The Problem
Global NOC teams in managed services face significant alert fatigue from overwhelming volumes of infrastructure alerts, with most being noise from cascading failures or maintenance windows. This desensitizes analysts, slows responses to critical incidents, and contributes to operational inefficiencies and staff burnout.
The challenge intensifies for follow-the-sun operations across global delivery centers, where shift handoffs must capture only actionable insights amid thousands of daily alerts, while adhering to ITIL incident management practices and ISO 20000 service management requirements for documented processes and audit trails.
Current solutions offer partial relief through AI triage, suppressing up to 54% of false positives in some cases, but lack deep integration with ITIL change correlation, ISO 20000-compliant logging, and LLM-driven root cause synthesis for concise, compliant shift handoffs—leaving teams to manually filter and document for regulatory adherence.
Our Approach
Key elements of this implementation
-
LLM-powered semantic alert correlation and root cause inference, generating ITIL-aligned executive summaries and ISO 20000-auditable shift handoffs integrated with ServiceNow, Splunk, and Datadog
-
Comprehensive compliance controls: full audit trails for every suppression/action with tamper-proof logging, ITIL change/incident linkage, ISO 20000 data governance, and global data residency options
-
Human-in-the-loop validation for low-confidence (under 85%) outputs with explainable AI reasoning, plus phased 12-week rollout with 60-day parallel running and NOC retraining
-
Risk mitigation via pilot testing on 10% alert volume, change champions program, and ROI tracking targeting 20-40% MTTR reduction based on industry AI benchmarks
Get the Full Implementation Guide
Unlock full details including architecture and implementation
Implementation Overview
This implementation delivers an intelligent alert digest system that addresses the core challenge facing global managed services NOCs: overwhelming alert volumes where most are noise from cascading failures or maintenance windows[1][6]. The architecture leverages LLM-powered semantic correlation to reduce false positives—industry benchmarks demonstrate up to 54% suppression with 95.1% detection rate[1]—while generating ITIL-aligned executive summaries for compliant shift handoffs.
The solution integrates with existing monitoring infrastructure (ServiceNow, Splunk, Datadog) through a normalized ingestion layer that addresses alert schema heterogeneity across tools. A critical architectural decision is the multi-tenant design supporting MSPs serving multiple clients with isolated configuration and data residency controls. The LLM layer includes explicit hallucination mitigation through confidence scoring, source attribution, and human-in-the-loop validation for outputs below 85% confidence—essential for root cause hypothesis generation in critical NOC environments.
The 24-week phased rollout includes a 60-day parallel running period where both legacy and new systems operate simultaneously, enabling thorough validation before cutover. This extended timeline accommodates global follow-the-sun operations across multiple delivery centers, with region-specific training schedules and change champion programs to ensure adoption across all shifts.
