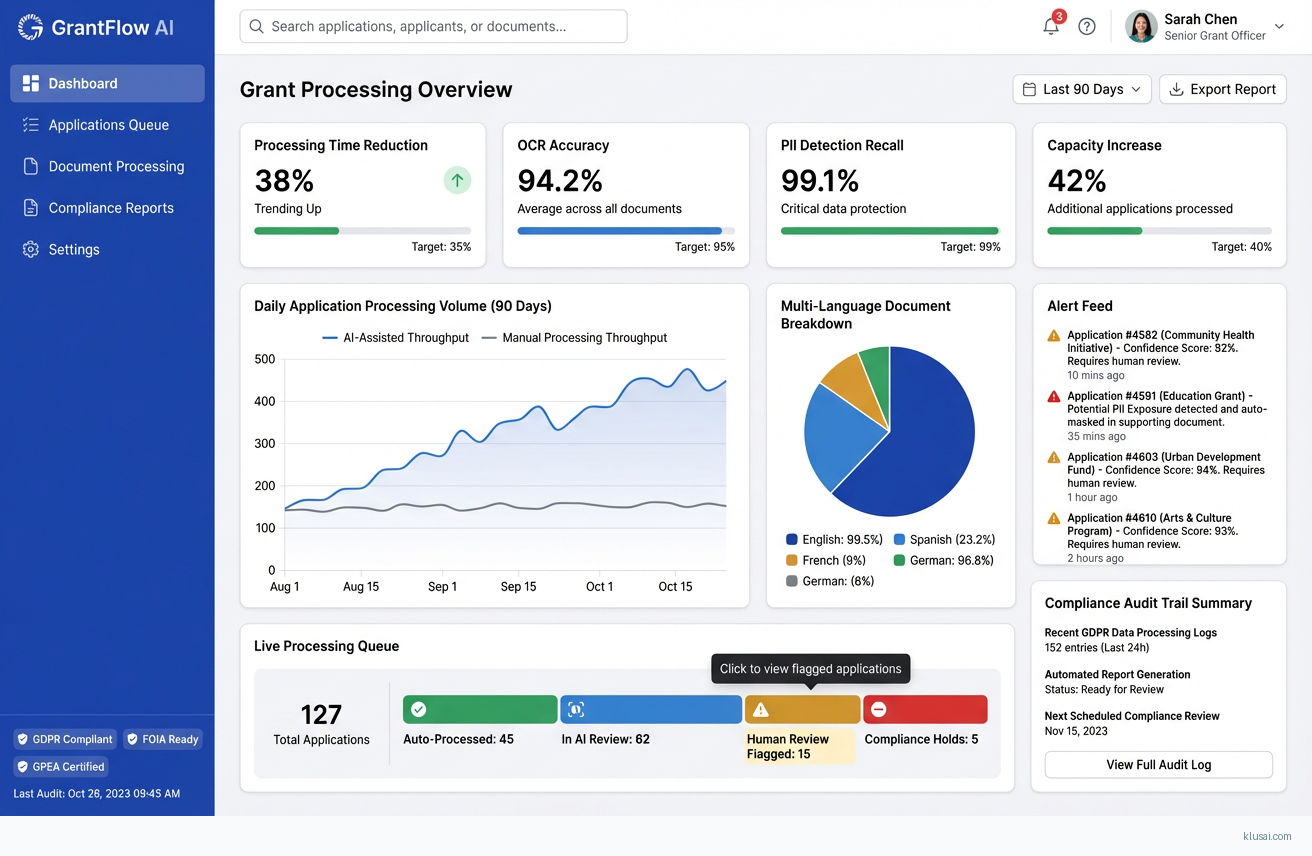
System Architecture
The architecture follows a layered design with clear separation between ingestion, processing, compliance, and integration concerns. The ingestion layer handles multi-channel document intake (email, web upload, API, physical mail scanning) with immediate encryption and classification. Documents are assigned unique processing identifiers and tracked through an immutable audit log from first contact.
The processing layer implements a staged pipeline: document classification identifies document types (application forms, certifications, financial statements, identity documents); OCR extraction converts images to structured text with language detection; field extraction maps content to grant-specific data schemas; and validation checks extracted data against eligibility rules and cross-references existing records. Each stage produces confidence scores that aggregate into an overall application confidence rating.
