The Problem
Care transitions between facilities represent a critical vulnerability in healthcare delivery. Approximately 30% of care transitions experience communication gaps between sending and receiving care teams, creating cascading risks: missed medication reconciliations, delayed follow-up appointments, and lost clinical context that can compromise patient safety and outcomes.
The challenge is compounded by fragmented systems across healthcare organizations. Care teams rely on manual processes—phone calls, faxes, spreadsheets, and disconnected EHRs—to coordinate handoffs. This creates operational bottlenecks where administrative staff spend hours tracking referral status, verifying task completion, and chasing missing information rather than supporting clinical care. When transitions span multiple care settings (hospital to home health, primary care to specialist, acute to post-acute), the coordination burden multiplies with no single system of record.
Current care coordination platforms offer workflows and task management, but lack end-to-end automation specifically designed for the care transition moment. They require manual initiation, don't automatically compile standardized handoff summaries, and don't orchestrate the sequence of downstream tasks (appointment scheduling, medication verification, caregiver notification) that must happen in parallel to close transition gaps.
Our Approach
Key elements of this implementation
-
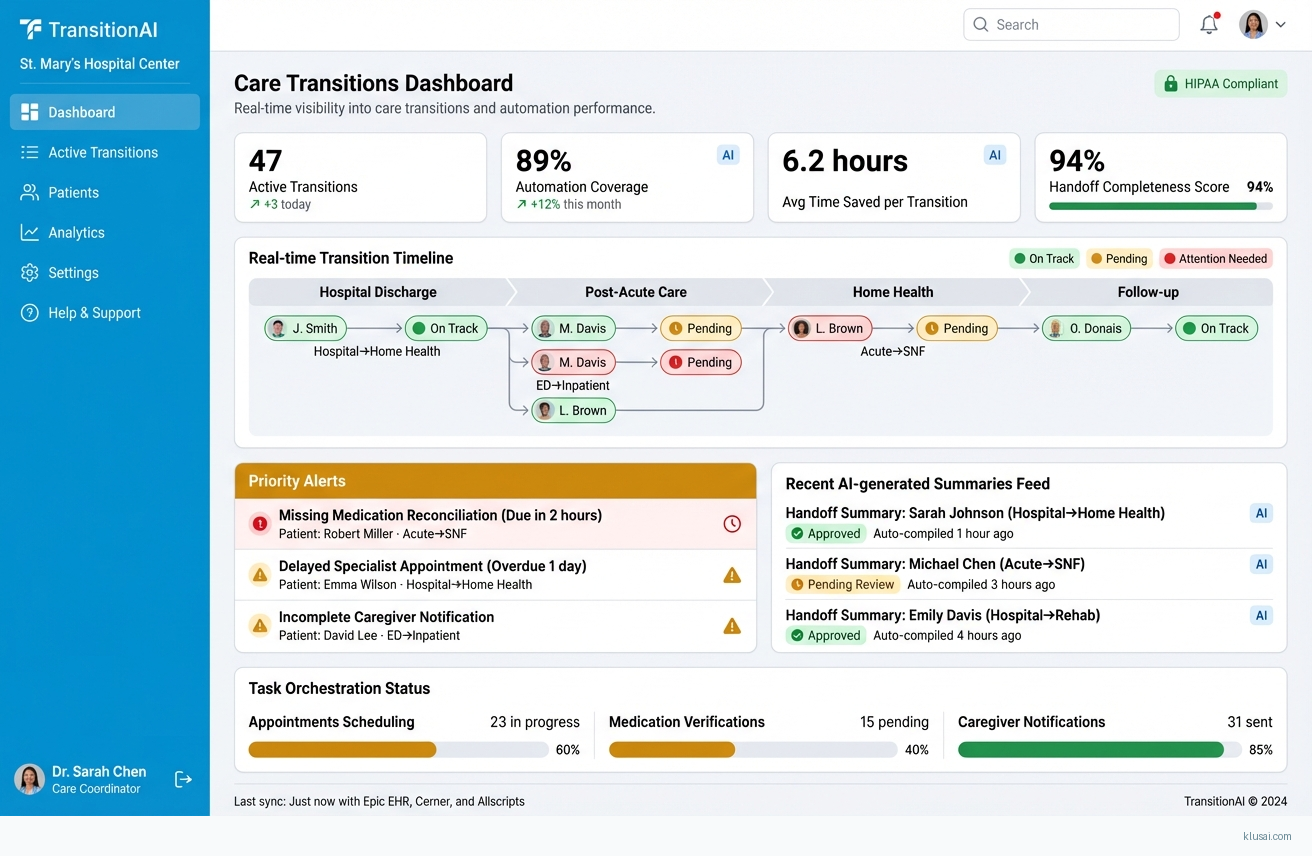
Automated trigger-based workflow engine that detects care transitions (discharge orders, referral submissions, department transfers) and initiates standardized handoff processes without manual intervention
-
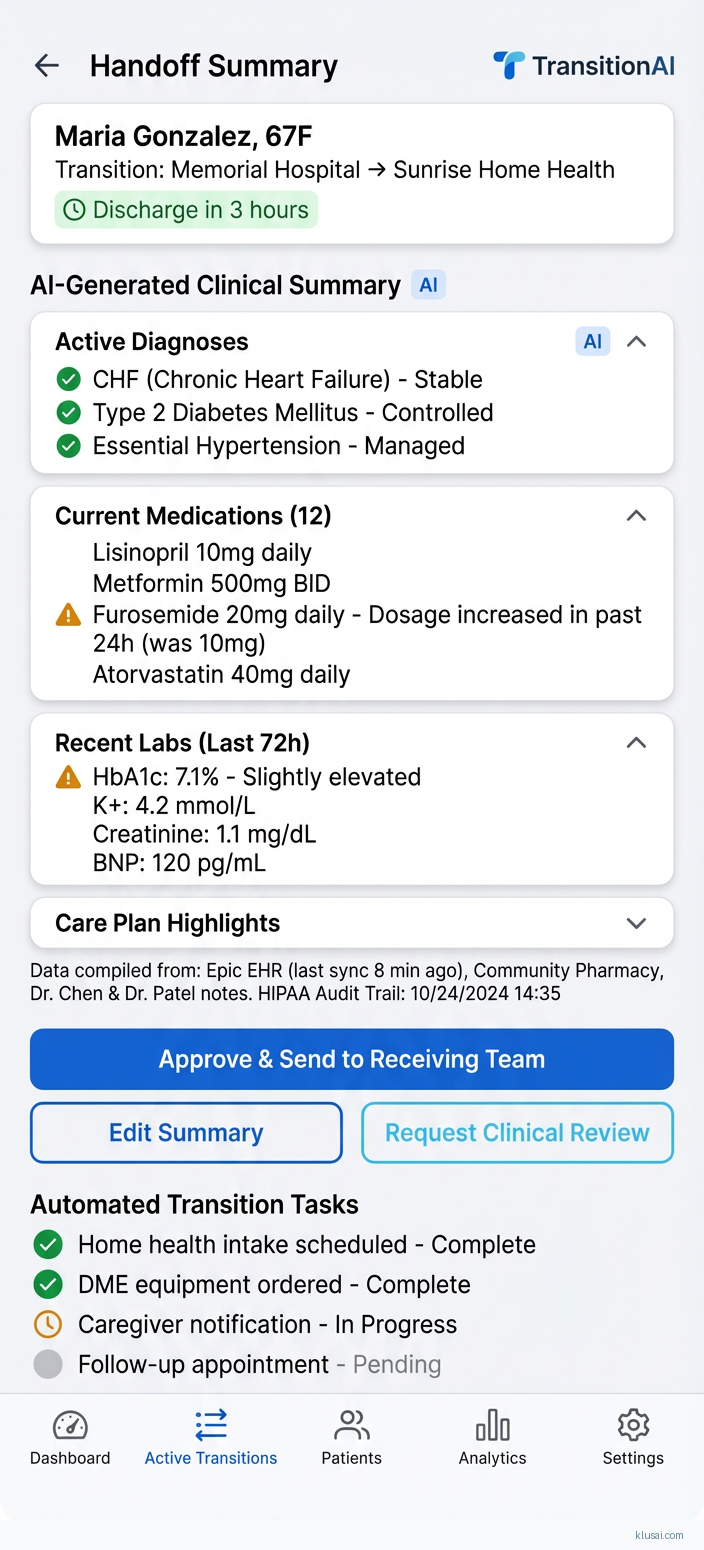
Intelligent clinical summary generation that automatically compiles relevant patient history, active medications, recent labs, and clinical context into receiving-team-ready documents with HIPAA audit trails
-
Real-time task orchestration that sequences and monitors critical transition activities—appointment scheduling, medication reconciliation verification, caregiver notifications—with escalation alerts for incomplete steps
-
Native EHR connectors (Epic, Cerner, Athenahealth) with bi-directional data sync and FHIR-compliant APIs, plus compliance-first architecture with encrypted data residency options for GDPR/HIPAA enforcement
Get the Full Implementation Guide
Unlock full details including architecture and implementation
Implementation Overview
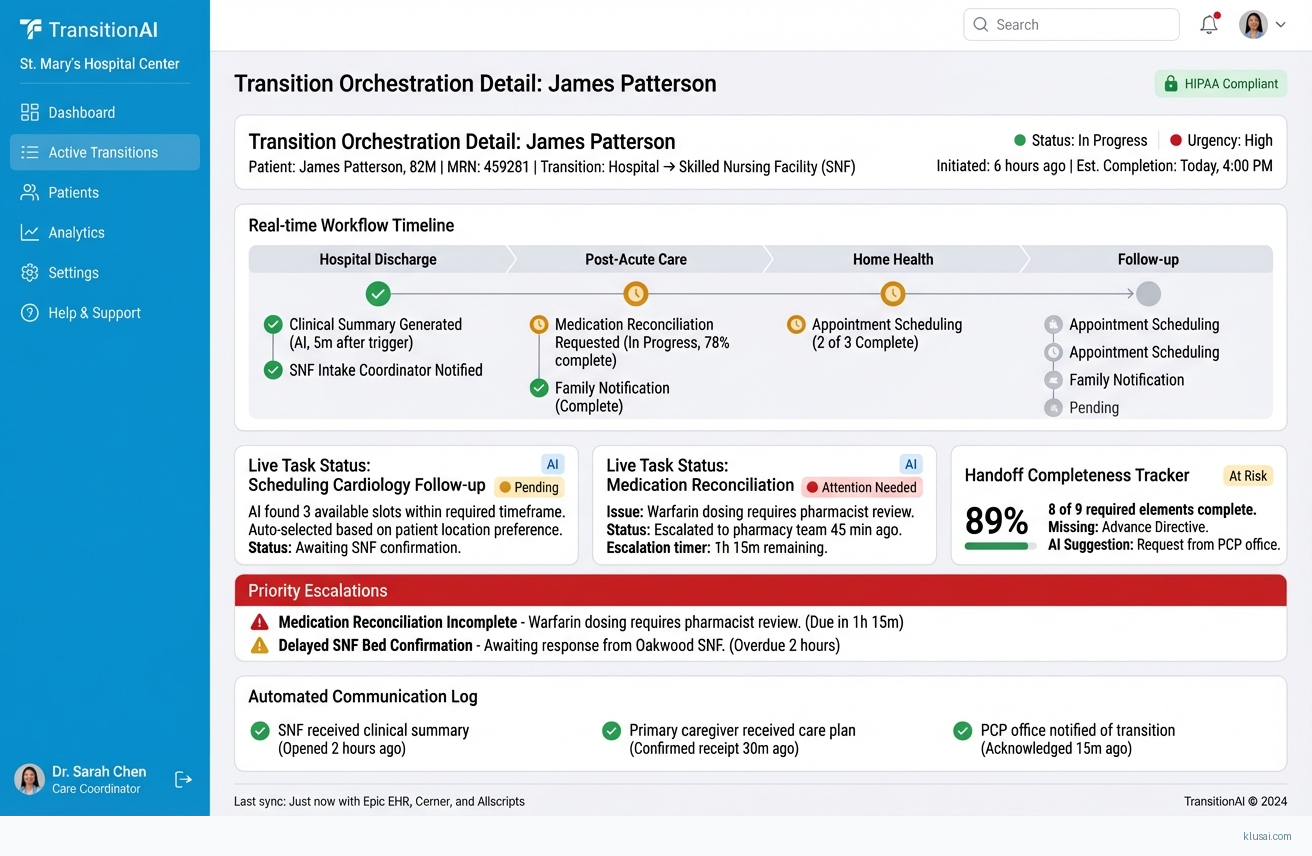
