The Problem
Insurance claims teams spend 20+ hours weekly searching for information across fragmented legacy systems, policy databases, and third-party adjuster platforms. This data fragmentation forces manual reconciliation across 5+ disconnected systems, creating delays, errors, and compliance violations that expose enterprises to regulatory penalties.
The challenge is compounded by increasingly stringent regulatory requirements. GDPR mandates explicit data governance and audit trails for all personal data processing, SOX requires immutable records of all financial transactions, and IFRS 17 demands precise, traceable claims reserves calculations. Current manual workflows cannot meet these requirements—data discrepancies go undetected, audit trails are incomplete, and cross-border data flows violate residency requirements.
Existing claims automation solutions address individual process steps (OCR, routing, payment) but fail to solve the core problem: they perpetuate data silos rather than eliminating them. They lack the orchestration layer needed to continuously synchronize data, detect inconsistencies in real-time, and maintain compliance across jurisdictions. Organizations need an integrated platform that unifies claims data while embedding compliance controls directly into the workflow.
Our Approach
Key elements of this implementation
-
AI-orchestrated data consolidation engine that synchronizes policy administration systems, adjuster platforms, and payment processors in real-time, with automatic conflict resolution and discrepancy flagging for human review
-
GDPR-compliant data governance with automatic data residency routing, consent tracking, and 90-day retention policies; SOX-compliant immutable audit trails for all claims modifications; IFRS 17-ready reserve calculations with full transaction traceability
-
Predictive AI models that assess claim severity, fraud, and litigation risk while maintaining explainability for regulatory audits; generative AI accelerates documentation while flagging compliance gaps before submission
-
Phased 12-week rollout with parallel-run period, embedded change champions in each claims center, and executive sponsorship model to drive adoption and maintain data quality standards
Get the Full Implementation Guide
Unlock full details including architecture and implementation
Implementation Overview
The Unified Claims Data Orchestration Engine addresses the fundamental challenge facing insurance claims operations: fragmented data across 5+ disconnected systems that forces claims handlers to spend 20+ hours weekly searching for information[1]. Rather than adding another point solution, this architecture creates an orchestration layer that continuously synchronizes data from policy administration systems, adjuster platforms, and payment processors while embedding compliance controls directly into the data flow.
The architecture is built on three core principles. First, change data capture (CDC) enables real-time synchronization without requiring modifications to legacy source systems—critical for organizations with decades-old policy administration platforms. Second, compliance is embedded at the data layer rather than bolted on afterward, with automatic data residency routing for GDPR Article 30 requirements, immutable audit trails for SOX Section 404 internal controls, and traceable reserve calculations for IFRS 17 disclosure requirements. Third, the orchestration engine uses durable workflow execution to guarantee exactly-once processing even during system failures, eliminating the data discrepancies that plague manual reconciliation.
The implementation follows a phased approach over 28-32 weeks, with explicit parallel-run periods and rollback capabilities at each stage. This timeline acknowledges the reality of enterprise insurance environments: legacy system integration is inherently complex, compliance hardening requires thorough validation, and organizational change management cannot be rushed. The architecture is designed for incremental value delivery, with measurable benefits beginning in Phase 2 while full capabilities mature through Phase 4.
