The Problem
Managed service providers (MSPs) face significant margin pressure from rising labor costs and competitive pricing, with labor accounting for up to 80% of total costs. Manual end-to-end service request workflows—from ticket creation to resolution—exacerbate this, involving handoffs between L1/L2/L3 teams and follow-the-sun coordination across global centers.
These inefficiencies lead to prolonged mean time to resolution (MTTR) and high operational overhead, diverting resources from value-added services amid regulatory demands for ITIL incident management and ISO 20000 service quality controls[context]. Complex customer environments and hiring challenges further intensify margin erosion.
Existing tools provide partial automation like ticket triage or self-service but fail at full lifecycle orchestration, lacking integrated ITIL/ISO 20000 compliance, global handoff automation, and CMDB synchronization—resulting in persistent high service desk costs and incomplete resolutions.
Our Approach
Key elements of this implementation
-
Agentic AI orchestration with RAG-based runbook retrieval, ITIL-compliant state machines for auto-routing, and bi-directional CMDB sync for ServiceNow/Jira
-
ITIL/ISO 20000 controls: immutable audit trails for all transitions, automated SLA monitoring with compliance dashboards, and logging per ISO 20000 requirements
-
Data governance: multi-region residency, end-to-end encryption, role-based access; regulatory reporting for audit readiness
-
Phased rollout with 60-day parallel run, human-in-loop for escalations >80% confidence, change champions training, and executive sponsorship for 90% adoption
Get the Full Implementation Guide
Unlock full details including architecture and implementation
Implementation Overview