UI Mockups
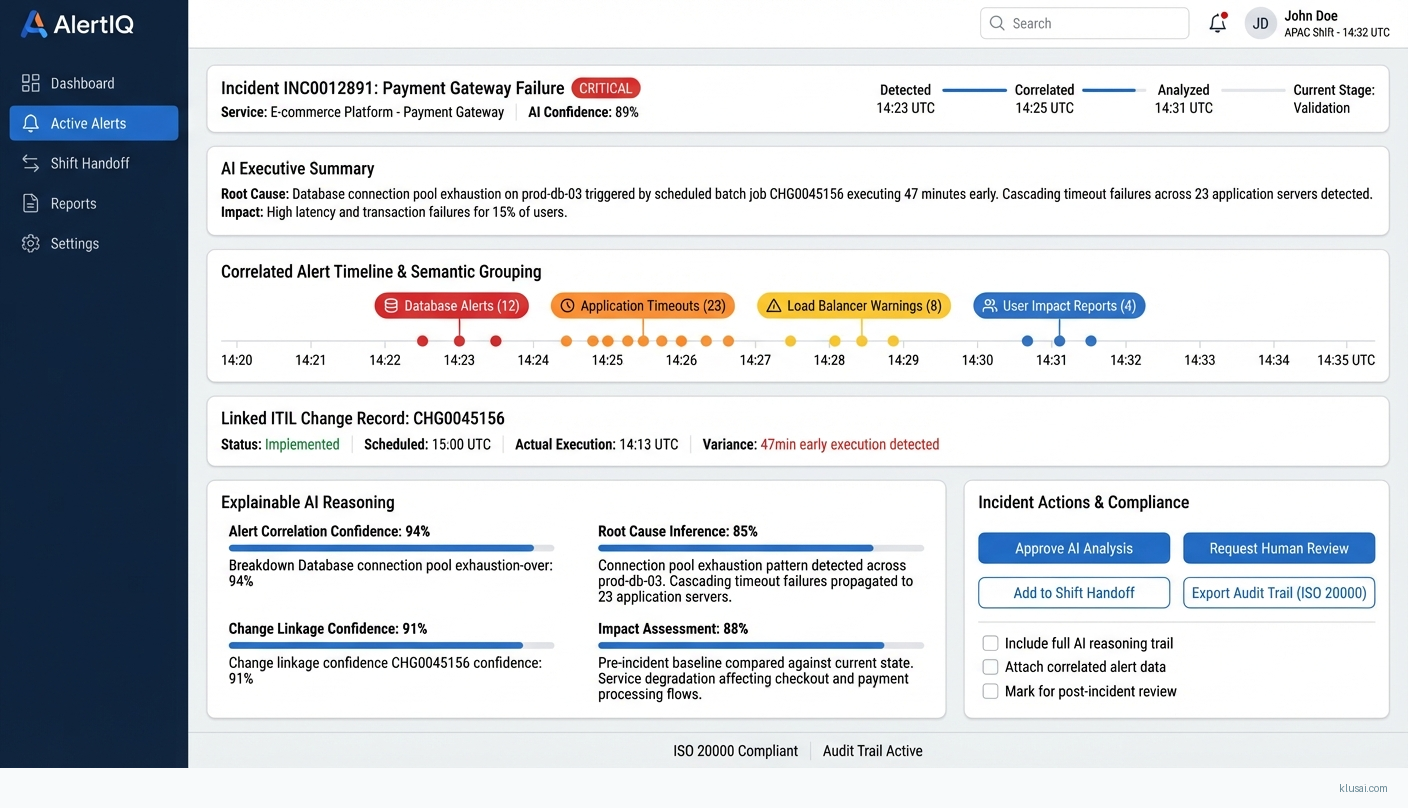
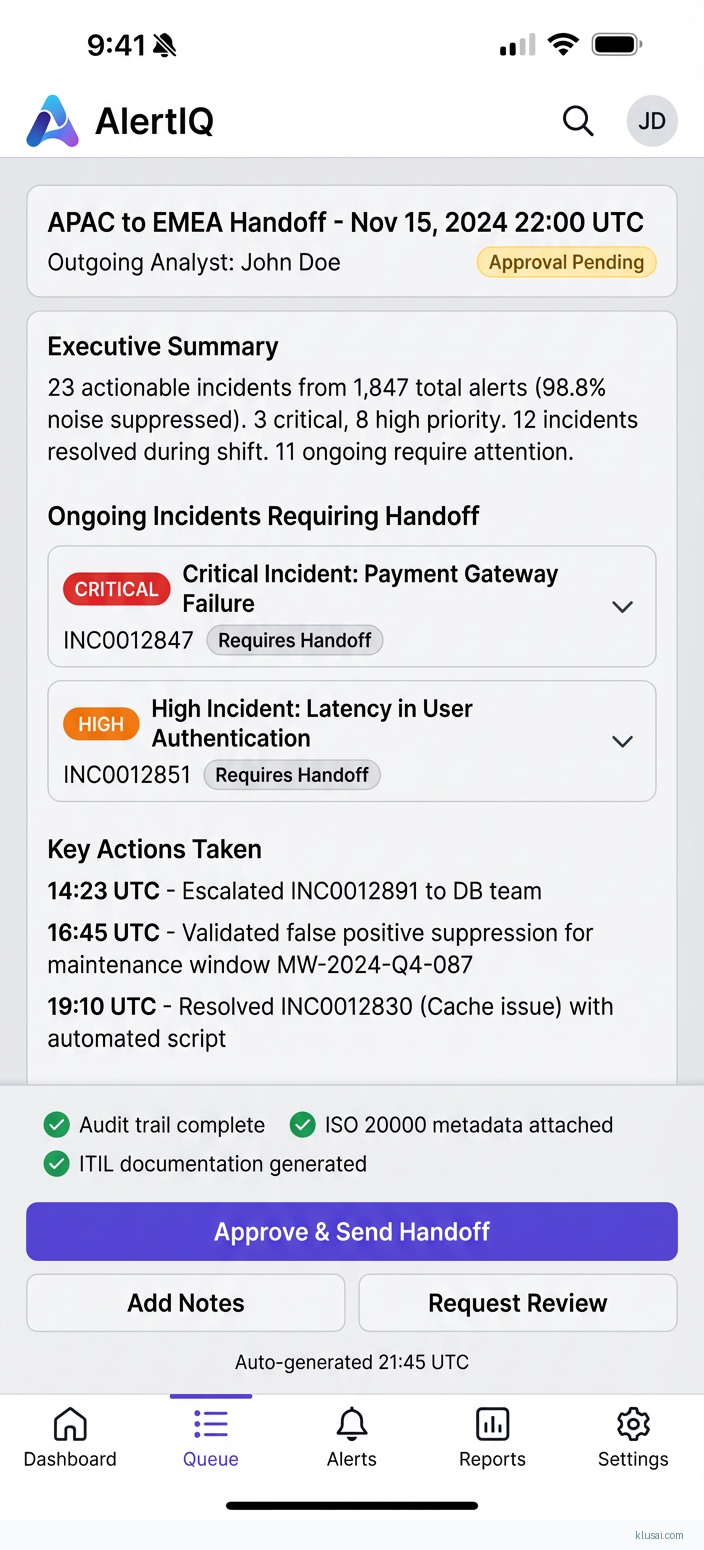
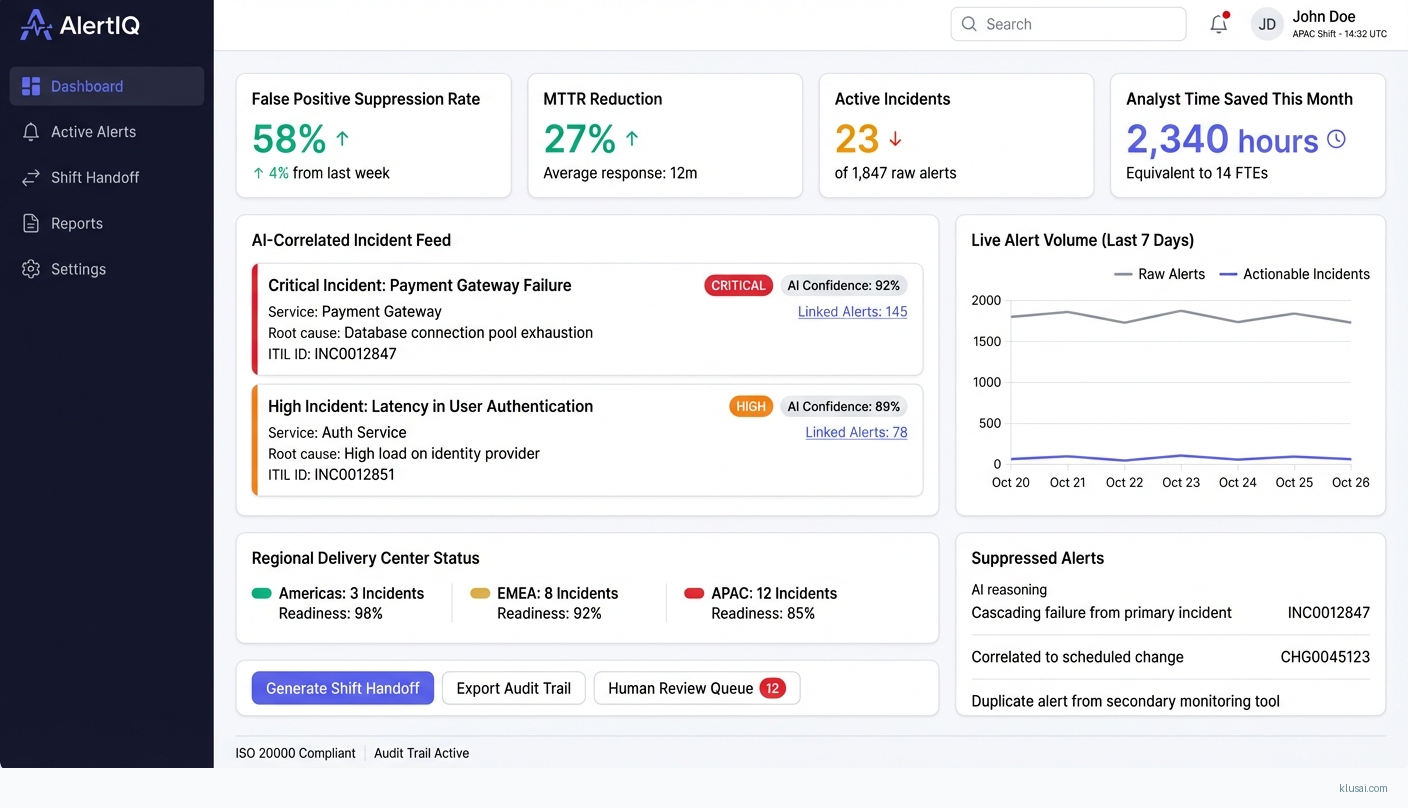
System Architecture
The architecture follows a layered approach with clear separation between ingestion, processing, and presentation tiers. The ingestion layer implements a schema normalization engine that transforms heterogeneous alert formats from multiple monitoring tools into a canonical alert model—addressing the significant complexity of alert schema variation across Datadog, Splunk, ServiceNow, and custom monitoring solutions.
The core processing layer combines traditional rule-based correlation with LLM-powered semantic analysis. Alerts are first enriched with CMDB context through a dedicated enrichment service that includes data quality validation—acknowledging that CMDB accuracy varies significantly across organizations. The LLM correlation engine uses embedding-based similarity detection combined with prompt-engineered root cause inference, with explicit hallucination controls including confidence scoring, source attribution, and reasoning chain transparency.
The compliance layer maintains tamper-proof audit trails for every suppression decision, linking to ITIL change records and incident tickets. ISO 20000-compliant logging captures the full decision chain with immutable storage. Multi-tenancy is implemented at the data layer with tenant-specific encryption keys and configurable data residency to meet regional requirements.
The presentation layer generates shift handoff digests tailored to each NOC's requirements, with executive summaries for management and detailed technical breakdowns for analysts. Human-in-the-loop interfaces surface low-confidence outputs for validation, with feedback loops that improve model accuracy over time.