UI Mockups
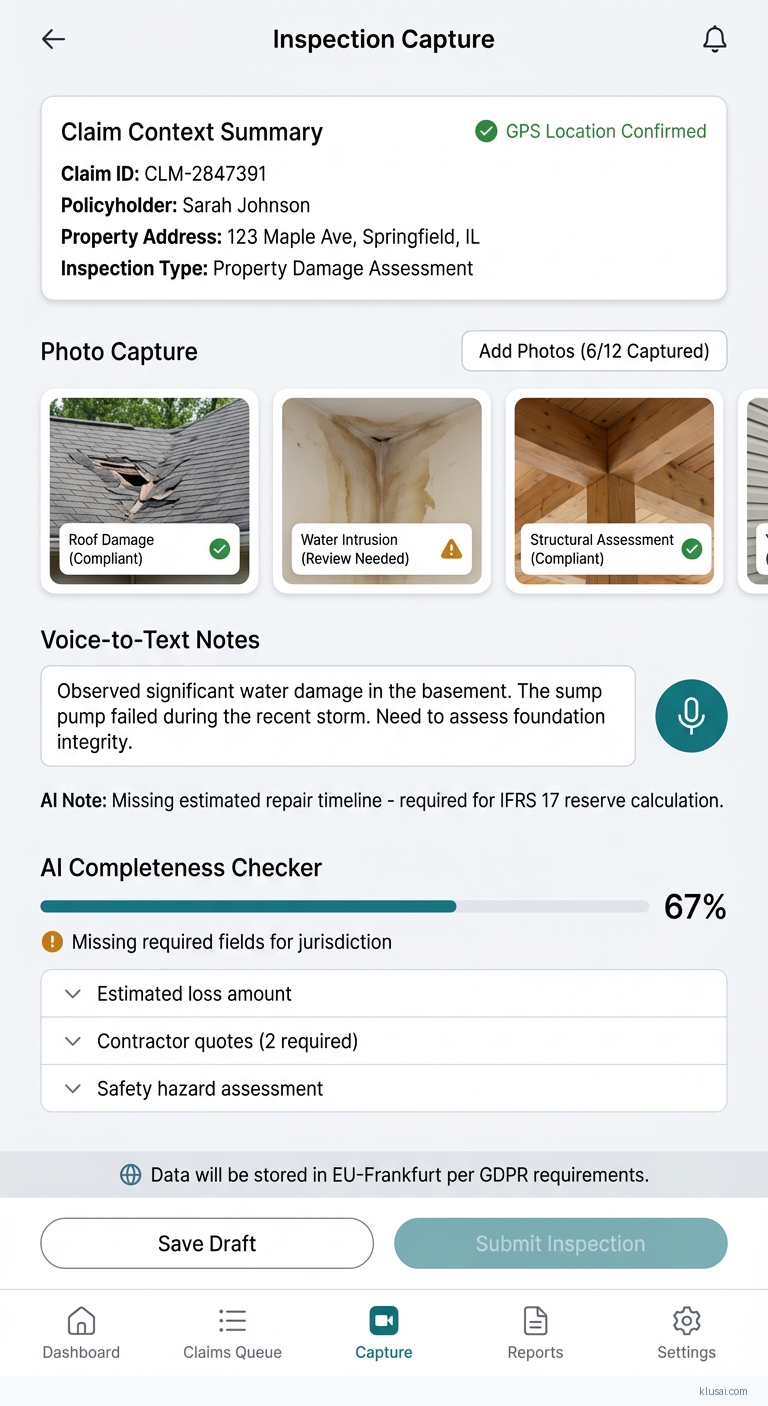
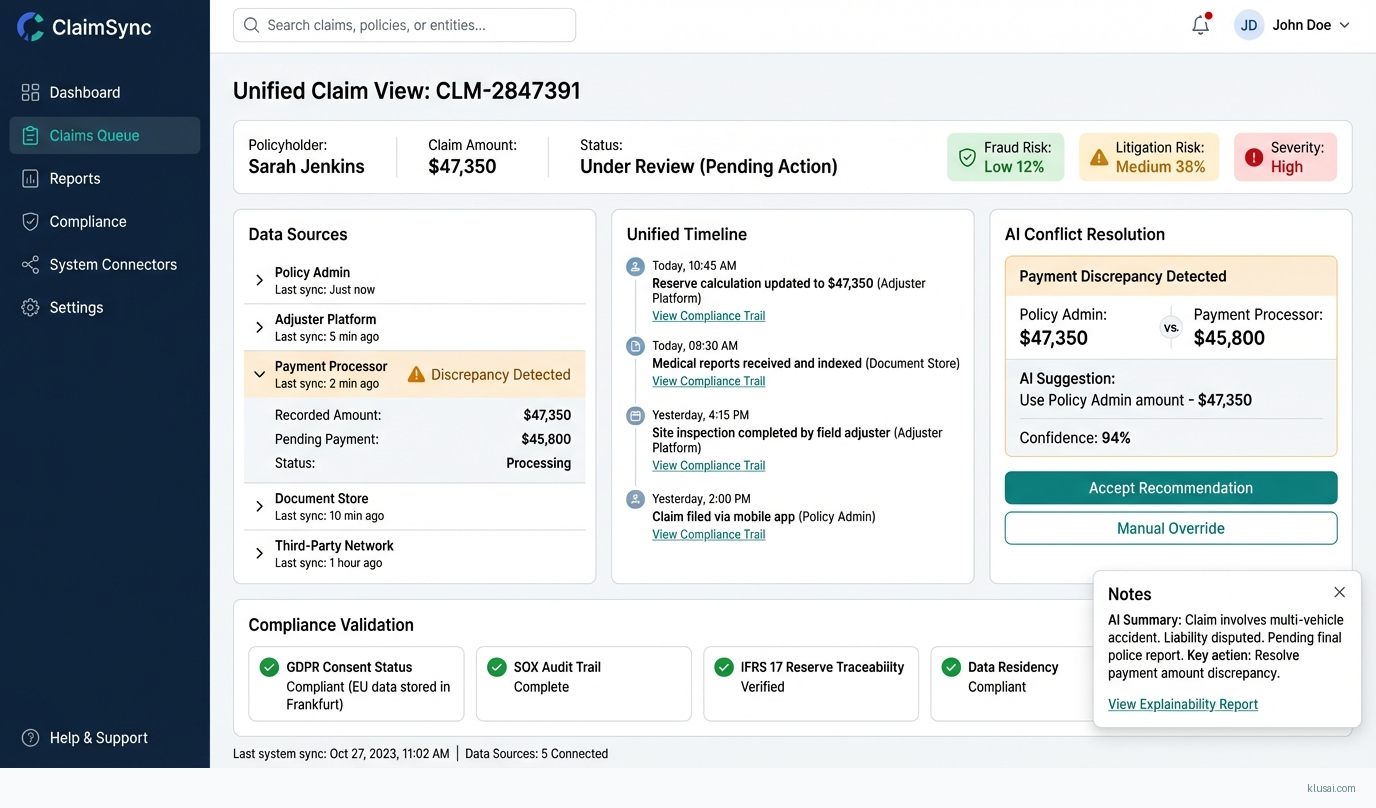
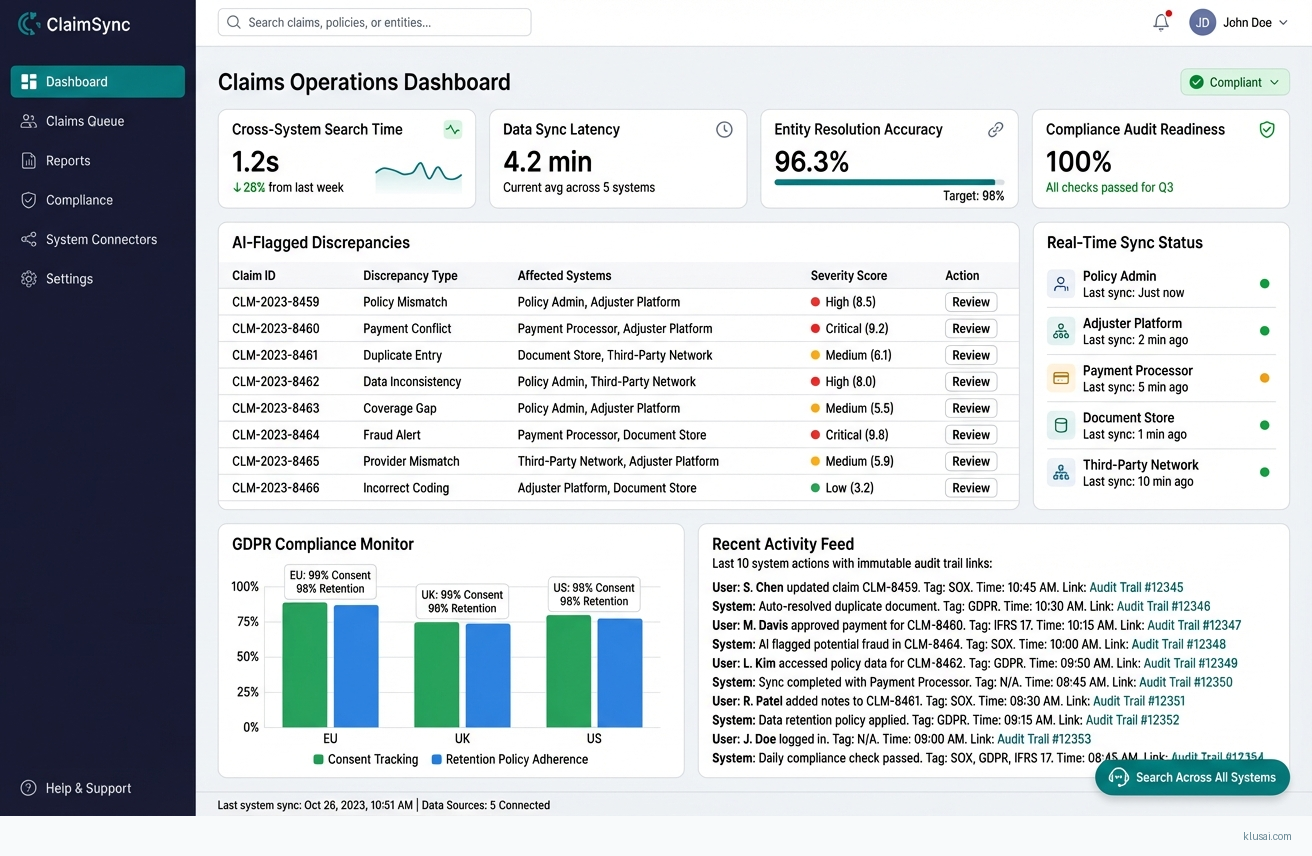
System Architecture
The architecture follows a hub-and-spoke pattern with the Claims Data Hub at the center, receiving change events from source systems and distributing unified data to consuming applications. This design isolates integration complexity at the edges while maintaining a clean, consistent data model at the core.
The data ingestion layer uses Debezium-based CDC connectors to capture changes from source databases without requiring application modifications. For systems without database-level access (common with third-party adjuster platforms), the architecture provides REST API polling adapters with configurable sync intervals. All ingested data flows through a compliance gateway that applies data residency rules, consent validation, and retention policies before data enters the central hub.
The Claims Data Hub maintains a unified claims graph that resolves entity relationships across systems—linking policy records, claimant information, adjuster notes, and payment transactions into a coherent view. The hub uses event sourcing to maintain complete history, enabling point-in-time queries for audit purposes and supporting the immutable record requirements of SOX Section 