The Care Transition Orchestrator addresses a critical gap in healthcare delivery: the 30% of care transitions that experience communication failures between sending and receiving care teams[1]. Rather than adding another point solution to fragmented healthcare IT ecosystems, this architecture creates an intelligent orchestration layer that detects transition events, automates handoff documentation, and coordinates downstream tasks across organizational boundaries.
The architectural approach centers on three principles: event-driven automation (eliminating manual workflow initiation), compliance-first design (HIPAA/GDPR enforcement at every layer), and pragmatic integration (working with existing EHR investments rather than replacing them). The system monitors ADT feeds, discharge orders, and referral submissions to automatically trigger standardized handoff processes. It then orchestrates parallel workstreams—appointment scheduling, medication reconciliation verification, caregiver notification—while maintaining complete audit trails for regulatory compliance.
Expected outcomes include 25-40% reduction in administrative time per transition (to be validated during pilot), measurable improvement in handoff completeness scores, and reduced care coordinator burden on manual tracking and status verification[3]. The phased implementation approach prioritizes early wins through single-facility deployment before expanding to complex cross-facility scenarios, allowing organizations to validate ROI assumptions before full commitment.
UI Mockups
System Architecture
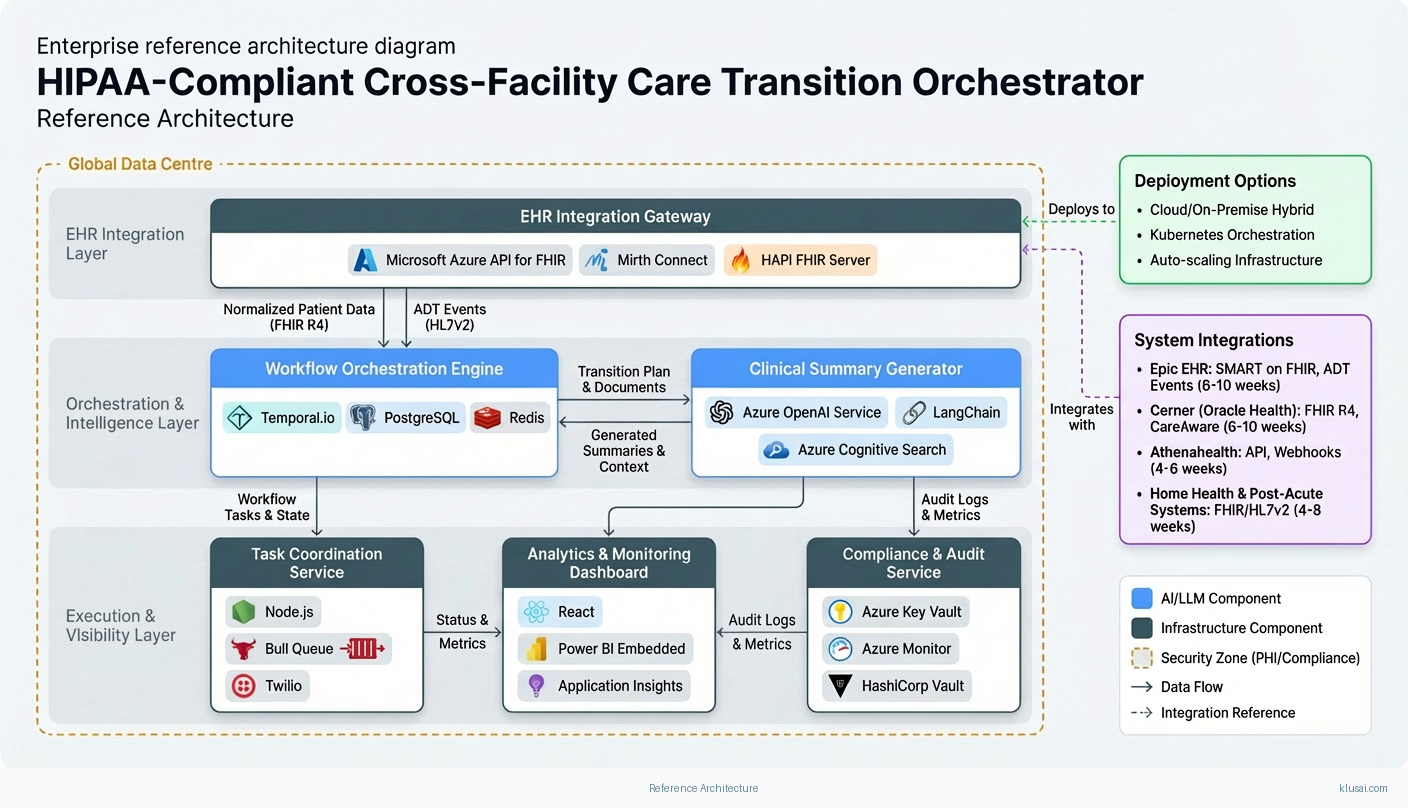
The architecture follows a layered design pattern with clear separation between integration, orchestration, intelligence, and presentation concerns. At the foundation, the Integration Layer provides bi-directional connectivity to EHR systems through FHIR R4 APIs and legacy HL7v2 interfaces, normalizing disparate data formats into a canonical transition model. This layer implements the HIPAA minimum necessary standard by extracting only clinically relevant data elements for each transition type.
The Orchestration Engine sits at the core, implementing a state machine that manages transition workflows from detection through completion. When a qualifying event occurs (discharge order, referral submission, department transfer), the engine instantiates a workflow instance, determines required tasks based on transition type and receiving facility capabilities, and monitors progress against configurable SLAs. The engine supports both automated task execution (API-driven scheduling, notification dispatch) and human-in-the-loop steps (clinical review, authorization) with appropriate escalation paths.
The Intelligence Layer provides two key capabilities: clinical summary generation and predictive risk scoring. Summary generation uses retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) to compile relevant patient history, active medications, recent labs, and clinical context into receiving-team-ready documents. The system retrieves structured data from the EHR integration layer and applies clinical templates to ensure completeness while maintaining appropriate detail levels for different receiving care settings. Risk scoring identifies transitions with elevated failure probability based on patient complexity, receiving facility characteristics, and historical patterns.
The Compliance Layer enforces HIPAA and GDPR requirements through encryption at rest and in transit, role-based access control, comprehensive audit logging, and configurable data residency. All PHI access is logged with user identity, timestamp, data elements accessed, and business justification. The layer supports Business Associate Agreement (BAA) requirements through contractual controls and technical enforcement of data handling policies.