The compliance layer operates as an orthogonal concern, intercepting data at each processing stage to apply PII detection, data minimization, and access controls. Personal data is masked in processing logs, with full data accessible only through role-based access controls. The layer maintains separate audit streams for GDPR Article 30 records of processing activities, FOIA request tracking, and operational metrics.
The integration layer provides secure API connectivity to grant management platforms (GovGrants, Fluxx, GrantSolutions) and government identity systems. Integrations use message queuing for resilience, with dead-letter handling for failed transmissions and automatic retry with exponential backoff. Legacy system integration is handled through adapter patterns that translate between modern APIs and older protocols (SOAP, file-based exchange).
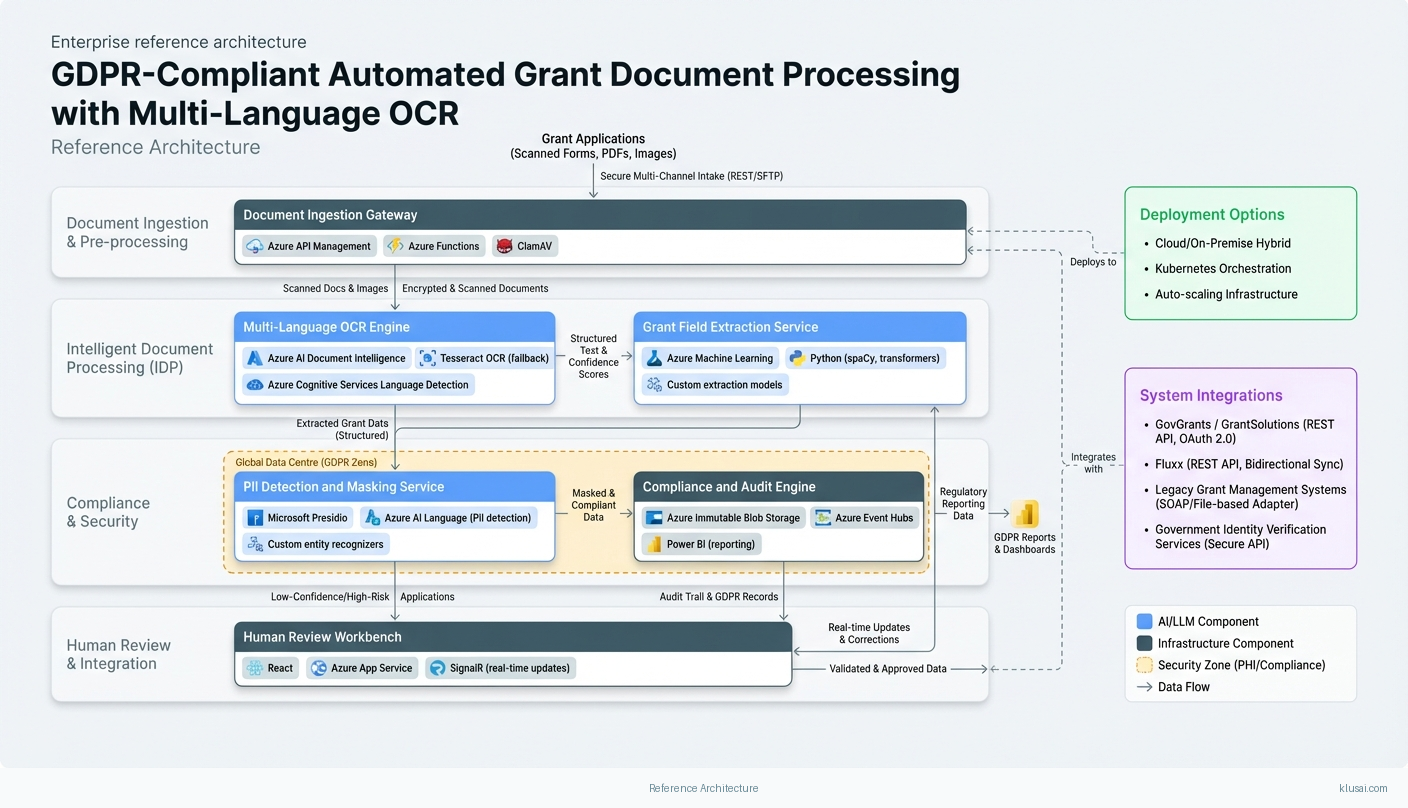
Key Components
| Component | Purpose | Technologies |
|---|---|---|
| Document Ingestion Gateway | Secure multi-channel document intake with immediate encryption, virus scanning, and initial classification | Azure API Management Azure Functions ClamAV |
| Multi-Language OCR Engine | Convert scanned documents and images to structured text with language detection and confidence scoring | Azure AI Document Intelligence Tesseract OCR (fallback) Azure Cognitive Services Language Detection |
| Grant Field Extraction Service | Map OCR output to grant-specific data schemas using trained extraction models and rule-based validation | Azure Machine Learning Python (spaCy, transformers) Custom extraction models |
| PII Detection and Masking Service | Identify and protect personal data throughout processing pipeline, ensuring GDPR compliance | Microsoft Presidio Azure AI Language (PII detection) Custom entity recognizers |
| Compliance and Audit Engine | Maintain immutable audit trails, generate GDPR Article 30 records, and support regulatory reporting | Azure Immutable Blob Storage Azure Event Hubs Power BI (reporting) |
| Human Review Workbench | Web-based interface for staff review of low-confidence extractions and high-risk applications | React Azure App Service SignalR (real-time updates) |
Technology Stack

Implementation Phases
Phase 1: Foundation and Compliance Framework
Establish GDPR-compliant infrastructure with data residency controls and encryption
- • Establish GDPR-compliant infrastructure with data residency controls and encryption
- • Deploy document ingestion pipeline with initial classification capabilities
- • Implement audit logging framework and compliance reporting foundation
- Production-ready Azure infrastructure with security controls and monitoring
- Document ingestion gateway supporting 3 intake channels (web, email, API)
- Compliance documentation including Data Protection Impact Assessment (DPIA) and Article 30 records template