404. Conflict resolution follows configurable rules: system-of-record priority for authoritative fields, timestamp-based resolution for operational data, and human escalation for material discrepancies.
The AI services layer operates on the unified data, providing predictive models for severity assessment, fraud detection, and litigation risk scoring. These models are designed for explainability, generating decision rationale that can be presented in regulatory audits. A separate generative AI service accelerates documentation tasks while maintaining compliance guardrails that flag potential issues before submission.
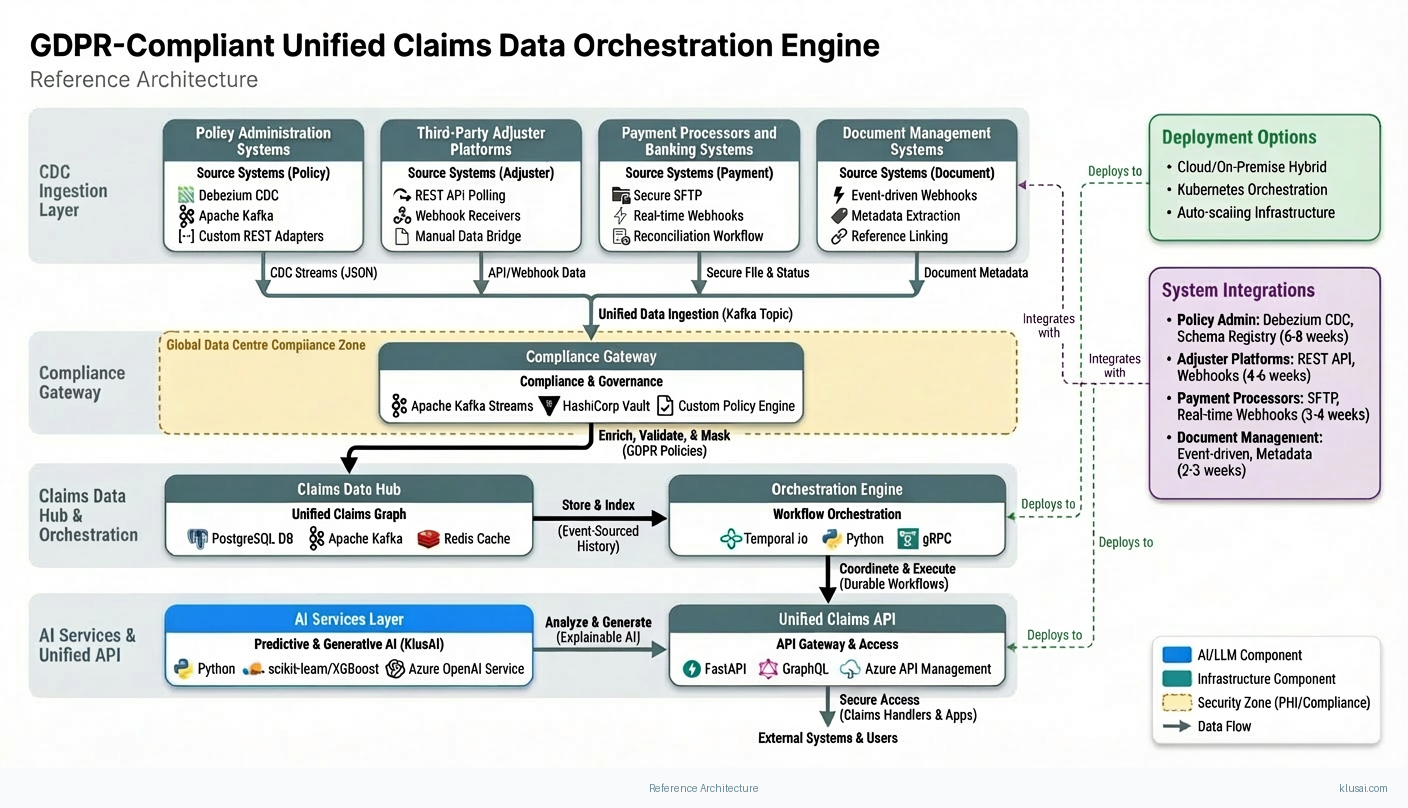
Key Components
| Component | Purpose | Technologies |
|---|---|---|
| CDC Ingestion Layer | Captures real-time changes from source systems without requiring application modifications | Debezium Apache Kafka Custom REST Adapters |
| Compliance Gateway | Enforces data residency, consent validation, and retention policies at ingestion time | Apache Kafka Streams HashiCorp Vault Custom Policy Engine |
| Claims Data Hub | Maintains unified claims graph with event-sourced history and conflict resolution | PostgreSQL Apache Kafka Redis |
| Orchestration Engine | Coordinates multi-step workflows with durable execution guarantees | Temporal.io Python gRPC |