This implementation delivers end-to-end automation of service request lifecycles for managed service providers facing margin pressure from labor costs that can reach 80% of total operational expenditure[2]. The solution combines agentic AI orchestration with RAG-based runbook retrieval, ITIL-compliant state machines, and bi-directional CMDB synchronization to automate routine requests while maintaining full compliance with ITIL incident management and ISO 20000 service quality controls.
The architecture prioritizes production reliability over cutting-edge complexity, using proven patterns for classification, routing, and resolution automation. A confidence-based human-in-loop design ensures that requests below 80% classification confidence are escalated to human agents, balancing automation benefits against resolution quality. Multi-tenant isolation enables MSPs to serve diverse client environments with client-specific workflow customizations while maintaining centralized operational visibility.
Expected outcomes include 50-65% automation of eligible service requests (validated during pilot phase against actual ticket composition), 30-40% reduction in mean time to resolution for automated categories, and continuous compliance audit trails eliminating manual evidence collection. The phased approach includes explicit knowledge base maturity assessment and remediation, with timeline adjustments based on actual readiness—organizations with mature, well-structured knowledge bases can achieve faster deployment, while those requiring significant remediation should plan for extended timelines.
UI Mockups
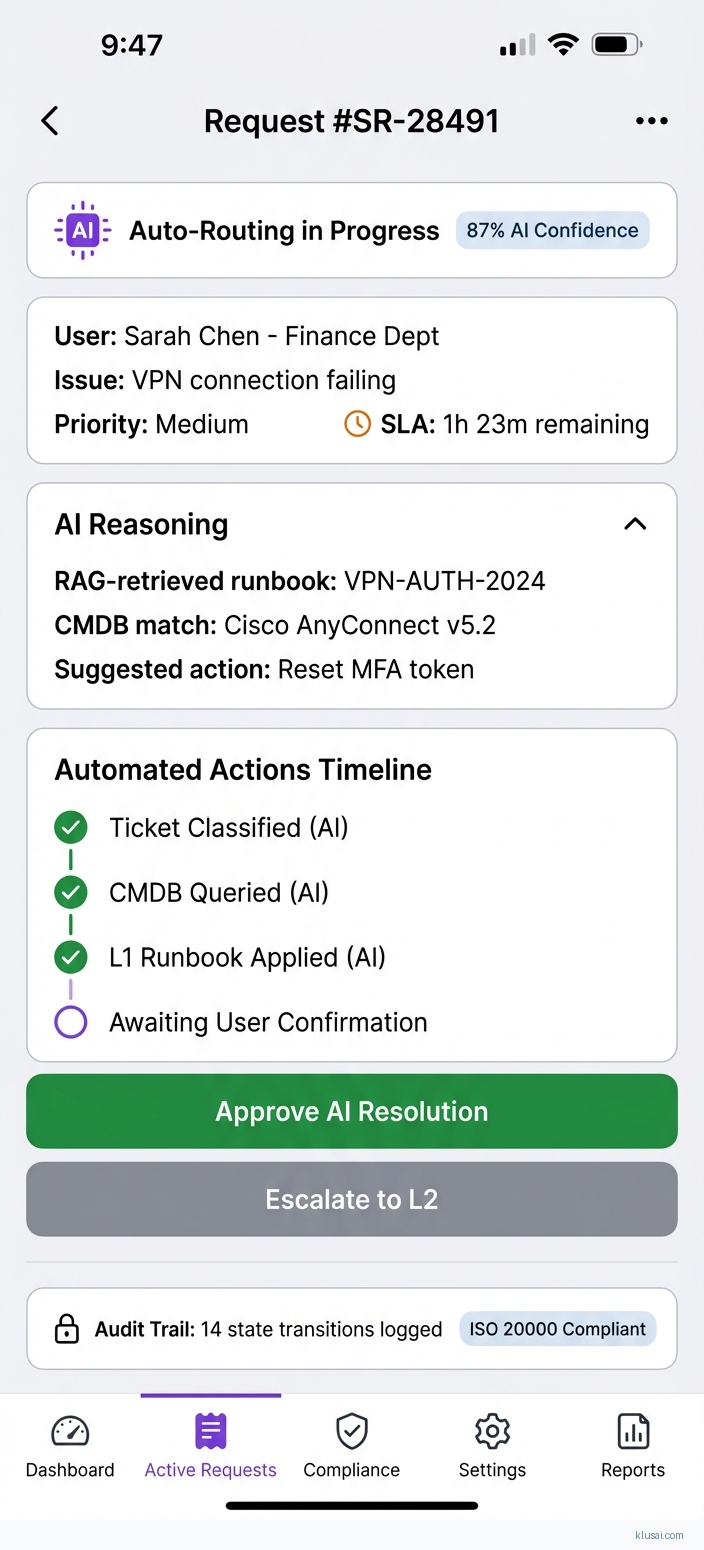
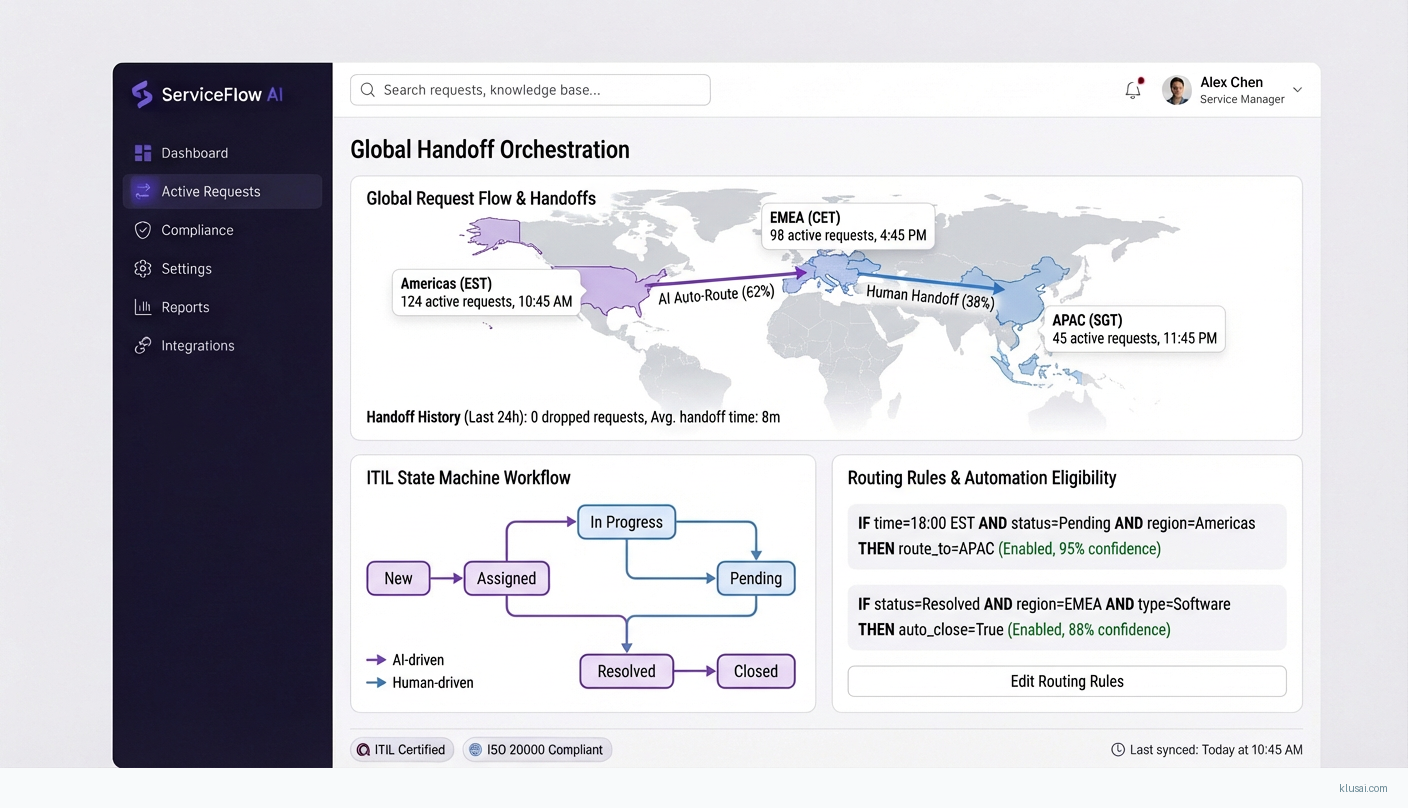
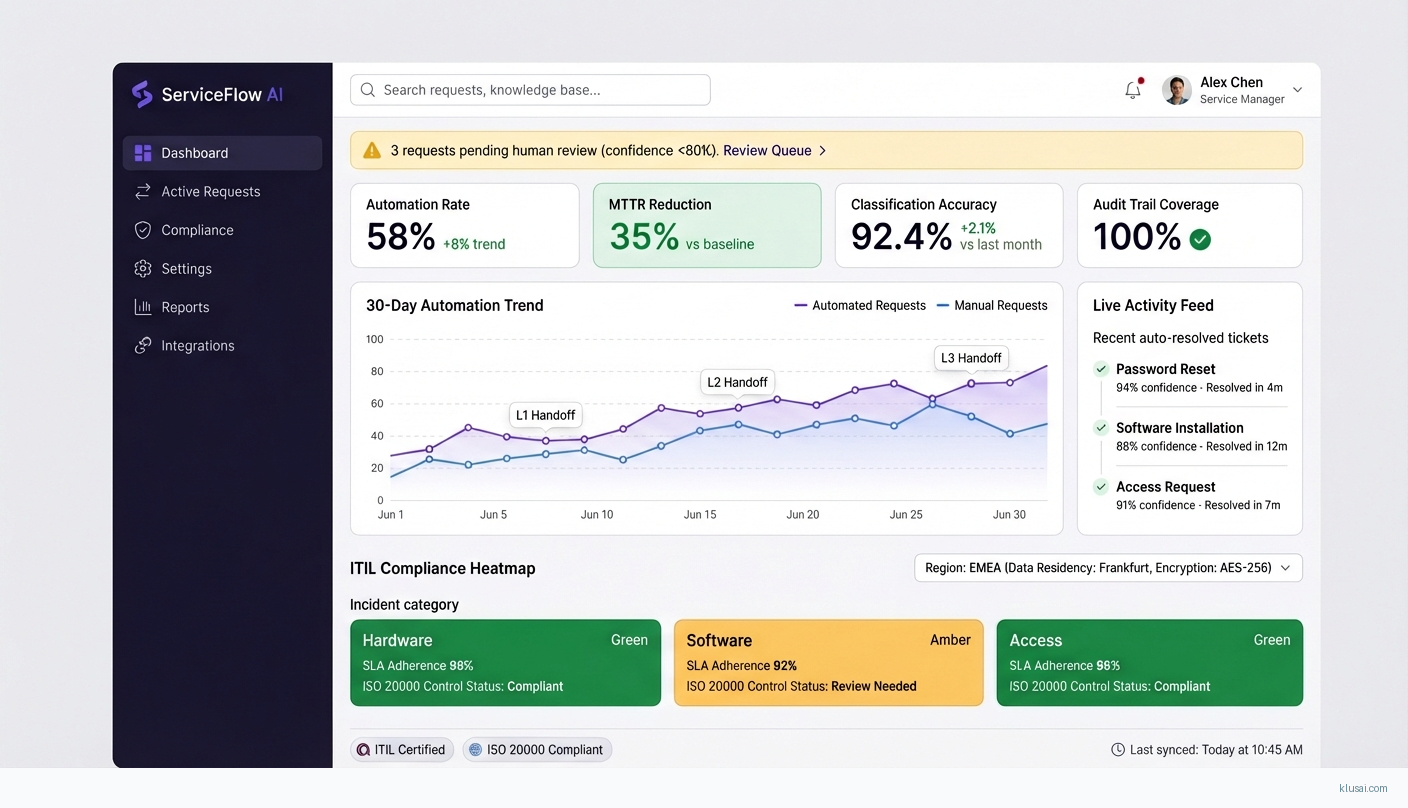
System Architecture