Phase 2: OCR and Extraction Development
Deploy multi-language OCR pipeline with 24 EU language support
- • Deploy multi-language OCR pipeline with 24 EU language support
- • Train and validate grant-specific field extraction models achieving 92%+ accuracy on test corpus
- • Implement PII detection and masking with 98%+ recall target on known PII categories
- Operational OCR pipeline processing documents in under 60 seconds average
- Field extraction models for top 5 grant programs by volume
- PII detection service with configurable sensitivity levels and masking rules
Phase 3: Integration and Parallel Validation
Complete integrations with primary grant management platform and 2 secondary systems
- • Complete integrations with primary grant management platform and 2 secondary systems
- • Execute 60-day parallel processing validation comparing AI extraction to manual baseline
- • Validate end-to-end processing time reduction and accuracy targets
- Production integrations with GovGrants/Fluxx/GrantSolutions (as applicable) with error handling and retry logic
- Parallel validation report with statistical analysis of accuracy, time savings, and error patterns
- Human review workbench deployed with role-based access and workflow routing
Phase 4: Production Rollout and Optimization
Complete phased production rollout across all grant programs
- • Complete phased production rollout across all grant programs
- • Achieve target processing capacity increase of 25-40% without additional headcount
- • Establish operational monitoring, model maintenance, and continuous improvement processes
- Full production deployment with all grant programs onboarded
- Operational runbook with incident response procedures and escalation paths
- Training materials and certification for staff on new workflows and human review processes
Key Technical Decisions
Should OCR processing use cloud-native AI services or self-hosted open-source models?
Azure AI Document Intelligence provides superior accuracy for structured documents (forms, tables) with continuous model improvements included. The service maintains EU data residency compliance and integrates natively with the Azure security model. Tesseract provides a cost-effective fallback for simple text extraction and reduces vendor lock-in risk. This hybrid approach balances accuracy, compliance, and cost optimization.
- Azure AI Document Intelligence achieves 95%+ accuracy on structured forms without custom training
- Managed service reduces operational burden and includes continuous improvements
- Per-page pricing can become significant at high volumes (mitigated by tiered pricing negotiations)
- Some dependency on Microsoft roadmap for language and document type support
How should the system handle documents with confidence scores below the 95% threshold?