| AI Services Layer | Provides predictive analytics and generative AI capabilities with explainability | Python scikit-learn/XGBoost Azure OpenAI Service |
| Unified Claims API | Provides consistent interface for claims handlers and downstream applications | FastAPI GraphQL Azure API Management |
Technology Stack
Implementation Phases
Phase 1: Foundation & Primary System Integration
Establish CDC infrastructure and connect primary policy administration system
- • Establish CDC infrastructure and connect primary policy administration system
- • Implement compliance gateway with GDPR data residency routing and consent validation
- • Deploy Claims Data Hub with initial schema and conflict resolution rules
- Production CDC pipeline from primary policy system with <5 minute sync latency
- Compliance gateway enforcing data residency for EU/UK/US regions
- Claims Data Hub with unified schema covering 80% of core claims fields
Phase 2: Secondary System Integration & Data Unification
Integrate 2-3 additional source systems (adjuster platforms, payment processors)
- • Integrate 2-3 additional source systems (adjuster platforms, payment processors)
- • Implement cross-system entity resolution and relationship mapping
- • Deploy Unified Claims API for read access by claims handlers
- CDC/API adapters for secondary systems with documented sync latency SLAs
- Entity resolution achieving >95% automatic match rate on test dataset
- Unified Claims API serving consolidated view to pilot user group
Phase 3: AI Capabilities & Compliance Hardening
Deploy predictive models for severity, fraud, and litigation risk assessment
- • Deploy predictive models for severity, fraud, and litigation risk assessment
- • Implement SOX-compliant audit trails with immutable logging
- • Complete IFRS 17 reserve calculation traceability requirements
- Predictive models in production with explainability reports for each prediction
- Audit trail system passing internal SOX control testing
- Reserve calculation pipeline with full transaction lineage for IFRS 17 disclosure
Phase 4: Production Hardening & Organizational Transition
Execute parallel-run validation with legacy processes
- • Execute parallel-run validation with legacy processes
- • Complete change management program and user training
- • Establish operational runbooks and support transition
- 4-week parallel-run with <2% discrepancy rate versus legacy processes
- All claims handlers trained with competency validation
- Operational runbooks, escalation procedures, and 24/7 support model documented
Key Technical Decisions
Should we use database-level CDC or application-level event capture for legacy systems?