The architecture follows a layered approach separating ingestion, intelligence, orchestration, and integration concerns. The ingestion layer handles multi-channel request capture from email, chat, portal, and API sources, normalizing inputs into a canonical request format with extracted entities and context. This layer includes confidence scoring for entity extraction quality, enabling downstream components to adjust processing strategies.
The intelligence layer combines a fine-tuned classification model with RAG-based knowledge retrieval. Classification determines request category, priority, and routing path, while RAG retrieves relevant runbooks, resolution scripts, and historical resolution patterns from the knowledge base. A confidence aggregation component combines classification and retrieval confidence scores to determine automation eligibility—requests meeting the 80% threshold proceed to automated resolution, while others route to human agents with AI-assisted context.
The orchestration layer implements ITIL-compliant state machines governing request lifecycle transitions. Each state transition generates immutable audit events for ISO 20000 compliance, with automated SLA monitoring triggering escalations when resolution targets are at risk. The orchestration engine supports client-specific workflow customizations through a configuration-driven approach, enabling MSPs to maintain distinct processes for different client environments without code changes.
The integration layer provides bi-directional synchronization with ITSM platforms (ServiceNow, Jira Service Management), CMDB systems, and monitoring tools. Webhook-based event propagation ensures near-real-time consistency, with reconciliation jobs detecting and resolving drift. Multi-region deployment supports data residency requirements, with request routing ensuring data remains within designated geographic boundaries.