Key Components
| Component | Purpose | Technologies |
|---|---|---|
| EHR Integration Gateway | Provides normalized connectivity to Epic, Cerner, Athenahealth, and other EHR systems through FHIR R4 and HL7v2 interfaces with bi-directional sync capabilities | Microsoft Azure API for FHIR Mirth Connect HAPI FHIR Server |
| Workflow Orchestration Engine | Manages transition state machines, coordinates parallel task execution, enforces SLAs, and handles escalation logic for incomplete steps | Temporal.io PostgreSQL Redis |
| Clinical Summary Generator | Automatically compiles patient history, medications, labs, and clinical context into standardized handoff documents tailored to receiving care settings | Azure OpenAI Service LangChain Azure Cognitive Search |
| Task Coordination Service | Orchestrates downstream activities including appointment scheduling, medication reconciliation verification, and caregiver notifications with real-time status tracking | Node.js Bull Queue Twilio |
| Compliance & Audit Service | Enforces HIPAA/GDPR requirements through access control, encryption, audit logging, and data residency controls with BAA support | Azure Key Vault Azure Monitor HashiCorp Vault |
| Analytics & Monitoring Dashboard | Provides operational visibility into transition status, completion rates, SLA compliance, and system health with role-based views for clinical and administrative users | React Power BI Embedded Application Insights |
Technology Stack
Implementation Phases
Foundation & Single-Facility Pilot
Establish secure infrastructure with HIPAA-compliant architecture and BAA execution
- • Establish secure infrastructure with HIPAA-compliant architecture and BAA execution
- • Implement EHR integration with primary pilot facility (single EHR system)
- • Deploy core workflow engine with 2-3 high-volume transition types (discharge to home, discharge to SNF)
- Production-ready infrastructure with security controls validated through penetration testing
- Bi-directional EHR integration with ADT feed processing and clinical data retrieval
- Functional workflow orchestration for pilot transition types with manual clinical review step
Intelligence Layer & Workflow Expansion
Deploy clinical summary generation with RAG-based document compilation
- • Deploy clinical summary generation with RAG-based document compilation
- • Expand workflow coverage to additional transition types (specialist referrals, home health)
- • Implement automated task coordination for appointment scheduling and caregiver notifications
- Clinical summary generator producing receiving-team-ready documents with 85%+ completeness scores
- Expanded workflow library covering 80% of facility transition volume
- Automated scheduling integration with at least one downstream system (home health, specialist practice)
Multi-Facility Expansion & Cross-Organization Workflows
Extend platform to 2-3 additional facilities with different EHR configurations
- • Extend platform to 2-3 additional facilities with different EHR configurations
- • Implement cross-facility transition workflows with appropriate data sharing controls
- • Deploy predictive risk scoring to prioritize high-risk transitions for proactive intervention
- Multi-facility deployment with centralized monitoring and facility-specific workflow configurations
- Cross-organization transition support with consent management and data sharing agreements
- Risk stratification model identifying transitions with elevated failure probability
Optimization & Scale
Optimize workflows based on pilot data and user feedback
- • Optimize workflows based on pilot data and user feedback
- • Implement advanced analytics for transition outcome tracking and continuous improvement
- • Prepare platform for enterprise-wide rollout with operational playbooks
- Refined workflow configurations with documented best practices per transition type
- Analytics dashboard with transition outcome metrics and benchmarking capabilities
- Enterprise deployment playbook including training materials, support procedures, and scaling guidelines
Key Technical Decisions
Should we build custom EHR integrations or use a healthcare integration platform?
Healthcare interoperability is complex and evolving rapidly with regulatory mandates (21st Century Cures Act, CMS Interoperability Rules) driving FHIR adoption. A platform approach provides pre-built connectors, handles message transformation, and adapts to changing standards without custom development. Mirth Connect has broad healthcare adoption and strong community support for edge cases.