Database CDC captures all changes including those made by batch processes and direct database updates, providing complete data lineage. Application-level capture misses changes made outside the application layer, which is common in legacy insurance systems with multiple integration points.
- Complete capture of all data changes regardless of source
- No modifications required to legacy application code
- Requires database-level access that may face security/governance barriers
- Schema changes in source systems require CDC configuration updates
How should we handle data residency requirements for multi-jurisdictional operations?
GDPR Article 30 requires records of processing activities including data transfers. By routing data at ingestion based on data subject location, we maintain compliance without requiring complex cross-border data transfer agreements. This approach also supports future regulatory requirements in other jurisdictions.
- Clear compliance posture with data never leaving required jurisdiction
- Simplified audit trail for regulatory inquiries
- Increased infrastructure complexity with multiple regional deployments
- Cross-region queries require federation layer adding latency
What orchestration approach best handles the complexity of multi-system workflows?
Insurance claims workflows span multiple systems and can take days or weeks to complete. Temporal provides durable execution guarantees, automatic retry with configurable backoff, and explicit workflow state that survives system failures. This eliminates the data consistency issues that plague message-queue-based approaches.
- Exactly-once execution semantics eliminate duplicate processing
- Workflow state is queryable, enabling operational visibility
- Additional infrastructure component to operate and maintain
- Learning curve for development team unfamiliar with workflow-as-code patterns
How should predictive models balance accuracy with regulatory explainability requirements?
Insurance regulators increasingly require explanation of automated decisions affecting policyholders. Interpretable models with SHAP values provide feature-level attribution that can be presented in plain language. Deep learning models, while potentially more accurate, create explainability challenges that complicate regulatory compliance.
- Clear feature attribution satisfies regulatory explainability requirements
- Easier validation by domain experts and actuaries
- May sacrifice some predictive accuracy compared to deep learning approaches
- Feature engineering requires more domain expertise upfront
Integration Patterns
| System | Approach | Complexity | Timeline |
|---|---|---|---|
| Policy Administration Systems (Guidewire, Duck Creek, legacy mainframe) | Debezium CDC connector for database-level change capture; schema registry for managing format evolution; initial full sync followed by incremental CDC | high | 6-8 weeks |
| Third-Party Adjuster Platforms (Xactimate, ClaimXperience) | REST API polling with configurable intervals; webhook receivers where available; manual data bridge for fields not exposed via API | medium | 4-6 weeks |
| Payment Processors and Banking Systems | Secure file transfer (SFTP) for batch payment files; real-time webhook integration for payment status updates; reconciliation workflow for discrepancy handling | medium | 3-4 weeks |
| Document Management Systems (FileNet, SharePoint) | Event-driven integration via system webhooks or polling; document metadata extraction and indexing; reference linking to claims in Data Hub | low | 2-3 weeks |
ROI Framework
ROI is driven primarily by elimination of manual cross-system search time[1], with secondary benefits from reduced compliance violation risk and improved claims processing throughput. The framework uses conservative efficiency assumptions that should be validated during pilot.
Key Variables
Example Calculation
Build vs. Buy Analysis
Internal Build Effort
Internal build would require 18-24 months with a team of 8-12 engineers including distributed systems specialists, compliance engineers, and ML practitioners. Key challenges include building durable workflow orchestration (typically 6+ months alone), implementing multi-region compliance controls with proper audit trails, and maintaining the system long-term. Estimated internal cost $1.8-2.8M for initial build plus $500-700K annually for maintenance, security updates, and evolution.
