The Problem
Healthcare providers face substantial revenue leakage from coding errors and undercoding due to inadequate documentation linking clinical evidence to codes.
Complex clinical notes must align with ICD-11 WHO standards, payer-specific guidelines, and procedures, while navigating varying regulations like HIPAA, GDPR across multinational systems, leading to frequent claim denials and audits.
Existing AI coding tools provide code suggestions or real-time checks but lack comprehensive, evidence-linked justification documents, requiring extensive human review and failing to produce fully audit-ready outputs with regulatory-compliant trails.
Our Approach
Key elements of this implementation
-
Multi-LLM RAG pipeline with semantic retrieval from de-identified clinical notes, ICD-11 codes, payer rules generating evidence-linked justifications
-
HIPAA/GDPR/ICD-11 compliance: end-to-end encryption, EU/US data residency options, immutable audit logs tracing code-to-evidence mappings
-
Native integrations with Epic, Cerner EHRs; human-in-the-loop for <95% confidence outputs; real-time payer rule validation
-
Phased rollout: 30-day pilot with 10 coders, 60-day parallel run, executive-sponsored training addressing adoption and data quality risks
Get the Full Implementation Guide
Unlock full details including architecture and implementation
Implementation Overview
The Global AI Coding Compliance Documentation Generator addresses the critical gap between AI-assisted code suggestions and audit-ready documentation by creating a multi-LLM pipeline that generates evidence-linked justifications for medical coding decisions. Unlike existing solutions that provide code recommendations requiring extensive human review[2][4], this system produces complete documentation packages that trace each code to specific clinical evidence, satisfying regulatory requirements across HIPAA, GDPR, and regional frameworks.
The architecture employs a retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) approach with semantic search across de-identified clinical notes, coding guidelines (supporting both ICD-10-CM for US operations and ICD-11 for WHO-aligned regions), and payer-specific rules. A confidence-calibrated human-in-the-loop workflow routes outputs below 90% confidence to certified coders, while high-confidence outputs proceed with automated audit trail generation. This approach directly addresses the documentation quality issues that drive coding-related claim denials[1][5].
Key architectural decisions include region-specific data residency (US, EU, and configurable regional deployments), immutable audit logging for regulatory compliance, and a modular integration layer supporting Epic, Cerner, and FHIR R4-compliant EHR systems. The phased rollout includes explicit change management activities, recognizing that coder adoption is as critical as technical accuracy. Implementation timeline of 6-8 months includes risk buffers for healthcare IT procurement cycles, clinical validation committees, and EHR vendor certification processes that typically extend standard software deployments.
System Architecture
The architecture follows a four-layer design: ingestion, processing, generation, and compliance. The ingestion layer receives clinical documentation through EHR integrations, applying PHI de-identification before any AI processing. Documents flow through a preprocessing pipeline that extracts structured data (diagnosis codes, procedures, demographics) and unstructured clinical narratives, storing both in region-appropriate data stores with encryption at rest.
The processing layer implements semantic retrieval using a vector store populated with coding guidelines, payer rules, and historical coding decisions. When a coding request arrives, the system retrieves relevant context—applicable ICD codes, payer-specific documentation requirements, and similar historical cases—creating a rich context window for the generation layer. The vector store is updated monthly with payer rule changes and quarterly with coding guideline updates, with version tracking for audit purposes.
The generation layer employs a multi-model approach: a primary LLM generates initial justification drafts, a secondary model performs compliance checking against regulatory requirements, and a calibrated confidence scorer determines routing. Outputs below 90% confidence enter the human-in-the-loop queue with specific uncertainty flags. The system validates that code combinations produce appropriate DRG assignments (for inpatient) and flags potential optimization opportunities or conflicts that could trigger audits.
The compliance layer maintains immutable audit logs linking every generated justification to source evidence, model versions, confidence scores, and human review decisions. Logs are stored with region-appropriate retention (7 years US, per GDPR requirements in EU) and support export for regulatory audits. A model monitoring subsystem tracks accuracy metrics, confidence calibration, and drift indicators, triggering alerts when performance degrades.