- Reduced integration development time (weeks vs. months per EHR)
- Built-in support for healthcare-specific protocols and message formats
- Additional platform licensing and operational complexity
- Less control over integration behavior for unusual requirements
How should we handle clinical summary generation—rules-based templates or LLM-powered generation?
Pure template approaches miss important clinical context and produce documents that feel mechanical to receiving clinicians. Pure LLM approaches risk hallucination and inconsistency in safety-critical content. The hybrid approach ensures accuracy for structured elements while providing readable, contextually appropriate narratives. All LLM-generated content should be clearly marked and subject to clinical review for high-risk transitions.
- Maintains accuracy for critical structured data (medications, allergies)
- Produces more readable, contextually appropriate documents
- Requires ongoing monitoring for LLM output quality and drift
- Higher computational cost than pure template approach
Should workflow orchestration use a dedicated workflow engine or custom state machine implementation?
Care transitions involve long-running workflows (hours to days), parallel task execution, human-in-the-loop steps, and complex retry/escalation logic. Temporal provides durable execution guarantees, built-in visibility, and proven patterns for these requirements. Custom implementations typically underestimate edge cases around failure handling, timeout management, and workflow versioning.
- Durable execution with automatic retry and failure recovery
- Built-in workflow visibility and debugging tools
- Additional infrastructure component to operate and maintain
- Learning curve for development team unfamiliar with workflow patterns
How should we approach multi-tenant data isolation for multi-facility deployments?
Full physical isolation (separate databases per tenant) provides maximum security but creates operational complexity and cost that scales poorly. Shared-everything approaches create compliance risk and complicate data residency requirements. Schema-level isolation with tenant-specific encryption keys balances security, compliance, and operational efficiency while supporting facility-specific data residency where required.
- Supports facility-specific compliance requirements (data residency, retention)
- Operational efficiency of shared infrastructure
- More complex application logic for tenant context management
- Requires careful attention to cross-tenant data leakage prevention
Integration Patterns
| System | Approach | Complexity | Timeline |
|---|---|---|---|
| Epic EHR | SMART on FHIR integration using Epic's App Orchard certified APIs for patient data access, ADT event subscriptions via Epic's Event Notifications, and CDS Hooks for workflow integration points. Fallback to Bridges interface engine for facilities on older Epic versions. | high | 6-10 weeks |
| Cerner (Oracle Health) | FHIR R4 APIs through Cerner's Ignite platform for clinical data access; CareAware integration for real-time ADT events; Millennium Objects for facilities requiring deeper integration. PowerChart integration for clinical workflow embedding. | high | 6-10 weeks |
| Athenahealth | Athenahealth API (More Disruption Please platform) for clinical data and scheduling; webhook subscriptions for real-time event notifications; athenaCollector integration for practice management workflows. | medium | 4-6 weeks |
| Home Health & Post-Acute Systems | FHIR-based integration where available (Homecare Homebase, MatrixCare); HL7v2 ADT/scheduling messages for legacy systems; secure document exchange via Direct messaging protocol as fallback. | medium | 4-8 weeks per system |
ROI Framework
The ROI model quantifies value from administrative time savings through automated workflow initiation and task tracking, plus the downstream impact of improved transition completeness on readmission rates. Conservative efficiency assumptions should be validated during pilot phase before enterprise-wide projections.
Key Variables
Example Calculation
Build vs. Buy Analysis
Internal Build Effort
Internal build requires 18-24 months with a dedicated team of 8-10 engineers including healthcare interoperability specialists (rare skillset), workflow developers, ML engineers, and compliance specialists. Key challenges include EHR integration expertise (typically 2-3 years to develop institutional knowledge with each major EHR vendor), HIPAA compliance infrastructure, and ongoing maintenance burden as EHR APIs evolve. Estimated fully-loaded cost: $1.8M - $2.8M for initial build plus $500K - $800K annual maintenance and enhancement.