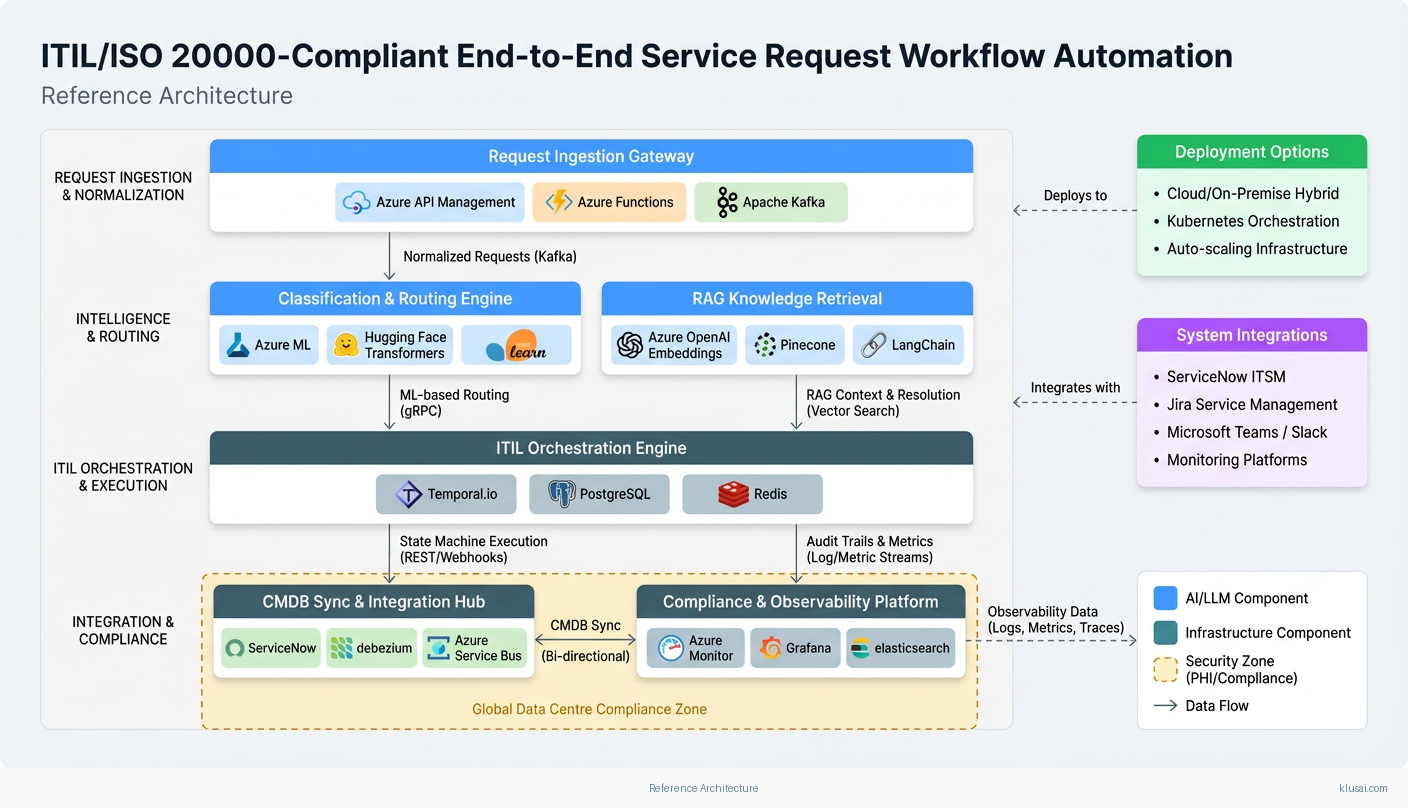
Key Components
| Component | Purpose | Technologies |
|---|---|---|
| Request Ingestion Gateway | Multi-channel request capture, normalization, and entity extraction with confidence scoring | Azure API Management Azure Functions Apache Kafka |
| Classification & Routing Engine | ML-based request categorization, priority assignment, and routing determination | Azure ML Hugging Face Transformers scikit-learn |
| RAG Knowledge Retrieval | Context-aware retrieval of runbooks, resolution scripts, and historical patterns | Azure OpenAI Embeddings Pinecone LangChain |
| ITIL Orchestration Engine | State machine execution for ITIL-compliant request lifecycle management | Temporal.io PostgreSQL Redis |
| CMDB Sync & Integration Hub | Bi-directional synchronization with ITSM platforms and configuration management databases | Apache Camel Debezium Azure Service Bus |
| Compliance & Observability Platform | Audit trail management, SLA monitoring, and ML model performance tracking | Azure Monitor Grafana Elasticsearch |
Technology Stack

Implementation Phases
Foundation & Knowledge Base Assessment
Complete knowledge base maturity assessment and remediation planning
- • Complete knowledge base maturity assessment and remediation planning
- • Deploy core infrastructure and establish ITSM integration patterns
- • Implement classification model training pipeline with baseline accuracy metrics
- Knowledge base maturity scorecard with remediation roadmap and effort estimates
- Infrastructure provisioned with security controls and networking configured