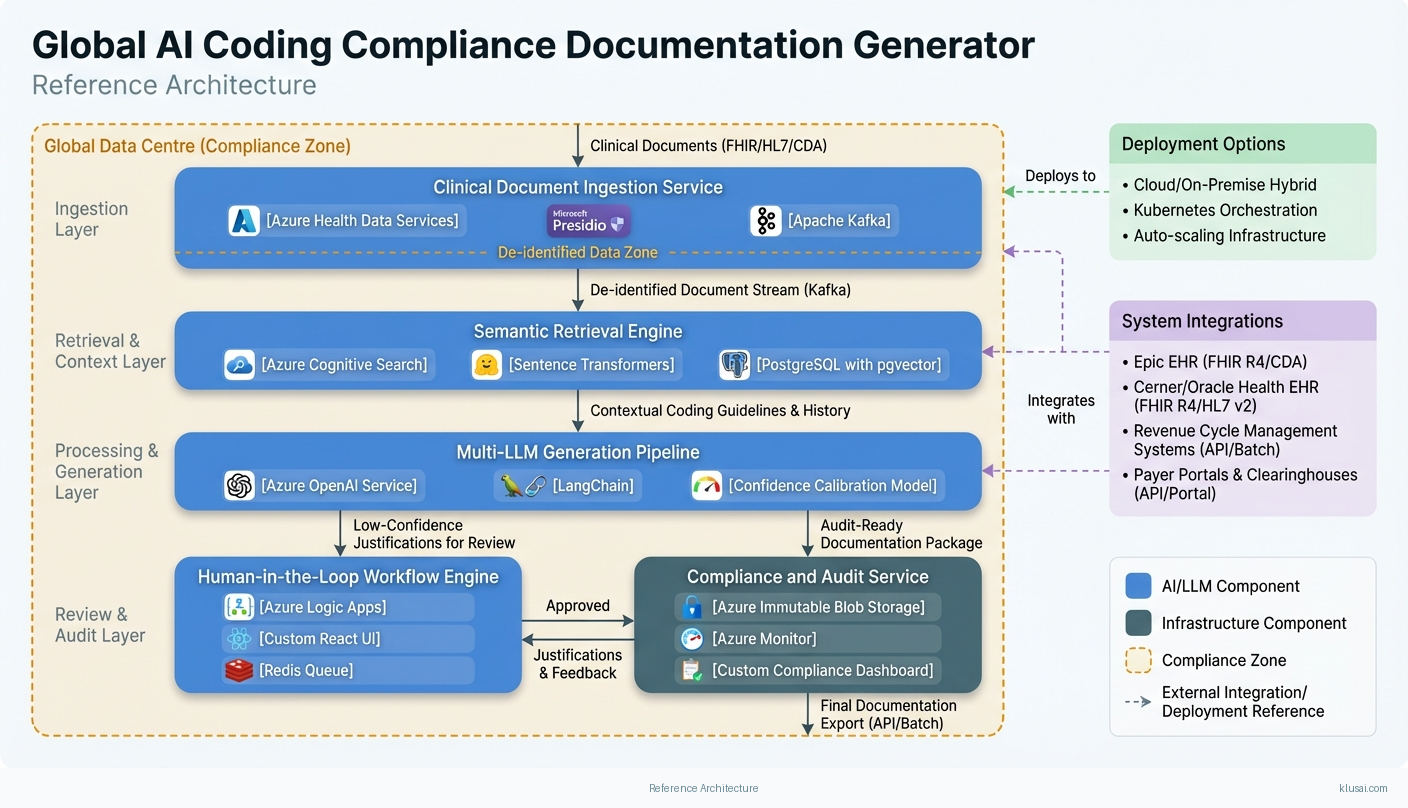
Key Components
| Component | Purpose | Technologies |
|---|---|---|
| Clinical Document Ingestion Service | Receives clinical documentation from EHR systems, applies PHI de-identification, and routes to appropriate regional processing pipelines | Azure Health Data Services Microsoft Presidio Apache Kafka |
| Semantic Retrieval Engine | Indexes and retrieves relevant coding guidelines, payer rules, and historical decisions to provide context for justification generation | Azure Cognitive Search Sentence Transformers PostgreSQL with pgvector |
| Multi-LLM Generation Pipeline | Generates evidence-linked coding justifications using retrieved context, with compliance validation and confidence scoring | Azure OpenAI Service LangChain Custom confidence calibration model |
| Human-in-the-Loop Workflow Engine | Routes low-confidence outputs to certified coders, captures feedback for model improvement, and manages review queues | Azure Logic Apps Custom React UI Redis Queue |
| Compliance and Audit Service | Maintains immutable audit trails, enforces data residency, and supports regulatory reporting requirements | Azure Immutable Blob Storage Azure Monitor Custom compliance dashboard |
| Model Monitoring and Observability Platform | Tracks model performance, confidence calibration, and drift indicators; triggers alerts for degradation | Azure Monitor MLflow Grafana Custom drift detection |
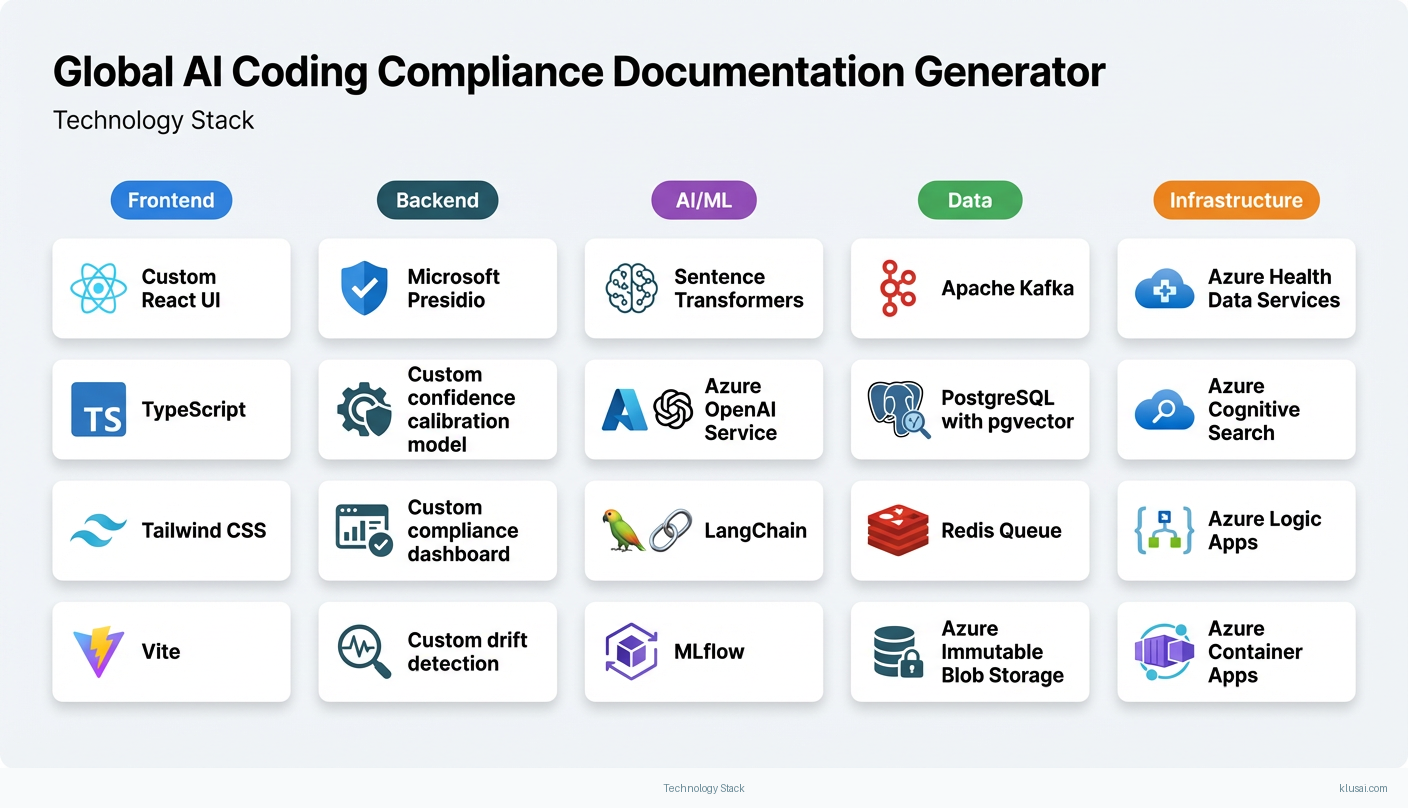
Technology Stack
Implementation Phases
Foundation and Security Certification
Establish secure infrastructure with regional data residency and complete security assessment documentation
- • Establish secure infrastructure with regional data residency and complete security assessment documentation
- • Implement core RAG pipeline with initial coding guideline corpus and validate retrieval accuracy