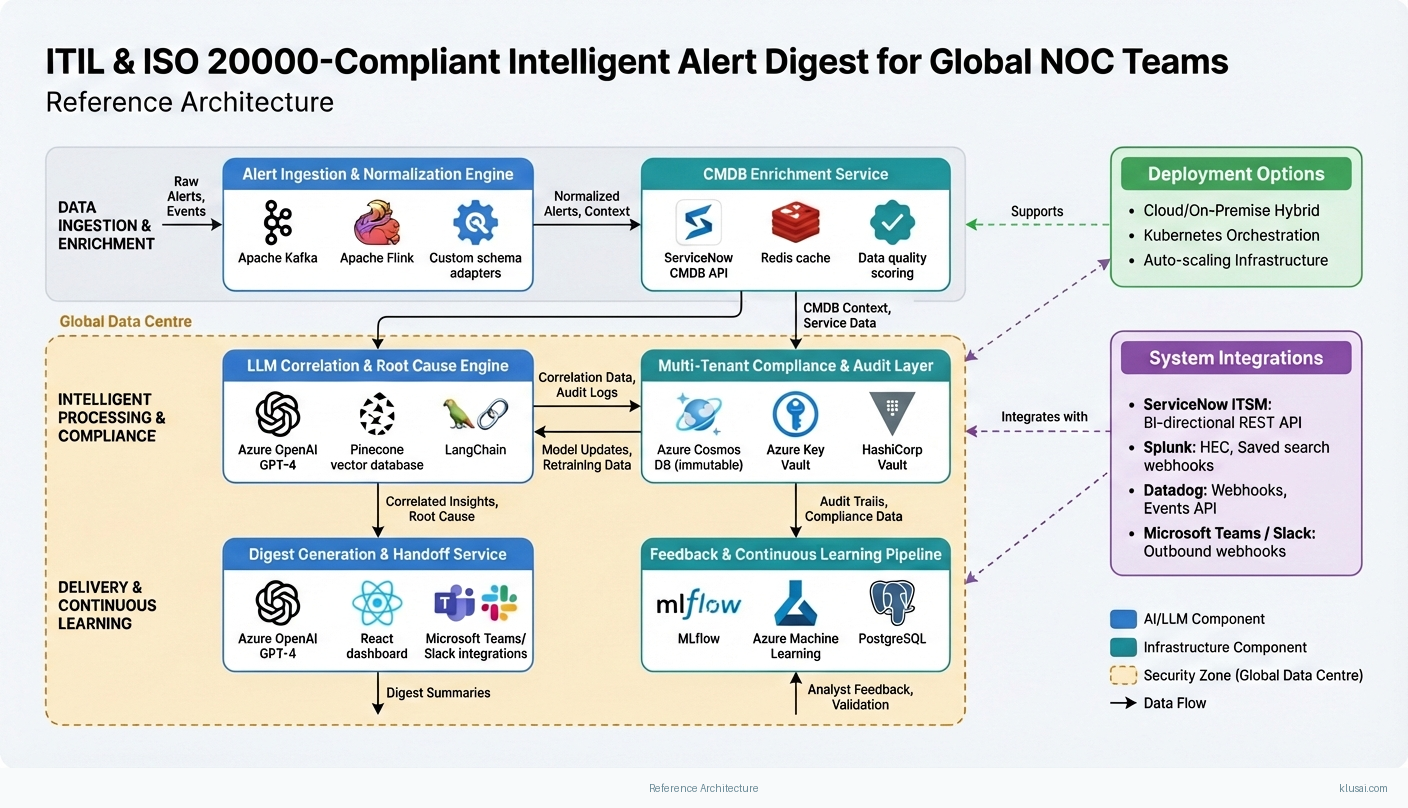
Key Components
| Component | Purpose | Technologies |
|---|---|---|
| Alert Ingestion & Normalization Engine | Ingest alerts from heterogeneous monitoring tools and normalize to canonical schema, handling format variations and deduplication | Apache Kafka Apache Flink Custom schema adapters |
| CMDB Enrichment Service | Enrich alerts with configuration item context, service dependencies, and ownership data with quality validation | ServiceNow CMDB API Redis cache Data quality scoring |
| LLM Correlation & Root Cause Engine | Semantic alert correlation, root cause hypothesis generation, and confidence-scored output with hallucination mitigation | Azure OpenAI GPT-4 Pinecone vector database LangChain |
| Multi-Tenant Compliance & Audit Layer | Maintain ISO 20000-compliant audit trails, ITIL change correlation, and tenant-isolated data governance | Azure Cosmos DB (immutable) Azure Key Vault HashiCorp Vault |
| Digest Generation & Handoff Service | Generate ITIL-aligned shift handoff summaries with configurable detail levels and multi-language support | Azure OpenAI GPT-4 React dashboard Microsoft Teams/Slack integrations |
| Feedback & Continuous Learning Pipeline | Capture analyst feedback on correlation accuracy and digest quality to improve model performance | MLflow Azure Machine Learning PostgreSQL |
Technology Stack

Implementation Phases
Foundation & Integration (Weeks 1-6)
Deploy core infrastructure with multi-tenant architecture and regional data residency configuration
- • Deploy core infrastructure with multi-tenant architecture and regional data residency configuration
- • Implement alert ingestion adapters for primary monitoring tools (ServiceNow, Splunk, Datadog)
- • Establish CMDB enrichment pipeline with data quality scoring and validation
- Production-ready ingestion pipeline processing 10% of alert volume in shadow mode
- Schema normalization adapters for 3 primary monitoring tools with documented mapping
- CMDB enrichment service with quality scoring dashboard and exception handling
LLM Correlation & Compliance (Weeks 7-12)
Deploy LLM correlation engine with hallucination mitigation controls and confidence scoring
- • Deploy LLM correlation engine with hallucination mitigation controls and confidence scoring
- • Implement ITIL change correlation and ISO 20000-compliant audit trail
- • Establish human-in-the-loop validation workflow for low-confidence outputs