- Classification model achieving >85% accuracy on historical ticket validation set
Core Automation & Single-Region Deployment
Deploy RAG pipeline with validated knowledge base content
- • Deploy RAG pipeline with validated knowledge base content
- • Implement ITIL state machines for top 5 request categories by volume
- • Establish human-in-loop workflows with confidence-based routing
- RAG pipeline operational with retrieval accuracy >80% on test queries
- Automated resolution for 3-5 high-volume, well-documented request categories
- Agent-assist interface providing context for non-automated requests
Expansion & Compliance Validation
Extend automation to additional request categories based on Phase 2 learnings
- • Extend automation to additional request categories based on Phase 2 learnings
- • Complete ISO 20000 compliance validation with audit trail verification
- • Implement SLA monitoring dashboards and automated escalation workflows
- Automation coverage expanded to 8-12 request categories
- Compliance documentation package with audit trail samples and control mappings
- Executive dashboard showing automation rates, MTTR trends, and SLA performance
Multi-Region & Optimization
Deploy to additional regions based on data residency requirements
- • Deploy to additional regions based on data residency requirements
- • Implement model retraining pipeline with drift detection triggers
- • Optimize automation rates based on production performance data
- Multi-region deployment with data residency controls validated
- Automated model monitoring with drift alerts and retraining triggers
- Performance optimization report with recommendations for continued improvement
Key Technical Decisions
Should classification use a fine-tuned transformer model or a traditional ML approach?