- • Complete organizational security review and begin EHR vendor certification applications
- Deployed infrastructure in primary region with security controls documented for compliance review
- Functional RAG pipeline achieving >85% retrieval relevance on test corpus
- Security assessment package submitted to organizational InfoSec and EHR vendor certification applications initiated
Pilot Deployment and Coder Adoption
Deploy to pilot group of 10-15 coders with structured change management program
- • Deploy to pilot group of 10-15 coders with structured change management program
- • Validate accuracy, confidence calibration, and user acceptance in production-like environment
- • Establish baseline metrics for denial rates, coding time, and user satisfaction
- Pilot system processing live cases with human-in-the-loop workflow operational
- Accuracy validation report with confidence calibration analysis and comparison to baseline
- Change management assessment including coder feedback, adoption barriers, and workflow optimization recommendations
Production Hardening and Expansion Preparation
Harden system based on pilot learnings with production-grade monitoring and alerting
- • Harden system based on pilot learnings with production-grade monitoring and alerting
- • Complete EHR integration certification and implement production connectivity
- • Prepare expansion playbook for additional regions and facilities
- Production-hardened system with full observability stack and runbook documentation
- Certified EHR integration operational (or documented timeline for certification completion)
- Multi-region expansion playbook with compliance checklists and deployment automation
Scaled Deployment and Optimization
Expand to full production deployment across initial region with all target facilities
- • Expand to full production deployment across initial region with all target facilities