- LLM correlation engine processing 10% alert volume with >90% analyst agreement on correlation quality
- Immutable audit trail capturing all suppression decisions with ITIL change linkage
- Human validation interface with <5 minute average review time per flagged output
Parallel Running & Validation (Weeks 13-20)
Execute 60-day parallel running with legacy and new systems operating simultaneously
- • Execute 60-day parallel running with legacy and new systems operating simultaneously
- • Train all NOC shifts across global delivery centers with region-specific scheduling
- • Validate correlation accuracy and digest quality against analyst feedback
- Parallel running report demonstrating >50% false positive suppression with <2% missed genuine incidents
- 80% NOC analyst certification across all shifts (adjusted for global operations complexity)
- Documented feedback-driven improvements to correlation prompts and confidence thresholds
Production Cutover & Optimization (Weeks 21-24)
Complete production cutover with legacy system decommissioning plan
- • Complete production cutover with legacy system decommissioning plan
- • Establish continuous improvement processes and feedback loops
- • Document operational runbooks and escalation procedures
- Production system handling 100% alert volume with defined SLOs met
- Operational runbooks for all failure scenarios and escalation paths
- ROI validation report with actual vs. projected metrics
Key Technical Decisions
How should LLM hallucination risks be mitigated in root cause hypothesis generation?
Root cause hypotheses in NOC environments directly influence incident response decisions. False hypotheses could misdirect troubleshooting efforts, extending MTTR and eroding analyst trust. The 85% confidence threshold balances automation benefits against accuracy requirements—industry experience suggests this threshold captures most uncertain outputs while maintaining meaningful automation rates.
- Maintains analyst trust through transparent reasoning and conservative automation
- Source attribution creates audit trail for compliance and continuous improvement
- Higher human-in-the-loop volume initially (expect 15-20% of outputs) until model tuning matures
- Requires additional analyst training on validation interface and feedback provision
Should alert embeddings use a general-purpose model or domain-fine-tuned model?