Market Alternatives
Innovaccer Care Management
$200K - $500K annually depending on patient volume and modulesEnterprise healthcare data platform with care management modules; strong data unification capabilities but transition orchestration is one module among many rather than primary focus[8]
- • Comprehensive healthcare data platform with proven EHR integrations
- • Strong analytics and population health capabilities
- • Transition orchestration requires significant configuration
- • Enterprise sales cycle and implementation timeline (12+ months typical)
Collective Medical (PointClickCare)
$150K - $350K annuallySpecializes in care collaboration and real-time notifications; strong network effects in post-acute transitions but less comprehensive for acute care workflow orchestration
- • Purpose-built for care transitions and collaboration
- • Broad provider network participation creates notification value
- • Notification-focused rather than full workflow orchestration
- • Less flexibility for custom workflow requirements
Qventus
$300K - $600K annuallyAI-powered operations platform focused on capacity management and discharge optimization; complementary but different focus than cross-facility transition orchestration[6]
- • Strong AI/ML capabilities for prediction and optimization
- • Proven results in discharge timing and capacity management
- • Primary focus is inpatient operations rather than cross-facility transitions
- • May require integration with separate transition management solution
Our Positioning
KlusAI is the right choice when organizations need a tailored solution that addresses their specific transition workflows, EHR landscape, and compliance requirements. Our approach assembles the right expertise—healthcare interoperability specialists, workflow architects, and clinical informatics professionals—for each engagement rather than forcing a one-size-fits-all platform. This is particularly valuable for health systems with complex multi-facility environments, non-standard EHR configurations, or specific regulatory requirements that commercial platforms don't address out of the box.
Team Composition
KlusAI assembles specialized teams tailored to each engagement, drawing from our network of healthcare technology professionals. The composition below represents a typical team structure for a care transition orchestration implementation, adjusted based on client EHR landscape, integration complexity, and organizational change management needs.
| Role | FTE | Focus |
|---|---|---|
| Technical Lead / Solutions Architect | 1.0 | Overall technical leadership, architecture decisions, EHR integration strategy, and client stakeholder management |
| Integration Engineer | 1.5 | EHR connectivity, data transformation, API development, and integration testing |
| Workflow Developer | 1.0 | Workflow orchestration implementation, business rules configuration, and task coordination logic |
| ML/AI Engineer | 0.5 | Clinical summary generation, RAG implementation, and predictive model development |
| Clinical Informaticist | 0.5 | Clinical workflow validation, summary template design, and end-user training |
Supporting Evidence
Performance Targets
80% of transition volume processed through automated workflows by end of Phase 3
25-40% reduction in care coordinator time per transition
90%+ of transitions meeting defined completeness criteria
>90% of generated summaries accepted without significant modification
Team Qualifications
- KlusAI's network includes professionals with healthcare interoperability experience across major EHR platforms including Epic, Cerner, and Athenahealth
- Our teams are assembled with specific expertise in HIPAA-compliant system design, including professionals experienced with healthcare cloud deployments and security frameworks
- We bring together technical specialists and clinical informatics professionals who understand both the technology and the care delivery workflows that drive adoption success
Source Citations
30% of care transitions have communication gaps
"30% of care transitions have communication gaps"exact
Care teams rely on manual processes—phone calls, faxes, spreadsheets, and disconnected EHRs
directionalAdministrative staff spend hours tracking referral status and verifying task completion
directionalCurrent care coordination platforms offer workflows and task management but lack end-to-end automation specifically designed for the care transition moment
directionalReady to discuss?
Let's talk about how this could work for your organization.
Schedule a Consultation
Pick a date that works for you
Times shown in your local timezone ()
Prefer email? Contact us directly
Almost there!
at
Your details
at
You're all set!
Check your email for confirmation and calendar invite.
Your booking is confirmed! Our team will reach out to confirm the details.
Your consultation
· min
( team time)
Quick Overview
- Technology
- Process Automation
- Complexity
- high
- Timeline
- 5-7 months
- Industry
- Healthcare