- • Implement continuous improvement processes based on production feedback
- • Document lessons learned and prepare for potential multi-region expansion
- Full production deployment with validated ROI metrics against pilot baselines
- Operational runbooks, training materials, and support processes documented
- Multi-region expansion assessment with timeline and resource requirements
Key Technical Decisions
How should we handle the transition between ICD-10-CM (dominant in US) and ICD-11 (WHO standard with limited global adoption)?
ICD-11 adoption remains limited globally despite WHO endorsement, with most US payers and CMS still requiring ICD-10-CM. A dual-coding approach provides future-proofing while maintaining current operational compatibility. The system should flag cases where ICD-10 to ICD-11 mappings are ambiguous.
- Maintains compatibility with current payer requirements while preparing for eventual ICD-11 transition
- Supports multinational organizations with varying regional requirements
- Increases complexity of coding guideline corpus and retrieval logic
- Requires ongoing maintenance of mapping tables as standards evolve
What confidence threshold should trigger human-in-the-loop review?
A 90% threshold balances automation benefits against accuracy requirements. Lower thresholds increase human review burden; higher thresholds risk quality issues. The threshold should be treated as a tunable parameter, not a fixed value, with calibration based on observed accuracy at different confidence levels.
- Provides clear routing logic with measurable accuracy at each confidence band
- Allows optimization based on actual production data rather than assumptions
- Requires ongoing calibration effort and monitoring infrastructure
- May need facility-specific thresholds based on case complexity mix
Should we implement federated learning for cross-organization model improvement?