Market Alternatives
Guidewire ClaimCenter with Analytics
$500K-2M implementation plus $300-500K annual licensingMarket-leading claims platform with strong workflow capabilities; best fit for organizations already in Guidewire ecosystem or planning full platform replacement
- • Mature platform with extensive insurance-specific functionality
- • Large partner ecosystem and implementation resources
- • Integrated analytics capabilities
- • Limited flexibility for custom orchestration logic across non-Guidewire systems
- • Data unification across external systems still requires significant custom integration
- • Platform replacement approach may not fit organizations with recent legacy investments
Duck Creek Claims
$400K-1.5M implementation plus usage-based licensingCloud-native claims platform with modern architecture; strong for greenfield implementations or organizations prioritizing SaaS delivery
- • Modern API-first architecture
- • Strong configuration capabilities without custom code
- • Cloud-native with managed infrastructure
- • Less mature than Guidewire in complex commercial claims scenarios
- • Orchestration across external legacy systems still requires custom development
- • Smaller implementation partner ecosystem
Custom Integration with iPaaS (MuleSoft, Boomi, or Azure Integration Services)
$300-800K implementation plus $150-300K annual platform costIntegration-focused approach using commercial middleware; suitable for organizations with existing iPaaS investment and strong internal integration team
- • Leverages existing integration platform investment
- • Broad connector ecosystem for common systems
- • Flexible for custom integration patterns
- • Lacks claims-specific intelligence and compliance controls
- • Durable execution guarantees require significant custom development
- • No built-in support for insurance regulatory requirements
Our Positioning
KlusAI's approach is ideal for organizations that need to unify data across existing systems without full platform replacement, have complex multi-jurisdictional compliance requirements, or want to maintain strategic control over their claims data architecture. We assemble teams with the specific distributed systems, compliance, and insurance domain expertise required—providing the flexibility of custom development with accelerated delivery through proven architectural patterns.
Team Composition
KlusAI assembles specialized teams tailored to each engagement, bringing together technical architects, compliance specialists, data engineers, and change management professionals. Team composition scales based on organization size, number of source systems, and regulatory complexity.
| Role | FTE | Focus |
|---|---|---|
| Solutions Architect | 1.0 | Overall architecture design, technology selection, integration patterns, and technical leadership |
| Data Engineer | 2.0 | CDC implementation, data pipeline development, schema management, and data quality controls |
| Compliance Engineer | 0.75 | GDPR residency controls, SOX audit trail implementation, consent management, and regulatory validation |
| ML Engineer | 1.0 | Predictive model development, explainability implementation, and MLOps pipeline setup |
| Change Management Lead | 1.0 | Stakeholder engagement, training program development, adoption tracking, and organizational transition |
Supporting Evidence
Performance Targets
25-35% reduction in time spent searching for information across systems
<5 minutes from source system change to unified view availability
>95% automatic match rate with <0.1% false positive rate
Audit trail queries return complete transaction history within 30 seconds
Team Qualifications
- KlusAI's network includes professionals with enterprise integration experience across insurance policy administration systems, claims platforms, and regulatory compliance implementations
- Our teams are assembled with specific expertise in event-driven architectures, durable workflow orchestration, and data governance frameworks required for financial services
- We bring together technical architects and domain specialists who understand both the technology patterns and the operational realities of insurance claims processing
Source Citations
20+ hours weekly searching for information
"Fragmented data across systems and departments (20+ hours/week searching for information)"exact
GDPR mandates explicit data governance and audit trails for all personal data processing
directionalSOX requires immutable records of all financial transactions
directionalCurrent automation solutions fail to solve data silos; they lack orchestration layer for continuous synchronization and compliance
directionalReady to discuss?
Let's talk about how this could work for your organization.
Schedule a Consultation
Pick a date that works for you
Times shown in your local timezone ()
Prefer email? Contact us directly
Almost there!
at
Your details
at
You're all set!
Check your email for confirmation and calendar invite.
Your booking is confirmed! Our team will reach out to confirm the details.
Your consultation
· min
( team time)
Quick Overview
- Technology
- Process Automation
- Complexity
- high
- Timeline
- 5-7 months
- Industry
- Finance