A binary high/low confidence approach would either overwhelm human reviewers or miss errors. The tiered approach routes documents to appropriate review levels: 90-95% confidence to junior reviewers for quick verification, 80-90% to experienced staff for detailed review, below 80% to specialists. Risk factors (grant value, applicant history, document type) adjust thresholds. This addresses the documented challenge that current solutions require 40-60% manual review [3] by focusing human effort where it adds most value.
- Optimizes human reviewer time by matching task complexity to skill level
- Maintains quality control while maximizing automation benefits
- Requires more complex workflow configuration and staff role definitions
- Initial threshold calibration requires iterative adjustment based on actual error patterns
How should legacy grant management system integration be approached given potential API limitations?
Legacy government systems often lack modern APIs, requiring flexible integration approaches. The adapter layer abstracts integration complexity from core processing logic, allowing different patterns per target system. API integration is preferred where available; file-based exchange (SFTP with structured formats) serves as reliable fallback; direct database integration is available for systems with no external interface. This approach acknowledges that integration complexity is often understated and provides contingency options.
- Accommodates diverse legacy system capabilities without redesigning core architecture
- File-based fallback provides reliable integration even for oldest systems
- Multiple integration patterns increase testing and maintenance complexity
- File-based integration introduces latency compared to real-time API calls
How should the system handle poor-quality scanned documents that degrade OCR accuracy?
Poor-quality documents (faded, skewed, low resolution, handwritten elements) are a primary cause of OCR failures. Rather than processing all documents identically, the system assesses quality metrics (resolution, contrast, skew angle, noise level) and routes documents to appropriate processing paths. High-quality documents proceed through standard OCR; medium-quality documents receive image preprocessing (deskew, contrast enhancement, noise reduction); low-quality documents are flagged for manual review or applicant resubmission request.
- Improves overall accuracy by matching processing approach to document characteristics
- Reduces wasted processing on documents unlikely to extract successfully
- Quality assessment adds processing latency (typically 2-5 seconds per document)
- Resubmission requests may frustrate applicants and delay processing
Integration Patterns
| System | Approach | Complexity | Timeline |
|---|---|---|---|
| GovGrants / GrantSolutions | REST API integration using OAuth 2.0 authentication with service principal credentials. Extracted application data pushed via batch API calls with transaction support. Status updates received via webhook notifications. Error handling includes automatic retry with exponential backoff and dead-letter queue for failed transmissions. | medium | 4-6 weeks |
| Fluxx | REST API integration with Fluxx's grant management endpoints. Bidirectional sync for application data and document attachments. Workflow triggers configured to initiate processing on new submissions. Custom fields mapped through Fluxx's flexible data model. | medium | 4-6 weeks |
| Legacy Grant Management Systems (SOAP/File-based) | Adapter layer implementing protocol translation between modern REST APIs and legacy interfaces. File-based integration via SFTP with structured XML/CSV formats and acknowledgment files. SOAP wrapper for systems with web service interfaces. Message queuing (Azure Service Bus) provides reliable delivery with retry logic. | high | 6-10 weeks |
| Government Identity Verification Services | Secure API integration with national identity verification services (where available) for applicant identity confirmation. Integration follows government API gateway standards with mutual TLS authentication. Fallback to document-based identity verification where API access unavailable. | high | 8-12 weeks |
ROI Framework
ROI is driven by three primary factors: reduction in manual document processing time, decreased error rates requiring rework, and increased grant processing capacity without additional headcount. The framework accounts for the documented challenge of staff manually searching through 200-page manuals [1] and the 10%+ annual increase in service requests [2] that agencies face under fixed budgets.
Key Variables
Example Calculation
Build vs. Buy Analysis
Internal Build Effort
Internal build would require 18-24 months with a team of 6-8 FTEs including ML engineers, cloud architects, compliance specialists, and grant domain experts. Key challenges include OCR model training requiring substantial document corpus (typically 10,000+ labeled documents per grant type), multi-language support complexity across 24 EU languages, and ongoing model maintenance. Estimated internal build cost €800,000-1,200,000 excluding opportunity cost, ongoing maintenance, and the significant risk of project delays common in public sector IT initiatives.