Traditional ML models provide faster training cycles, easier interpretability for compliance requirements, and lower infrastructure costs. They achieve 85-90% accuracy for well-defined categories with clean training data. Transformer models offer potential accuracy improvements but require more training data, longer iteration cycles, and GPU infrastructure. Starting with traditional ML enables faster time-to-value while establishing the data pipeline needed for future transformer adoption.
- Faster initial deployment with lower infrastructure requirements
- Easier model interpretability for compliance and debugging
- May plateau at lower accuracy ceiling for complex categories
- Requires feature engineering effort that transformers would automate
How should multi-tenant isolation be implemented in the orchestration layer?
Physical isolation (separate infrastructure per tenant) provides strongest guarantees but dramatically increases operational complexity and cost. Logical isolation with strict tenant context propagation, row-level security in databases, and separate encryption keys per tenant provides adequate isolation for most MSP requirements while enabling efficient resource utilization. Configuration-driven workflows allow client-specific customizations without code deployment.
- Cost-efficient resource sharing across tenants
- Simplified operations with single deployment to manage
- Requires rigorous tenant context validation throughout codebase
- Noisy neighbor risk during traffic spikes requires careful capacity planning
What approach should be used for knowledge base quality assessment?
RAG pipeline effectiveness depends critically on knowledge base quality—incomplete, outdated, or poorly structured content produces poor retrieval results regardless of embedding quality. A structured assessment covering completeness (category coverage), currency (update recency), structure (consistent formatting), and accessibility (clear language) enables objective remediation planning. Automated scoring during ingestion provides ongoing quality monitoring.
- Objective basis for timeline and effort estimation
- Identifies specific remediation priorities rather than general concerns
- Requires 2-3 weeks of assessment effort before automation development
- May surface uncomfortable truths about knowledge management practices
Integration Patterns
| System | Approach | Complexity | Timeline |
|---|---|---|---|
| ServiceNow ITSM | Bi-directional integration using ServiceNow REST API and webhook subscriptions for real-time event propagation; batch reconciliation for drift detection | medium | 4-6 weeks |
| Jira Service Management | Integration via Atlassian REST API with webhook subscriptions; custom field synchronization for automation metadata | medium | 3-5 weeks |
| Microsoft Teams / Slack | Bot integration for request submission, status updates, and agent notifications; adaptive cards for rich interaction | low | 2-3 weeks |
| Monitoring Platforms (Datadog, PRTG, Zabbix) | Webhook receivers for alert-to-ticket automation; bi-directional status sync for incident correlation | low | 2-4 weeks |
ROI Framework
ROI is driven by labor cost reduction through automation of routine service requests, reduced escalation costs from improved first-contact resolution, and compliance efficiency gains from automated audit trail generation. With MSPs spending up to 80% of costs on labor[2], automation of even modest ticket volumes delivers meaningful margin improvement.
Key Variables
Example Calculation
Build vs. Buy Analysis
Internal Build Effort
Internal build requires 14-20 months with a team of 8-10 engineers including ML/AI specialists, ITSM integration experts, and compliance-focused architects. Key challenges include RAG pipeline optimization for production reliability, ITIL state machine design with proper audit trail generation, and achieving consistent classification accuracy across diverse request types. Estimated fully-loaded cost of $1.4-2.2M before ongoing maintenance, with significant risk of timeline extension given complexity of multi-tenant CMDB integration and ISO 20000 compliance requirements. Most internal builds underestimate knowledge base remediation effort and ongoing model maintenance requirements.