Federated learning in healthcare contexts faces significant governance, legal, and technical challenges that would extend initial deployment timeline by 6+ months. Initial deployment should focus on proven single-organization approaches, with federated learning as a future enhancement once operational stability is established.
- Reduces initial deployment complexity and timeline risk
- Allows governance frameworks to mature before cross-organization data sharing
- Limits initial model improvement to single-organization data
- May require architecture changes when federated learning is implemented
How should DRG validation be integrated into the coding justification workflow?
DRG assignment directly impacts reimbursement for inpatient cases, and code combinations that produce suboptimal DRG assignments represent a significant revenue opportunity. The system should validate that generated codes produce appropriate DRG assignments and flag cases where alternative coding might be clinically appropriate and improve reimbursement.
- Identifies revenue optimization opportunities beyond basic coding accuracy
- Reduces risk of audit triggers from unusual DRG patterns
- Requires integration with DRG grouper software (3M, Optum, or similar)
- Must carefully balance optimization suggestions against compliance requirements
Integration Patterns
| System | Approach | Complexity | Timeline |
|---|---|---|---|
| Epic EHR | FHIR R4 APIs for clinical document retrieval with App Orchard certification; fallback to CDA document export for organizations without FHIR enabled; results returned via SMART on FHIR or secure API | high | 12-16 weeks including certification |
| Cerner/Oracle Health EHR | FHIR R4 APIs via CODE certification program; Millennium integration for legacy deployments; HL7 v2 interfaces for organizations without FHIR capability | high | 12-16 weeks including certification |
| Revenue Cycle Management Systems | API integration with major RCM platforms (Optum360, R1 RCM, Conifer) for claim status and denial data; batch file exchange for systems without API capability | medium | 6-8 weeks |
| Payer Portals and Clearinghouses | Integration with clearinghouses (Availity, Change Healthcare) for payer rule updates and claim status; direct payer portal integration for major payers where available | medium | 8-10 weeks |
ROI Framework
ROI is driven by three primary factors: reduction in claim denials through improved documentation quality[1][5], decreased time spent on manual coding justification, and reduced audit preparation effort through pre-generated evidence trails. Benefits scale with coding volume and current denial rates. All projections use conservative estimates and should be validated during the pilot phase against actual baseline metrics.
Key Variables
Example Calculation
Build vs. Buy Analysis
Internal Build Effort
Internal build requires 18-24 months with a team of 10-14 FTEs including ML engineers with medical NLP expertise, healthcare informaticists with coding certification (CCS, CPC), compliance specialists familiar with HIPAA/GDPR, integration developers with EHR experience, and change management specialists. Key challenges include acquiring medical NLP expertise, maintaining current payer rules across jurisdictions, achieving EHR vendor certification (4-6 months alone), and managing ongoing model drift. Estimated internal cost $2.5-4.0M before ongoing maintenance, with significant risk of timeline extension due to healthcare IT complexity and certification requirements.