Fine-tuning requires substantial labeled data (10K+ examples) which won't be available at launch. General-purpose embeddings with well-engineered prompts achieve 80-90% of fine-tuned performance for correlation tasks. The feedback loop architecture enables data collection for future fine-tuning if accuracy targets aren't met.
- Faster time to value—no data collection delay before deployment
- Lower initial cost and complexity
- May require more aggressive confidence thresholds initially
- Domain-specific terminology (vendor-specific error codes) may correlate less accurately
How should multi-tenancy be implemented for MSP environments?
MSPs serving multiple clients require strict data isolation for compliance and contractual obligations. Per-tenant encryption keys enable client-specific key rotation and revocation. Logical separation in Kafka (tenant-specific partitions) and Cosmos DB (partition keys) provides isolation without the operational overhead of fully separate deployments.
- Meets enterprise security and compliance requirements for data isolation
- Enables per-client configuration of correlation rules and digest formats
- Adds 15-20% infrastructure overhead compared to single-tenant deployment
- Cross-tenant learning (e.g., correlation patterns) requires explicit data sharing agreements
What approach should be used for alert schema normalization across heterogeneous monitoring tools?
Alert schema heterogeneity is a primary implementation risk—Datadog, Splunk, and ServiceNow use fundamentally different data models. A canonical model with adapters provides flexibility while maintaining processing consistency. Quality scoring enables the correlation engine to weight normalized fields by confidence.
- Decouples correlation logic from source-specific schemas
- New monitoring tool integration requires only adapter development, not core changes
- Adapter development requires 2-3 weeks per tool with deep schema analysis
- Some source-specific context may be lost in normalization
Integration Patterns
| System | Approach | Complexity | Timeline |
|---|---|---|---|
| ServiceNow ITSM | Bi-directional REST API integration for incident creation, change window retrieval, and CMDB enrichment. Webhook-based event subscription for real-time change notifications. | high | 4-6 weeks |
| Splunk | Splunk HTTP Event Collector (HEC) for alert ingestion. Saved search webhook triggers for real-time alert forwarding. REST API for historical alert retrieval during initial training. | medium | 2-3 weeks |
| Datadog | Datadog Webhooks for real-time alert forwarding. Events API for enrichment data. Monitors API for alert configuration synchronization. | medium | 2-3 weeks |
| Microsoft Teams / Slack | Outbound webhooks for digest delivery. Interactive message components for human-in-the-loop validation. Bot framework for on-demand status queries. | low | 1-2 weeks |
ROI Framework
ROI is driven by analyst time savings from reduced manual triage, faster incident resolution through accurate correlation, and reduced escalation costs. Industry benchmarks demonstrate AI-driven alert management can suppress 54% of false positives while maintaining 95.1% detection rate[1], directly translating to operational efficiency gains.
Key Variables
Example Calculation
Build vs. Buy Analysis
Internal Build Effort
Internal build requires 14-20 months with a team of 8-10 engineers (ML engineers, platform developers, integration specialists, compliance specialists) plus ongoing maintenance. Key challenges include LLM prompt engineering for NOC domain, ITIL/ISO 20000 compliance implementation, multi-tenant architecture, and alert schema normalization across heterogeneous monitoring tools. Estimated internal cost: £900K-1.4M first year, £350-450K annually thereafter.