Market Alternatives
ServiceNow Virtual Agent + Predictive Intelligence
$150-300K annually depending on instance size and modulesNative ServiceNow AI capabilities for organizations heavily invested in ServiceNow ecosystem with standardized ITIL processes
- • Deep native integration with ServiceNow ITSM and CMDB
- • No additional vendor relationship to manage
- • Continuous improvement from ServiceNow's AI investments
- • Limited flexibility for non-ServiceNow integrations or multi-ITSM environments
- • Predictive Intelligence requires significant training data within ServiceNow
- • Less customizable for MSP-specific multi-tenant requirements
Moveworks
$200-400K annually for mid-sized deploymentsEnterprise conversational AI platform focused on employee service automation with strong NLU capabilities
- • Strong natural language understanding for employee requests
- • Pre-built integrations with major ITSM platforms
- • Proven enterprise deployments with measurable ROI
- • Higher cost for comprehensive deployment
- • Less focus on MSP-specific workflows and multi-tenant requirements
- • May require significant customization for complex ITIL workflows
Aisera
$150-350K annuallyAI service management platform with strong automation capabilities and good balance of out-of-box and customizable features
- • Comprehensive AI-driven service desk automation
- • Good balance of out-of-box and customizable features
- • Strong focus on measurable automation rates
- • Integration depth varies by ITSM platform
- • May require professional services for complex multi-tenant deployments
- • Less established in MSP-specific use cases
Our Positioning
KlusAI's approach is ideal for MSPs requiring deep customization of ITIL workflows across multi-tenant environments, organizations operating multiple ITSM platforms, or those with specific compliance requirements that off-the-shelf solutions don't address. We assemble teams with the specific ITSM, AI/ML, and compliance expertise needed for your context, providing flexibility that product-based solutions cannot match while avoiding the risk and extended timeline of pure internal builds. Our methodology includes explicit knowledge base assessment and remediation planning—a critical success factor that product implementations often overlook.
Team Composition
KlusAI assembles specialized teams tailored to each engagement, combining AI/ML expertise with ITSM domain knowledge, compliance experience, and change management capabilities. Team composition scales based on deployment complexity, knowledge base remediation requirements, and timeline constraints.
| Role | FTE | Focus |
|---|---|---|
| Solution Architect | 1.0 | Overall architecture design, integration patterns, and technical decision-making |
| ML/AI Engineer | 1.5 | Classification model development, RAG pipeline implementation, and model observability |
| ITSM Integration Specialist | 1.0 | ServiceNow/Jira integration, CMDB synchronization, and workflow configuration |
| DevOps/Platform Engineer | 1.0 | Infrastructure provisioning, CI/CD pipelines, and observability implementation |
| Change Management & Training Lead | 0.5 | Stakeholder engagement, change champion coordination, and training program delivery |
Supporting Evidence
Performance Targets
50-65%
30-40% reduction vs. baseline
>90% on production traffic
100% audit trail coverage for automated requests
Team Qualifications
- KlusAI's network includes professionals with extensive ITSM platform implementation experience across ServiceNow, Jira Service Management, and enterprise integration patterns
- Our teams are assembled with ML/AI specialists experienced in production NLP systems, classification models, and RAG architectures for enterprise applications
- We bring together compliance and process specialists familiar with ITIL frameworks and ISO 20000 certification requirements for managed services environments
Source Citations
significant margin pressure from rising labor costs and competitive pricing
directionallabor accounting for up to 80% of total costs
"MSPs spend up to 80% of their total costs on labor"exact
margin pressure as customer environments grow more complex and hiring remains difficult
directionalMSPs rely on a patchwork of ... tools. They don’t integrate cleanly
directionalReady to discuss?
Let's talk about how this could work for your organization.
Schedule a Consultation
Pick a date that works for you
Times shown in your local timezone ()
Prefer email? Contact us directly
Almost there!
at
Your details
at
You're all set!
Check your email for confirmation and calendar invite.
Your booking is confirmed! Our team will reach out to confirm the details.
Your consultation
· min
( team time)
Quick Overview
- Technology
- Process Automation
- Complexity
- high
- Timeline
- 4-6 months
- Industry
- Managed Services