Market Alternatives
3M CodeAssist / M*Modal
$200,000-$500,000 annually depending on volumeEstablished enterprise solution with deep EHR integration and extensive validation data; best fit for large US health systems already in 3M ecosystem seeking proven, certified solution with comprehensive support
- • Mature product with extensive clinical validation and regulatory certifications
- • Strong Epic and Cerner integrations with established App Orchard/CODE certification
- • Comprehensive compliance certifications and dedicated audit support
- • Limited customization for organization-specific payer rules or specialty workflows
- • Primarily US-focused; limited support for multinational regulatory requirements
- • Less transparency in AI decision-making for detailed audit explanation
Emerging AI-Native Solutions (Ambience, Suki, Fathom)
$100,000-$300,000 annuallyModern AI-first approaches with state-of-the-art language models; best for organizations prioritizing cutting-edge technology and willing to accept newer vendor risk for faster innovation cycles
- • State-of-the-art language models with rapid innovation and frequent updates
- • Often better user experience and modern interfaces that improve coder adoption
- • Faster deployment timelines for standard use cases without complex customization
- • Less proven at enterprise scale across multiple regions and high volumes
- • Compliance certifications still maturing; may require additional validation
- • Limited customization for complex multinational requirements
Optum360 / AAPC Coding Solutions
$150,000-$400,000 annuallyComprehensive RCM suite with coding assistance; best for organizations seeking integrated revenue cycle platform with coding as one component of broader workflow
- • End-to-end revenue cycle integration with denial management and analytics
- • Strong payer relationship data and claims intelligence
- • Established training and certification programs for coder development
- • AI capabilities less advanced than specialized coding solutions
- • May require broader platform adoption beyond coding module
- • Limited audit trail granularity for evidence-linked justifications
Our Positioning
KlusAI's approach is optimal for multinational health systems requiring customized compliance across jurisdictions (HIPAA, GDPR, regional frameworks), organizations with unique payer relationships or specialty coding requirements that off-the-shelf solutions don't address, and those needing transparent, auditable AI that satisfies rigorous regulatory scrutiny. We assemble teams with the specific expertise your context requires—healthcare informaticists, compliance specialists, integration engineers, and change management professionals—rather than offering a one-size-fits-all product. This flexibility is particularly valuable for complex implementations where standard solutions require significant customization or where organizational change management is as important as technical capability.
Team Composition
KlusAI assembles specialized teams tailored to each engagement, drawing from our network of healthcare technology, compliance, and AI implementation professionals. Team composition scales based on deployment scope, with core roles supplemented by specialists as needed for specific EHR integrations, regional compliance requirements, or change management intensity.
| Role | FTE | Focus |
|---|---|---|
| Healthcare AI Solutions Architect | 1.0 | Overall technical architecture, LLM pipeline design, and integration strategy |
| Healthcare Informaticist / Clinical SME | 0.75 | Coding guideline corpus development, accuracy validation, and clinical workflow optimization |
| Compliance and Privacy Specialist | 0.5 | HIPAA/GDPR compliance, audit trail design, and regulatory documentation |
| Integration Engineer | 1.0 | EHR integration development, API implementation, and data pipeline engineering |
| Change Management and Training Lead | 0.5 | Coder adoption strategy, training program development, and organizational change support |
Supporting Evidence
Performance Targets
>92% agreement with certified coder review
15-25% reduction in coding-related denials
40-55% reduction in justification documentation time
>80% of pilot coders rating system as 'helpful' or 'very helpful'
Team Qualifications
- KlusAI's network includes professionals with healthcare informatics backgrounds, medical coding certifications, and experience implementing AI solutions in clinical environments
- Our teams are assembled with specific expertise in healthcare data standards (HL7 FHIR, CDA), privacy regulations (HIPAA, GDPR), and EHR integration patterns
- We bring together technical AI/ML specialists and healthcare domain experts tailored to each engagement's specific regulatory and operational context
Source Citations
substantial revenue leakage from coding errors and undercoding due to inadequate documentation
directionalExisting AI coding tools provide real-time checks but require human review and lack full compliance features
"AI-generated codes still require review and validation to ensure compliance and accuracy"directional
chart audits needed for coding compliance with regulatory requirements like Medicare, OIG standards
directionalAI assists with coding but requires human oversight, does not fully replace manual review
directionalAI detects coding inconsistencies leading to claim denials; monitors for regulatory compliance gaps
directionalReady to discuss?
Let's talk about how this could work for your organization.
Schedule a Consultation
Pick a date that works for you
Times shown in your local timezone ()
Prefer email? Contact us directly
Almost there!
at
Your details
at
You're all set!
Check your email for confirmation and calendar invite.
Your booking is confirmed! Our team will reach out to confirm the details.
Your consultation
· min
( team time)
Quick Overview
- Technology
- Large Language Models
- Complexity
- high
- Timeline
- 4-6 months
- Industry
- Healthcare