Market Alternatives
BigPanda AIOps
£150-300K annually depending on alert volumeEnterprise AIOps platform with strong alert correlation and noise reduction; established market leader with broad enterprise deployments
- • Mature platform with proven enterprise deployments and established support
- • Strong out-of-box integrations with major monitoring tools
- • Dedicated customer success and 24x7 support
- • Limited customization of correlation logic for organization-specific patterns
- • ISO 20000 audit trail customization requires professional services engagement
- • LLM-powered summarization capabilities still emerging; primarily rule-based correlation
Moogsoft (Dell)
£100-250K annuallyAI-driven incident management with focus on noise reduction and situation awareness
- • Strong noise reduction algorithms with proven effectiveness
- • Good ServiceNow integration out-of-box
- • Flexible deployment options (cloud/on-premises)
- • Recent Dell acquisition creates product roadmap uncertainty
- • Less focus on compliance and audit trail requirements
- • Regional data residency options limited compared to custom deployment
PagerDuty AIOps
£80-200K annuallyIncident response platform with AI-powered alert grouping and noise reduction
- • Excellent incident response workflow and mobile experience
- • Broad integration ecosystem
- • Strong on-call management capabilities
- • AIOps features less mature than core incident management
- • Limited ITIL process integration depth
- • Summarization and root cause inference capabilities still developing
Our Positioning
KlusAI's approach is ideal for organizations requiring deep customization of correlation logic, specific ITIL/ISO 20000 compliance controls with audit trail customization, or integration with proprietary monitoring systems not supported by off-the-shelf platforms. Commercial platforms excel for standard deployments but struggle with organization-specific correlation patterns, custom compliance requirements, and regional data residency needs. Our assembled teams combine LLM implementation expertise with managed services domain knowledge, enabling rapid iteration on prompts and models tailored to your specific infrastructure, processes, and compliance obligations.
Team Composition
KlusAI assembles specialized teams tailored to each engagement, combining LLM implementation expertise with managed services domain knowledge. The team composition scales based on deployment complexity, number of monitoring tool integrations, and global rollout requirements.
| Role | FTE | Focus |
|---|---|---|
| Solutions Architect | 0.5 | Overall architecture design, integration patterns, compliance framework alignment, client stakeholder engagement |
| ML/LLM Engineer | 1.5 | LLM prompt engineering, correlation model development, embedding optimization, hallucination mitigation, accuracy tuning |
| Platform Engineer | 1.0 | Infrastructure deployment, Kafka/Flink pipeline development, multi-tenant architecture, observability implementation |
| Integration Specialist | 1.0 | Monitoring tool adapters, ServiceNow integration, CMDB connectivity, schema normalization |
| Change Management Lead | 0.5 | NOC analyst training, change champion program, adoption tracking, resistance management |
Supporting Evidence
Performance Targets
50-60%
20-30%
2,000-3,000 hours/month
<15% of outputs requiring validation
Team Qualifications
- KlusAI's network includes professionals with extensive experience in enterprise AIOps implementations and managed services operations
- Our teams are assembled with specific expertise in LLM implementation, ITIL/ISO 20000 compliance frameworks, and global NOC operations
- We bring together technical specialists in alert correlation, ServiceNow integration, and change management tailored to each engagement's requirements
Source Citations
overwhelming volumes of infrastructure alerts, with most being noise; suppressing up to 54% of false positives
"Run on real-world data, the TEQ model reduced response time to actionable incidents by 22.9% and suppressed 54% of false positives (with a 95.1% detection rate.)"exact
integrates monitoring tools and response workflows, ensuring a seamless flow from detection to resolution
"It integrates monitoring tools and response workflows, ensuring a seamless flow from detection to resolution. This is critical for all IT teams and MSPs in particular."exact
thousands of alerts received weekly, most being noise
"Alert fatigue is a critical challenge for DevOps teams, with thousands of alerts received weekly, most being noise that slows responses"exact
contributes to operational inefficiencies and staff burnout
directionalReady to discuss?
Let's talk about how this could work for your organization.
Schedule a Consultation
Pick a date that works for you
Times shown in your local timezone ()
Prefer email? Contact us directly
Almost there!
at
Your details
at
You're all set!
Check your email for confirmation and calendar invite.
Your booking is confirmed! Our team will reach out to confirm the details.
Your consultation
· min
( team time)
Quick Overview
- Technology
- Large Language Models
- Complexity
- high
- Timeline
- 4-6 months
- Industry
- Managed Services