Market Alternatives
Newgen Grants Management Platform
€200,000-500,000 annual licensing depending on volume and modulesEnterprise grants management with AI capabilities; strong for organizations seeking end-to-end platform replacement rather than document processing augmentation. Best fit when replacing legacy grant management system entirely.
- • Comprehensive grants lifecycle management beyond document processing
- • Established vendor with public sector references and compliance certifications
- • May require replacing existing grant management systems rather than augmenting
- • Less flexibility for custom compliance requirements or unique grant workflows
ABBYY FlexiCapture
€100,000-300,000 annual licensing plus €150,000-300,000 implementationEnterprise document capture platform; excellent OCR capabilities but requires significant configuration for grant-specific workflows. Best fit for organizations with strong internal IT capability to customize.
- • Mature OCR technology with excellent accuracy across document types
- • Broad language support including all EU official languages
- • Generic platform requires extensive customization for grant-specific validation rules
- • Limited native grant management integrations; requires custom development
Microsoft Azure AI Document Intelligence (standalone)
€50,000-150,000 annually based on volume (pay-per-use) plus internal development costCloud-native document processing; excellent for organizations already invested in Azure ecosystem with internal capability to build grant workflows. Best fit for organizations with strong development teams.
- • Seamless Azure integration and security model compliance
- • Continuous model improvements included; no retraining burden
- • Requires custom development for grant workflows, validation rules, and compliance reporting
- • No built-in compliance reporting for GDPR Article 30 or grant-specific audit requirements
Our Positioning
KlusAI's approach is ideal for organizations that need grant-specific document processing integrated with existing systems rather than platform replacement. We assemble teams with the specific regulatory, technical, and domain expertise required for your context—particularly valuable when navigating multi-jurisdictional GDPR compliance requirements, integrating with legacy grant management systems, or requiring customized validation rules for unique grant programs. Our methodology emphasizes parallel validation and measurable outcomes before full deployment, with clear go/no-go criteria at each phase.
Team Composition
KlusAI assembles specialized teams tailored to each engagement, drawing from our network of vetted professionals with public sector, AI/ML, and compliance expertise. The team composition below represents a typical engagement for this implementation scope; actual composition is adjusted based on specific organizational context, existing capabilities, integration complexity, and regulatory requirements.
| Role | FTE | Focus |
|---|---|---|
| Solution Architect | 0.5 | Overall architecture design, integration patterns, security architecture, and technical decision-making |
| ML/AI Engineer | 1.0 | OCR pipeline development, document classification model training, field extraction optimization, model monitoring |
| Data Engineer | 0.75 | Data pipeline development, integration implementation, audit logging infrastructure |
| Compliance/GDPR Specialist | 0.25 | DPIA development, Article 30 records, compliance documentation, audit preparation |
| Change Management Lead | 0.5 | Stakeholder engagement, training program development, change champion coordination, union liaison |
Supporting Evidence
Performance Targets
25-40% reduction in average application processing time
>92% field-level accuracy on production documents
>98% recall on known PII categories
Process 25-40% more applications without additional headcount
Team Qualifications
- KlusAI's network includes professionals with extensive public sector digital transformation experience across EU member states
- Our teams are assembled with specific expertise in GDPR compliance, document AI, and grant management system integration
- We bring together technical specialists and domain experts with experience navigating public sector procurement, security accreditation, and change management requirements
Source Citations
Staff manually searching through 200-page manuals causing significant delays in grant approval workflows
"The traditional approach required staff to manually search through a 200-page manual, which created significant delays in grant approval workflows"exact
Budget constraints with 10%+ annual increase in service requests
"Limited budgets with increasing demands (10%+ annual increase in service requests)"exact
Current solutions require 40-60% manual review
directionalGrant-native AI platforms are emerging to address workflow challenges
directionalReady to discuss?
Let's talk about how this could work for your organization.
Schedule a Consultation
Pick a date that works for you
Times shown in your local timezone ()
Prefer email? Contact us directly
Almost there!
at
Your details
at
You're all set!
Check your email for confirmation and calendar invite.
Your booking is confirmed! Our team will reach out to confirm the details.
Your consultation
· min
( team time)
Quick Overview
- Technology
- Computer Vision
- Complexity
- high
- Timeline
- 5-7 months
- Industry
- Public Sector